Am Fam Physician. 2011;84(11):1298-1306
| Guideline source: American College of Cardiology Foundation, American Heart Association, and Heart Rhythm Society |
| Evidence rating system used? Yes |
| Literature search described? Yes |
| Guideline developed by participants without relevant financial ties to the industry? No |
| Published source:Circulation, January 2011 |
| Available at: http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/123/1/104.full |
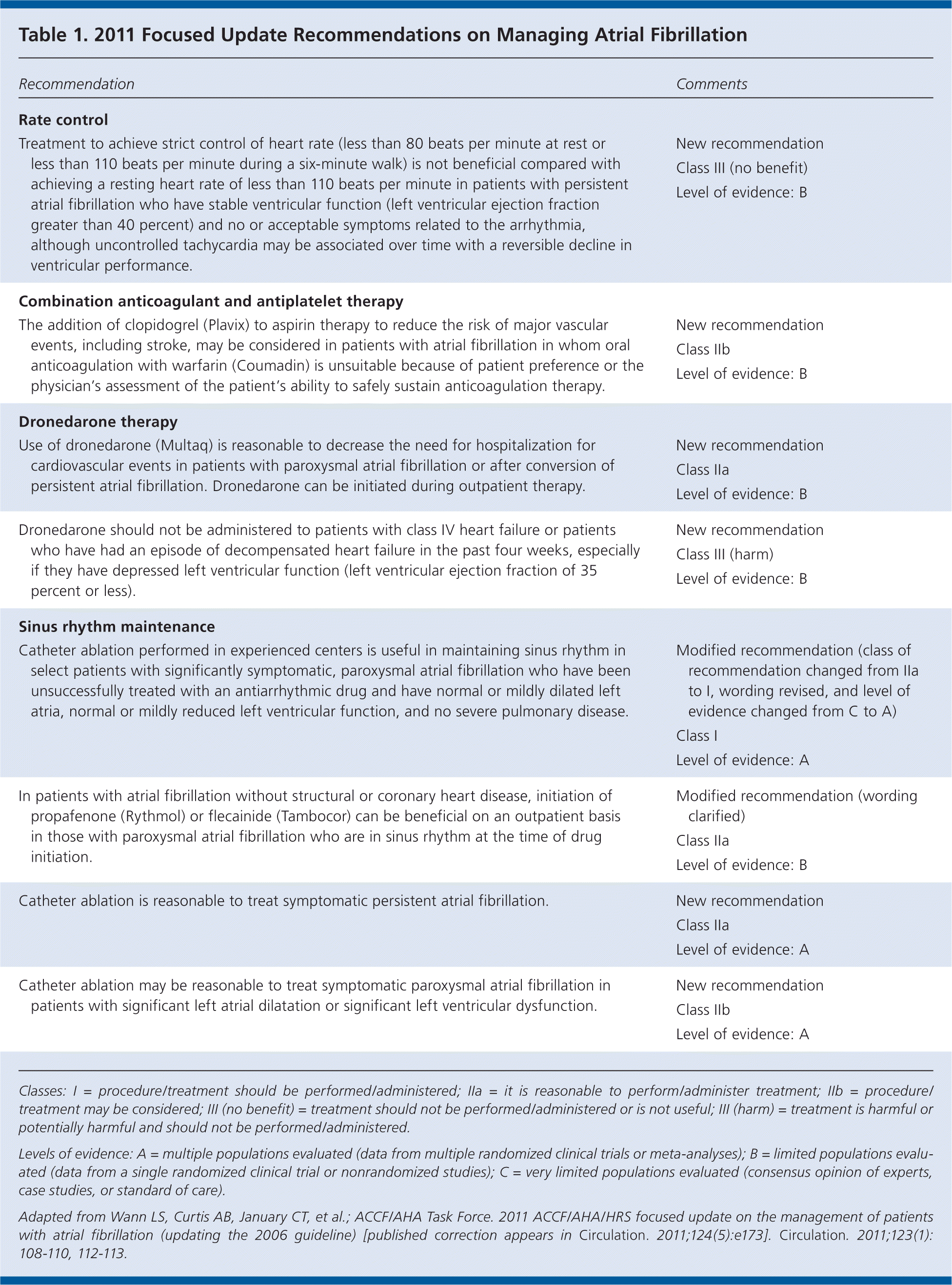
The American College of Cardiology Foundation (ACCF), the American Heart Association (AHA), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) have released updated guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Since the previous guidelines were issued in 2006, new data have become available on strict versus lenient heart rate control, the combined use of antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy, and the use of dronedarone (Multaq). Table 1 summarizes the new and modified recommendations. Recommendations on the thrombotic agent dabigatran (Pradaxa) and the Watchman device for atrial appendage closure were not included in this update because neither was approved for clinical use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration at the time of organizational approval of these guidelines.
| Recommendation | Comments |
|---|---|
| Rate control | |
| Treatment to achieve strict control of heart rate (less than 80 beats per minute at rest or less than 110 beats per minute during a six-minute walk) is not beneficial compared with achieving a resting heart rate of less than 110 beats per minute in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation who have stable ventricular function (left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 40 percent) and no or acceptable symptoms related to the arrhythmia, although uncontrolled tachycardia may be associated over time with a reversible decline in ventricular performance. | New recommendation |
| Class III (no benefit) | |
| Level of evidence: B | |
| Combination anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy | |
| The addition of clopidogrel (Plavix) to aspirin therapy to reduce the risk of major vascular events, including stroke, may be considered in patients with atrial fibrillation in whom oral anticoagulation with warfarin (Coumadin) is unsuitable because of patient preference or the physician's assessment of the patient's ability to safely sustain anticoagulation therapy. | New recommendation |
| Class IIb | |
| Level of evidence: B | |
| Dronedarone therapy | |
| Use of dronedarone (Multaq) is reasonable to decrease the need for hospitalization for cardiovascular events in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or after conversion of persistent atrial fibrillation. Dronedarone can be initiated during outpatient therapy. | New recommendation |
| Class IIa | |
| Level of evidence: B | |
| Dronedarone should not be administered to patients with class IV heart failure or patients who have had an episode of decompensated heart failure in the past four weeks, especially if they have depressed left ventricular function (left ventricular ejection fraction of 35 percent or less). | New recommendation |
| Class III (harm) | |
| Level of evidence: B | |
| Sinus rhythm maintenance | |
| Catheter ablation performed in experienced centers is useful in maintaining sinus rhythm in select patients with significantly symptomatic, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation who have been unsuccessfully treated with an antiarrhythmic drug and have normal or mildly dilated left atria, normal or mildly reduced left ventricular function, and no severe pulmonary disease. | Modified recommendation (class of recommendation changed from IIa to I, wording revised, and level of evidence changed from C to A) |
| Class I | |
| Level of evidence: A | |
| In patients with atrial fibrillation without structural or coronary heart disease, initiation of propafenone (Rythmol) or flecainide (Tambocor) can be beneficial on an outpatient basis in those with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation who are in sinus rhythm at the time of drug initiation. | Modified recommendation (wording clarified) |
| Class IIa | |
| Level of evidence: B | |
| Catheter ablation is reasonable to treat symptomatic persistent atrial fibrillation. | New recommendation |
| Class IIa | |
| Level of evidence: A | |
| Catheter ablation may be reasonable to treat symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients with significant left atrial dilatation or significant left ventricular dysfunction. | New recommendation |
| Class IIb | |
| Level of evidence: A |
Rate Control
Parameters for optimal rate control in patients with atrial fibrillation are controversial, and there is no standard method for assessing heart rate control to guide treatment. Generally accepted criteria for rate control include a ventricular rate between 60 and 80 beats per minute at rest and between 90 and 115 beats per minute during moderate exercise. The definition of adequate rate control has been based primarily on short-term hemodynamic benefits. This definition has not been well studied with respect to quality of life, symptoms, development of cardiomyopathy, and ventricular response to atrial fibrillation. Data have not demonstrated clinically relevant differences in outcomes between strict rate control (less than 80 beats per minute at rest and less than 110 beats per minute during moderate exercise) and lenient rate control (less than 110 beats per minute at rest). Lenient rate control requires fewer outpatient visits and examinations, and is generally more convenient for patients. Because it has not been proven inferior to strict rate control, lenient rate control is a reasonable strategy in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation. Data also have shown no benefit of rhythm control compared with rate control in patients with atrial fibrillation and systolic heart failure.
Combination Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Therapy
Studies have shown that oral anticoagulation therapy with warfarin (Coumadin) is superior to the combination of aspirin and the antiplatelet agent clopidogrel (Plavix) for preventing vascular events in patients with atrial fibrillation. Treatment with clopidogrel and aspirin was associated with a risk of bleeding similar to that of treatment with warfarin. In patients with atrial fibrillation who are not suitable candidates for warfarin therapy, treatment with clopidogrel and aspirin was shown to reduce the risk of major vascular events, especially stroke, compared with patients taking aspirin plus placebo. However, the combination of aspirin and clopidogrel also increased the risk of major hemorrhage. Use of clopidogrel and aspirin plus warfarin (i.e., triple therapy) has been proposed for treating and preventing complications of two or more coexisting conditions (e.g., atrial fibrillation, mechanical valve prosthesis, presence of drug-eluting stent). This combination is associated with an increased risk of bleeding complications, and no randomized trials of this strategy have been reported.
Dronedarone Therapy
Dronedarone, which is similar to amiodarone, has been shown to reduce hospitalization for cardiovascular problems in patients with paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter and risk factors for thromboembolism. The recommended oral dosage of dronedarone is 400 mg twice per day with meals. Major adverse effects include bradycardia and QT prolongation. Dronedarone also has been shown to increase mortality in patients with a recent episode of decompensated heart failure and depressed left ventricular function.
Sinus Rhythm Maintenance
Catheter ablation has been shown to provide one year or more of freedom from recurrent atrial fibrillation; however, additional studies are needed to determine long-term effectiveness of sinus rhythm maintenance. Ablation has been studied in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal atrial fibrillation that has not responded to treatment with one or more antiarrhythmic drugs, with normal or mildly dilated atria, normal or mildly reduced ventricular function, and absence of severe pulmonary disease.