
A more recent article on polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis is available.
Am Fam Physician. 2013;88(10):676-684
Patient information: See related handout on polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis, written by the authors of this article.
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Polymyalgia rheumatica affects proximal muscles and joints, causing disability in older adults. Giant cell arteritis affects medium and large arteries and can result in blindness. These conditions overlap significantly, often occurring together. Despite the similarities, each has distinct symptoms, corticosteroid dosing requirements, and prognosis. The hallmark of both conditions is inflammation. Polymyalgia rheumatica primarily affects the shoulders, neck, and hips with prominent bilateral pain. Systemic findings such as fatigue and weight loss are common, and there is no definitive diagnostic test. Moderate-dose corticosteroid therapy with a slow taper rapidly resolves symptoms. Management of patients responding to treatment can occur in the primary care setting, if there is no concomitant giant cell arteritis. The clinical presentation of giant cell arteritis varies widely, from new-onset headache and constitutional symptoms, to jaw claudication, to less common isolated visual changes and upper extremity claudication. Treatment requires higher dosages of corticosteroids and urgent referral to a rheumatologist. Relapse is common in both diseases. Surveillance is important, as is monitoring for long-term complications of corticosteroid use. Osteoporosis management and gastrointestinal ulcer prophylaxis should be initiated. The primary care physician's coordination of care with a rheumatologist and with other subspecialists, if needed, is essential in the management of giant cell arteritis.
Polymyalgia rheumatica, the most common chronic inflammatory condition in older adults, primarily affects proximal muscles and joints, causing disability. Giant cell arteritis, the most common type of vasculitis in adults, affects medium and large arteries and can result in blindness.1,2 These conditions often occur together and are among the most common diseases that necessitate long-term corticosteroid use in older adults.3,4 They are often identified and treated, at least in part, by the primary care physician. Polymyalgia rheumatica is two to three times more common than giant cell arteritis,3 but there is significant overlap between the two conditions. Approximately 18% to 26%3,5 of cases of polymyalgia rheumatica involve giant cell arteritis; conversely, 27% to 53%6,7 of cases of giant cell arteritis involve polymyalgia rheumatica. Polymyalgia rheumatica can occur before, with, or after the emergence of giant cell arteritis.8
Both conditions affect similar populations (typically older white persons of Northern European descent).5 The prevalence varies by age and population. In areas with higher concentrations of persons of Northern European descent and in persons older than 50 years, the prevalence is one in 143 persons for polymyalgia rheumatica and one in 500 for giant cell arteritis.9 The incidence of both conditions increases with age, peaking between 70 and 80 years of age.3 Women are two to three times more likely than men to be affected by either condition.1,5 Blacks, Asians, and Alaska natives have a much lower incidence of these diseases.3,10,11 Despite their similarities, polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis have distinct symptoms, corticosteroid requirements, and prognoses. When the conditions occur together, the higher corticosteroid doses used to treat giant cell arteritis are needed to prevent significant complications.12
The hallmark of these conditions is inflammation.3,13 The etiologies are not clearly defined. Environmental exposures and genetics both play a role, with antigen-mediated inflammation the likely culprit.3,13 Seasonal, cyclical variations implicate infectious agents (e.g., viruses, Mycoplasma pneumoniae) as triggers, although specific pathogens have not yet been identified.13 Until recently, evidence of actual muscle inflammation was lacking in polymyalgia rheumatica, given normal muscle enzymes and inconsistent immunohistologic findings or vasculitis.14,15 Traditionally, inflammation was thought to be limited to the synovial and bursal linings.14,16 However, inflammatory cytokines have now been found in symptomatic muscles, indicating muscle involvement.17 In giant cell arteritis, inflammation affects medium and large arteries.1 Histologically, focal and segmental lesions are characterized by granulomatous, inflammatory infiltrates at the intimamedia junction that form skip lesions.18
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Straightforward polymyalgia rheumatica should be treated with low-dose corticosteroids and a slow taper. | C | 20, 24 | Prednisone in a starting dosage of 15 mg per day is the consensus recommendation. |
| Medications should be instituted to decrease fracture risk in patients on high-dose, long-term glucocorticoid therapy. | B | 30–32 | Alendronate (Fosamax) and risedronate (Actonel) have been shown to increase bone mineral density and decrease vertebral fractures in patients on long-term glucocorticoid therapy. |
| Low-dose aspirin should be used as an adjunctive treatment to decrease the risk of ischemic events in patients with giant cell arteritis. | C | 24, 48 | There are no prospective trials of aspirin therapy, but its use is associated with a reduced risk of both stroke and visual loss. |
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Polymyalgia rheumatica primarily affects the muscles and joints of the shoulder, neck, and hip girdles, with prominent bilateral pain and morning stiffness.1,19 The shoulders are affected in 95% of cases.19 Proximal myalgias and arthralgias typically develop over weeks to months, worsening at night and with movement. True muscle weakness, as opposed to limited effort because of pain or atrophy from disuse, is not associated with pure polymyalgia rheumatica; distinguishing weakness from limited effort requires careful examination.19 Up to 50% of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica display distal, transient, asymmetrical arthritis, primarily in the knee or wrist.7,19 Tenosynovitis, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, is common. Pitting edema can affect the wrists, hands, ankles, and feet, and occasionally is the presenting finding.1 Systemic symptoms (low-grade fever, fatigue, malaise, and weight loss) occur in 30% to 50% of patients.19
DIAGNOSIS

| Core criteria for diagnosis |
| Age > 50 years |
| Bilateral aching of the shoulder and/or pelvic girdle |
| Duration of symptoms > two weeks |
| Evidence of acute phase response (elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level) |
| Morning stiffness in shoulder and/or pelvic girdle > 45 minutes |
| Conditions that decrease the likelihood of polymyalgia rheumatica |
| Chronic pain syndromes |
| Drug-induced myopathy |
| Endocrine diseases |
| Neurologic conditions (e.g., Parkinson disease) |
| Other inflammatory rheumatic diseases |
| Symptoms or signs that suggest concomitant giant cell arteritis and the need for urgent high-dose corticosteroids |
| Abrupt-onset headache |
| Jaw or tongue claudication |
| Limb claudication or suggestion of large vessel involvement |
| Prominence, beading, or diminished pulse of the temporal artery |
| Temporal tenderness |
| Upper cranial nerve palsies |
| Visual disturbances |
| Response to corticosteroids that supports the diagnosis of polymyalgia rheumatica |
| Global patient symptom improvement within one week of starting treatment |
| Normalization of inflammatory markers within four weeks of starting treatment |
| Suggested criteria for rheumatology referral |
| Age < 60 years at onset |
| Chronic presentation (> two years) |
| Features of other rheumatologic disease |
| Lack of expected response to corticosteroids |
| Lack of inflammatory stiffness |
| Lack of shoulder involvement |
| Prominent systemic features (weight loss, night pain, neurologic symptoms) |
| Very high or very low levels of inflammatory markers |
STUDIES
Inflammatory Markers. Although the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is a nonspecific measurement, it is often used to determine the level of suspicion for polymyalgia rheumatica.5 A normal ESR for a patient's age is best calculated as age/2 for men, and age+10/2 for women.21 The mean ESR is 65 mm per hour in polymyalgia rheumatica (83 mm per hour with concomitant giant cell arteritis).22 An ESR of 40 mm per hour or more is seen in up to 91% of patients with polymyalgia rheumatica.23 An ESR greater than 100 mm per hour raises concern for concomitant giant cell arteritis or underlying malignancy.8 A normal ESR is found in 6% to 20% of persons with polymyalgia rheumatica, although in those cases C-reactive protein level is elevated. ESR predicts relapse more reliably, but C-reactive protein is more sensitive, and is less affected by age and other factors.23
TESTING RECOMMENDATIONS
Many diseases mimic polymyalgia rheumatica, and it may be a component of a paraneoplastic syndrome (Table 2).1,8,20 To assist in differentiating polymyalgia rheumatica from other conditions, the BSR and BHPR recommend obtaining a complete blood count, inflammatory markers, thyroid studies, blood chemistries, creatine kinase level, rheumatoid factor measurement, urinalysis, and protein electrophoresis.20 If clinically indicated, chest radiography should be performed because a paraneoplastic syndrome from lung cancer can mimic the disease.20 In patients whose disease follows the expected course, an intensive search for underlying occult infections or cancers is not routinely advised.1
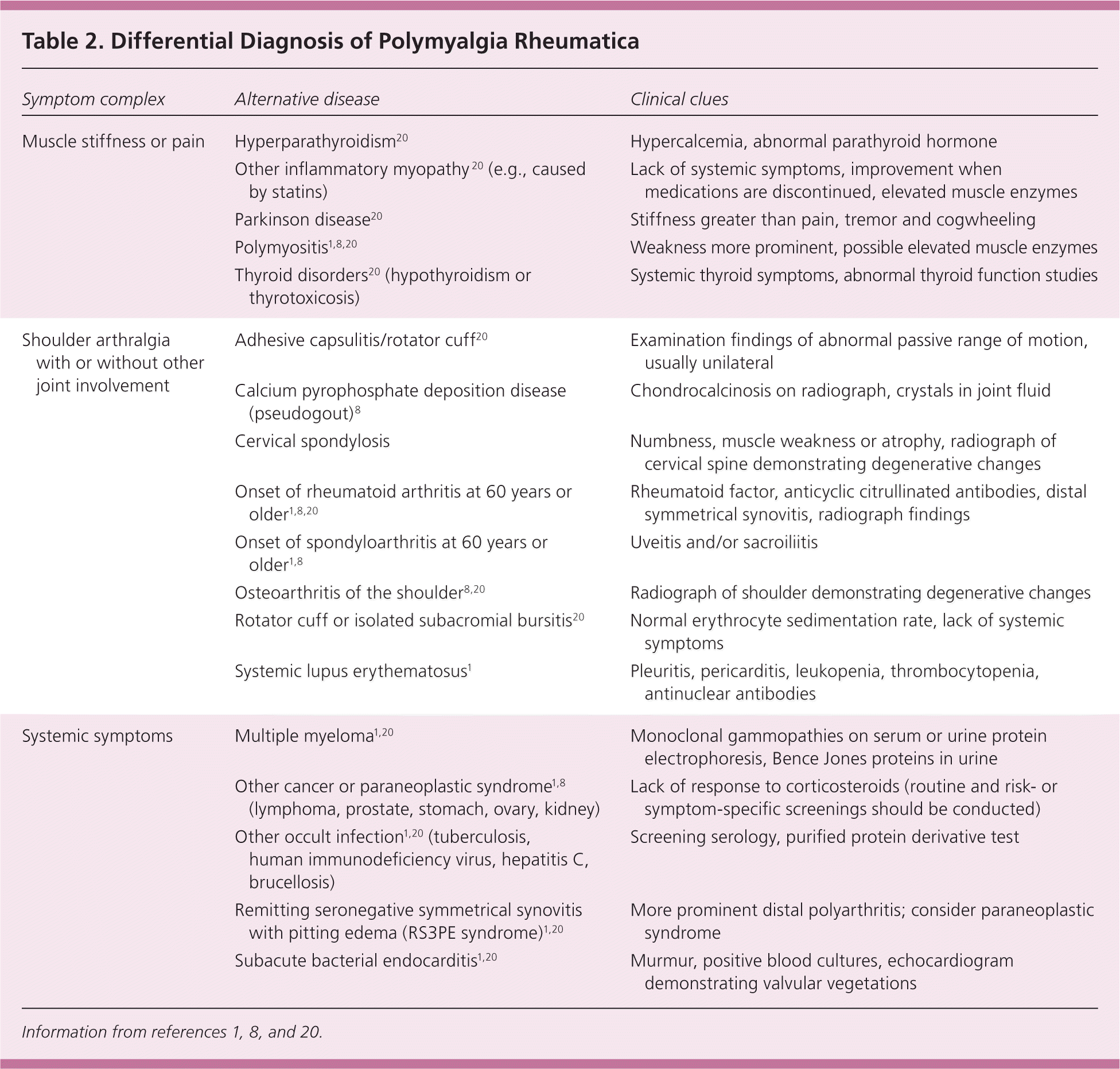
| Symptom complex | Alternative disease | Clinical clues |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle stiffness or pain | Hyperparathyroidism20 | Hypercalcemia, abnormal parathyroid hormone |
| Other inflammatory myopathy 20 (e.g., caused by statins) | Lack of systemic symptoms, improvement when medications are discontinued, elevated muscle enzymes | |
| Parkinson disease20 | Stiffness greater than pain, tremor and cogwheeling | |
| Polymyositis1,8,20 | Weakness more prominent, possible elevated muscle enzymes | |
| Thyroid disorders20 (hypothyroidism or thyrotoxicosis) | Systemic thyroid symptoms, abnormal thyroid function studies | |
| Shoulder arthralgia with or without other joint involvement | Adhesive capsulitis/rotator cuff20 | Examination findings of abnormal passive range of motion, usually unilateral |
| Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (pseudogout)8 | Chondrocalcinosis on radiograph, crystals in joint fluid | |
| Cervical spondylosis | Numbness, muscle weakness or atrophy, radiograph of cervical spine demonstrating degenerative changes | |
| Onset of rheumatoid arthritis at 60 years or older1,8,20 | Rheumatoid factor, anticyclic citrullinated antibodies, distal symmetrical synovitis, radiograph findings | |
| Onset of spondyloarthritis at 60 years or older1,8 | Uveitis and/or sacroiliitis | |
| Osteoarthritis of the shoulder8,20 | Radiograph of shoulder demonstrating degenerative changes | |
| Rotator cuff or isolated subacromial bursitis20 | Normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate, lack of systemic symptoms | |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus1 | Pleuritis, pericarditis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, antinuclear antibodies | |
| Systemic symptoms | Multiple myeloma1,20 | Monoclonal gammopathies on serum or urine protein electrophoresis, Bence Jones proteins in urine |
| Other cancer or paraneoplastic syndrome1,8 (lymphoma, prostate, stomach, ovary, kidney) | Lack of response to corticosteroids (routine and risk- or symptom-specific screenings should be conducted) | |
| Other occult infection1,20 (tuberculosis, human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis C, brucellosis) | Screening serology, purified protein derivative test | |
| Remitting seronegative symmetrical synovitis with pitting edema (RS3PE syndrome)1,20 | More prominent distal polyarthritis; consider paraneoplastic syndrome | |
| Subacute bacterial endocarditis1,20 | Murmur, positive blood cultures, echocardiogram demonstrating valvular vegetations |
TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS
The mainstay of treatment is corticosteroids with a slow taper, which normally reduces symptoms rapidly.1,20,24 Dosing must be tailored to the patient's symptoms and inflammatory markers because up to 13% of patients require higher initial doses.24 Treatment regimens (Table 3)20 include recommendations for prevention of corticosteroid-related conditions.
The mean length of treatment for polymyalgia rheumatica is 1.8 years, although occasionally a more prolonged course of treatment is necessary.25 Risk of relapse, which is common,25 and of concomitant giant cell arteritis correlates with high baseline ESR, older age, female sex, lower (10 mg or less) and higher (greater than 20 mg) starting doses of corticosteroids, fast taper, longer duration of symptoms, and specific human leukocyte antigen alleles.24–26 Patients with frequent symptom flare-ups, and those who cannot undergo a gentle taper after one year, should be referred to a rheumatologist for consideration of corticosteroid-sparing disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs such as methotrexate and etanercept (Enbrel).20 Despite risks such as bone marrow suppression, these drugs provide some benefit in selected patients. Their use does not decrease corticosteroid-related complications.27–29
Recommendations that address long-term corticosteroid complications are listed in Table 3.20 Studies show that use of bisphosphonates, specifically alendronate (Fosamax) and risedronate (Actonel), can increase bone mineral density and decrease vertebral fractures in patients on long-term glucocorticoid therapy.30–32 Surveillance is important. Elevated inflammatory markers do not necessarily indicate increasing corticosteroid requirements but may imply a need for further investigation.20 Conversely, symptoms without elevation of markers do not rule out relapse.20 Mortality rates in polymyalgia rheumatica do not differ from those in age-matched cohorts.5

| Standard initial treatment |
| Oral prednisone: 15 mg per day for three weeks, then 12.5 mg per day for three weeks, then 10 mg per day for four to six weeks, then decrease by 1 mg every four to eight weeks |
| Expect one to two years of treatment |
| Alternate treatment |
| Intramuscular methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol): depot formulation, 120 mg every three to four weeks; decrease by 20 mg every two to three months |
| note: For both polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis, treatment must be tailored to patient's symptoms and inflammatory markers followed; in giant cell arteritis, persistence of ESR/CRP elevation may indicate underlying large vessel disease or other diagnosis |
| Bone protection |
| Patients at high risk of fracture (≥ 65 years or prior fracture): bisphosphonate, calcium, and vitamin D |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica, low-dose corticosteroid without high fracture risk: calcium and vitamin D, DEXA scan at onset of treatment, bisphosphonate if T-score is –1.5 or lower |
| Follow-up visits |
| At one to three weeks (corticosteroids started after laboratory tests, assessment one week after starting corticosteroids); six weeks; and three, six, nine, and 12 months, with extra visits as needed |
| Monitor for relapse, adverse events, or atypical symptoms |
| Relapse symptoms: proximal pain, fatigue, morning stiffness |
| note: Older adults may have degenerative disorders that cause persistent pain |
| Development of giant cell arteritis: headaches, jaw or tongue claudication, visual disturbances |
| Adverse events related to corticosteroid therapy |
| Atypical symptoms that point to a different diagnosis |
| Follow-up laboratory tests (each visit) |
| Complete blood count, ESR/CRP, electrolyte level, blood urea nitrogen/creatinine ratio, glucose level |
| Management of relapse |
| Signs or symptoms of giant cell arteritis: follow guidelines for corticosteroid dosing (Table 5) |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica symptoms during taper: increase to previous dose or give a single intramuscular injection |
| Further relapses or inability to taper: refer to rheumatologist for consideration of disease-modifying antirheumatic drug therapy |
Giant Cell Arteritis
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Giant cell arteritis can affect any medium or large artery, although it has a predilection for the extracranial carotid branches33; therefore, the clinical presentation varies (Table 4).6–8,34–39 Onset can be gradual or sudden.33 The classic presentation includes new-onset headache with constitutional symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, and weight loss in a patient older than 50 years, with or without jaw claudication.33
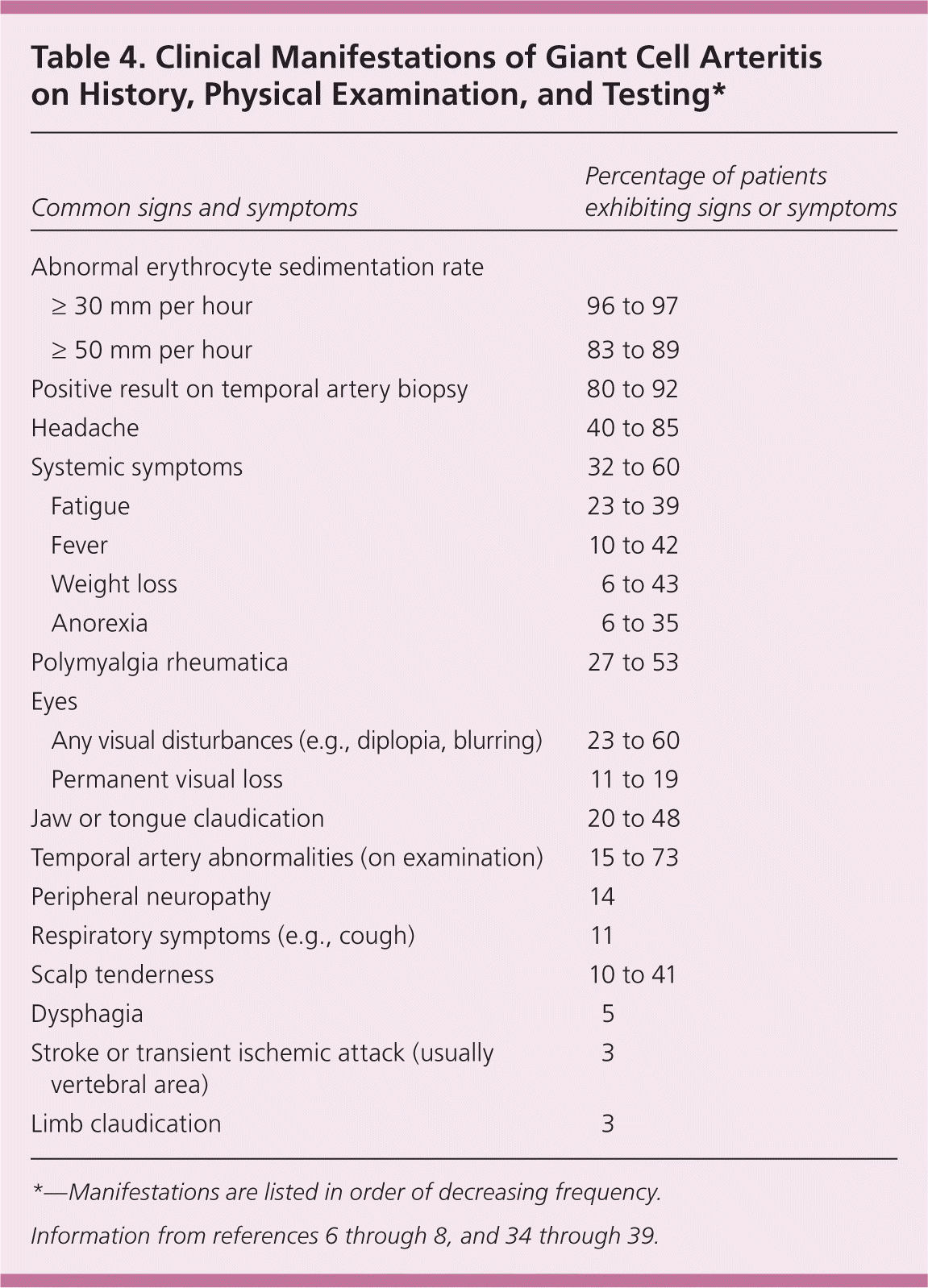
| Common signs and symptoms | Percentage of patients exhibiting signs or symptoms | |
|---|---|---|
| Abnormal erythrocyte sedimentation rate | ||
| ≥ 30 mm per hour | 96 to 97 | |
| ≥ 50 mm per hour | 83 to 89 | |
| Positive result on temporal artery biopsy | 80 to 92 | |
| Headache | 40 to 85 | |
| Systemic symptoms | 32 to 60 | |
| Fatigue | 23 to 39 | |
| Fever | 10 to 42 | |
| Weight loss | 6 to 43 | |
| Anorexia | 6 to 35 | |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | 27 to 53 | |
| Eyes | ||
| Any visual disturbances (e.g., diplopia, blurring) | 23 to 60 | |
| Permanent visual loss | 11 to 19 | |
| Jaw or tongue claudication | 20 to 48 | |
| Temporal artery abnormalities (on examination) | 15 to 73 | |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 14 | |
| Respiratory symptoms (e.g., cough) | 11 | |
| Scalp tenderness | 10 to 41 | |
| Dysphagia | 5 | |
| Stroke or transient ischemic attack (usually vertebral area) | 3 | |
| Limb claudication | 3 | |
Headache is the most common presentation, affecting up to 85% of patients.38 Typically, pain localizes to the temporal region (although it can occur elsewhere) as a boring, moderate-intensity pain that responds poorly to analgesics and is sensitive to the touch or combing.34 Jaw or tongue claudication, defined as pain or weakness in the muscles of mastication that begins just after the onset of chewing and is relieved by rest, occurs with giant cell arteritis and, rarely, other vasculitides.1
Jaw claudication and visual symptoms are ischemic warning signs.6 Patients presenting with these signs but without headache, when the diagnosis is delayed, are at increased risk of neuro-ophthalmic complications such as blindness or stroke.6 Diplopia, blurring, or amaurosis fugax often precedes permanent visual loss.6 Loss of vision occurs within hours to days.6 The contralateral eye is often affected within one to two weeks, making prompt recognition and treatment critical.6
In atypical cases involving large vessels, symptoms include upper extremity claudication or Raynaud phenomenon.2 Thoracic aortic aneurysm or dissection is typically a late complication, but rarely may be the first finding leading to the diagnosis.2 Aortic involvement occurs in 15% of cases.2 Giant cell arteritis is the most common noninfectious cause of aortitis.2 Other atypical presentations include mesenteric ischemia40 or isolated neurologic manifestations such as transient ischemic attacks or sudden neurosensory hearing loss.41 Physicians must remain alert to recognize and diagnose patients who present with atypical symptoms.
DIAGNOSIS
The temporal artery (palpated above the tragus and compared with the contralateral side) can be nodular, thickened, tender, pulseless, or normal. Scalp tenderness also may be present.8
The BSR/BHPR guidelines recommend biopsy of the temporal artery for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis.42 With clinical suspicion of giant cell arteritis, serum inflammatory markers should be obtained.42 Patients who are older than 50 years with a new headache or other symptoms suggestive of impending neuro-ophthalmic complications (e.g., jaw claudication, amaurosis fugax, diplopia) and who have an elevated ESR and C-reactive protein level require immediate treatment and consultation.42 Because prompt recognition and treatment lower the risk of neuro-ophthalmic complications, suspected giant cell arteritis should be considered a medical emergency.6 Administration of corticosteroids should not be delayed while waiting for a biopsy to be performed, because visual loss occurs early in 20% of patients and rarely improves once present.6,42 Laboratory tests should be performed expeditiously and a biopsy should be scheduled, preferably for within one week of initiation of corticosteroids.42 Histologic lesions are present for at least two weeks after initiation of corticosteroid therapy.43
STUDIES
Inflammatory Markers. An ESR greater than 50 mm per hour is seen in up to 89%35 of patients with giant cell arteritis (mean ESR = 88 mm per hour).34 A normal ESR does not exclude giant cell arteritis, however.34 The highest rate of visual loss occurs in patients who have an ESR of 70 to 100 mm per hour; values greater than 100 mm per hour may reflect a protective influence.38 The C-reactive protein measurement is more sensitive; when this test is combined with the ESR, the sensitivity reaches 99% and specificity increases to 97%.39
Other Laboratory Findings. Mild to moderate normochromic anemia and thrombocytosis are common. An elevated level of alkaline phosphatase occurs in up to one-half of patients, many of whom have a decreased albumin level.38
TESTING RECOMMENDATIONS
Many diseases mimic giant cell arteritis, including neoplasms, systemic infections, intracranial pathology, herpes zoster, cervical spondylosis, temporomandibular disorder, and other vasculitides.34,42 Based on BSR/BHPR guidelines, in addition to biopsy the evaluation should include a complete blood count, measurement of inflammatory markers, blood chemistries, urinalysis, and chest radiography, along with any test needed based on symptoms.42
TEMPORAL ARTERY BIOPSY
An abnormal biopsy result (the first choice for diagnosing giant cell arteritis), combined with the clinical presentation described in the preceding text and an elevated ESR, strongly predicts neuro-ophthalmic complications.38,39 However, in light of strong clinical suspicion, a negative biopsy result does not preclude the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis,33 and treatment should continue.36 To ensure the best chance of identifying giant cell arteritis, the temporal artery should be biopsied on the patient's most symptomatic side, with a sample of 1 cm or greater, although more than 2 cm is preferred.42 Only 8% to 20% of cases of giant cell arteritis have negative temporal artery biopsy results, with most negative results due to skip lesions or inadequate samples.36,37 If disease suspicion remains strong after a negative biopsy, a biopsy of the contralateral temporal artery should be considered.36 This approach may increase diagnostic sensitivity by 9% to 12%, although it is not shown to change management if the size of the first sample was adequate.36,44 Risks include hemorrhage, scalp necrosis, and infection, but are rare.39 A temporal artery biopsy has prognostic value as well; most patients at risk of neuro-ophthalmic complications have positive histology.45 Higher degrees of pathology findings are associated with increasing neuro-ophthalmic complications.45
IMAGING
Routine imaging studies are not recommended.42 Trials involving temporal artery ultrasonography for the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis are promising, but due to variability in equipment and operator technique, along with lack of prognostic ability, this type of imaging is not recommended by current guidelines.42,46 In the future, ultrasonography may assist in targeting the biopsy location or avoiding biopsies.46 Presence of limb claudication or persistently high inflammatory markers despite treatment may indicate large artery involvement, necessitating complex imaging to confirm the diagnosis.47
TREATMENT AND PROGNOSIS
Initial treatment of giant cell arteritis involves immediate initiation of high-dose corticosteroids followed by urgent referral to a rheumatologist, with additional attention given to prevention of corticosteroid-related conditions (Table 5).42 Surveillance for osteoporosis and treatment with agents proven to increase bone mineral density and decrease fracture risk in patients with glucocorticoidinduced osteoporosis, such as alendronate and risedronate, are recommended.30–32 In addition, studies show the use of low-dose aspirin decreases cranial-ischemic complications.24,48

| Initial treatment of suspected giant cell arteritis | |
| Uncomplicated (no jaw or tongue claudication or visual changes) | |
| Prednisolone, 40 to 60 mg per day (but not < 0.75 mg per kg) | |
| Complicated | |
| Evolving visual loss or history of amaurosis fugax: intravenous methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), 500 mg to 1 g per day for three days, then oral prednisolone, 60 mg per day | |
| Established visual loss: prednisolone, 60 mg per day | |
| Taper (after four weeks of treatment and resolution of symptoms and normalization of ESR/CRP level) | |
| Decrease by 10 mg every two weeks until 20 mg is reached, then decrease by 2.5 mg every two to four weeks until 10 mg is reached, then decrease by 1 mg every one to two months | |
| Antiplatelet therapy | |
| Low-dose aspirin, 81 mg per day (decreases cranial ischemic complications) | |
| Gastrointestinal protection with proton pump inhibitor | |
| Rheumatologists should be involved immediately in the treatment of suspected giant cell arteritis; treatment must be tailored to patient's symptoms and inflammatory markers followed; in giant cell arteritis, persistence of ESR/CRP elevation may indicate underlying large vessel disease or other diagnosis | |
| Bone protection | |
| Bisphosphonate, calcium, vitamin D | |
Corticosteroid-sparing agents are occasionally used as an adjunctive treatment for giant cell arteritis.42 The adjunct of choice, methotrexate, reduces corticosteroid dose and symptom flare-ups.49 Tumor necrosis factor antagonists do not yet look promising.50 Small studies of interleukin-6 antagonists show potential, although large trials are needed.51
CLINICAL COURSE
The BSR/BHPR guidelines recommend “shared care,” with a consultant managing the acute condition and communicating treatment and disease course to the primary care physician. The goal is for the patient to return to his or her primary care physician's care after the disease stabilizes, usually at three months (Table 6).42
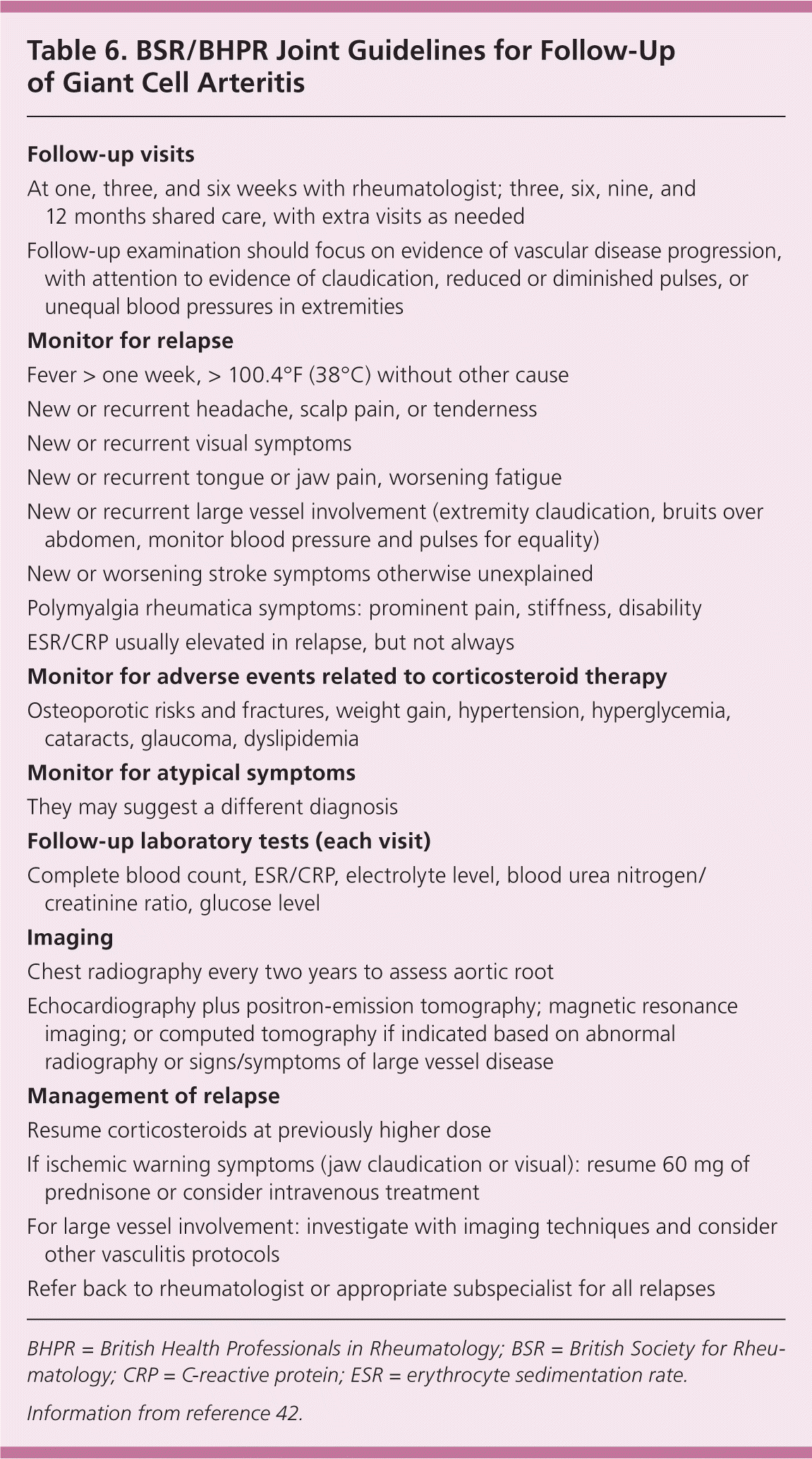
| Follow-up visits |
| At one, three, and six weeks with rheumatologist; three, six, nine, and12 months shared care, with extra visits as needed |
| Follow-up examination should focus on evidence of vascular disease progression, with attention to evidence of claudication, reduced or diminished pulses, or unequal blood pressures in extremities |
| Monitor for relapse |
| Fever > one week, > 100.4°F (38°C) without other cause |
| New or recurrent headache, scalp pain, or tenderness |
| New or recurrent visual symptoms |
| New or recurrent tongue or jaw pain, worsening fatigue |
| New or recurrent large vessel involvement (extremity claudication, bruits over abdomen, monitor blood pressure and pulses for equality) |
| New or worsening stroke symptoms otherwise unexplained |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica symptoms: prominent pain, stiffness, disability |
| ESR/CRP usually elevated in relapse, but not always |
| Monitor for adverse events related to corticosteroid therapy |
| Osteoporotic risks and fractures, weight gain, hypertension, hyperglycemia, cataracts, glaucoma, dyslipidemia |
| Monitor for atypical symptoms |
| They may suggest a different diagnosis |
| Follow-up laboratory tests (each visit) |
| Complete blood count, ESR/CRP, electrolyte level, blood urea nitrogen/creatinine ratio, glucose level |
| Imaging |
| Chest radiography every two years to assess aortic root |
| Echocardiography plus positron-emission tomography; magnetic resonance imaging; or computed tomography if indicated based on abnormal radiography or signs/symptoms of large vessel disease |
| Management of relapse |
| Resume corticosteroids at previously higher dose |
| If ischemic warning symptoms (jaw claudication or visual): resume 60 mg of prednisone or consider intravenous treatment |
| For large vessel involvement: investigate with imaging techniques and consider other vasculitis protocols |
| Refer back to rheumatologist or appropriate subspecialist for all relapses |
Recommended surveillance, in the absence of concern for large vessel involvement, includes limited monitoring for thoracic aneurysms with chest radiography every two years.1,42 If the results are abnormal, echocardiography plus positron-emission tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or computed tomography is recommended.1,52 Alternatively, annual chest radiography and echocardiography may be reasonable for monitoring the aortic root under certain conditions.2
All patients should be monitored for long-term complications of high-dose corticosteroid use.42 Although patients respond quickly, relapses are common and many patients require years of corticosteroid treatment.8 Care should be taken to use the lowest dose necessary.42 Medications that protect patients from osteoporosis (such as bisphosphonates) and gastrointestinal ulcers (such as proton pump inhibitors) should be initiated.42 Immunization against pneumococcus and influenza is also necessary.53
Data Sources: Essential Evidence and PubMed were the primary sources for references. We also searched the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) and Cochrane databases, EULAR (European Union League Against Rheumatism), and the British Society of Rheumatology using the terms polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis. Additional references came from the bibliography sections of other papers and suggestions made by reviewers. Search dates: May 2011 (Essential Evidence and PubMed) and July 2011 (AHRQ and Cochrane databases, EULAR, and British Society of Rheumatology).
