Am Fam Physician. 2020;101(8):502-503
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Galcanezumab (Emgality) is a once-monthly injected monoclonal antibody that inhibits calcitonin gene–related peptide, a vasodilator. Galcanezumab is labeled for the treatment of cluster headache and is one of three monoclonal antibodies labeled for migraine prophylaxis in adults.1
Safety
In otherwise healthy adults, galcanezumab has not been shown to cause significant safety concerns or drug interactions. Hypersensitivity reactions including dyspnea, urticaria, and rash may occur. Galcanezumab may be taken with other headache medications such as topiramate (Topamax), propranolol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen, triptans, and inhaled oxygen. Galcanezumab may cause vasoconstriction and has not been evaluated in patients with a history of thrombosis or cardiovascular disease, or in those with significant cardiovascular risk factors. Galcanezumab has not been studied in children, patients older than 65 years, or pregnant or lactating women and should not be used in these patients. No dose adjustments are needed for body weight, sex, age, or renal or hepatic impairment. Galcanezumab has not been studied in patients with severe renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL per minute per 1.73 m2 [0.50 mL per second per m2]) and should be avoided in these patients.1
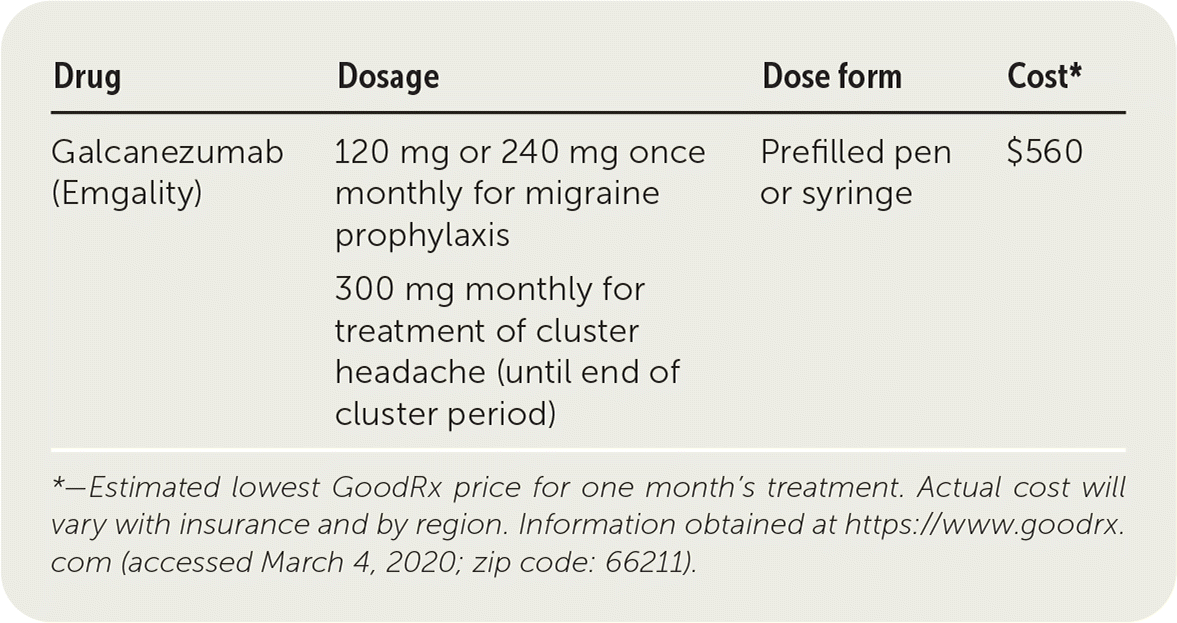
| Drug | Dosage | Dose form | Cost* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Galcanezumab (Emgality) | 120 mg or 240 mg once monthly for migraine prophylaxis 300 mg monthly for treatment of cluster headache (until end of cluster period) | Prefilled pen or syringe | $560 |
Tolerability
Galcanezumab is well tolerated by most patients. Injection site reactions will occur in up to 23% of patients. Up to 4% will discontinue use due to adverse effects.
Effectiveness
In two studies that included a total of 1,773 patients with episodic migraines (average of nine migraine days per month), approximately 60% of patients receiving galcanezumab and no other preventive medications experienced at least a 50% reduction in mean monthly migraine days after six months of treatment, compared with 37% of patients receiving placebo (P < .001; number needed to treat [NNT] = 5).2–4
Based on a study of 1,113 patients with chronic migraines (average of 19 migraine days per month), significantly more patients receiving galcanezumab had at least a 50% reduction in mean monthly migraine days after three months of prophylaxis vs. placebo (28% vs. 13%; P < .001; NNT = 8). Galcanezumab has been studied in 80 patients with chronic migraines who are concurrently on stable doses of topiramate or propranolol, but effectiveness in this subgroup has not been reported.4,5
In one small study of 106 patients with an average of 17 cluster headache attacks per week, significantly more patients receiving 300 mg of galcanezumab had at least a 50% reduction in weekly frequency of cluster headache attacks after three weeks of treatment, compared with patients receiving placebo (71% vs. 53%; P = .046; NNT = 6). Effectiveness beyond eight weeks has not been studied.6 Galcanezumab has not been demonstrated to be effective for the prevention of cluster headaches; it is only used once the cluster period begins.
Galcanezumab has not been compared directly with other calcitonin gene–related peptide inhibitors, other preventive migraine medications such as topiramate or propranolol, or other cluster headache treatments. It has not been studied in patients with fewer than four episodic migraines per month or four cluster headaches per week.
Price
Galcanezumab costs approximately $560 per month depending on the dose and indication. It is significantly more expensive than oral migraine prophylaxis and cluster headache treatments, which are available in generic formulations.
Simplicity
For the prevention of migraines, galcanezumab should be administered once monthly in doses of 120 mg or 240 mg, although there is no demonstrated benefit with the higher dose.4,5 Galcanezumab is available in single-use 120-mg pens or syringes for self-administered subcutaneous injection. Patients prescribed a 240-mg dose should administer two injections.
For the treatment of cluster headache, galcanezumab is available in single-use 100-mg syringes. Patients should administer three injections together at the start of the cluster period and may repeat this dose monthly until the cluster period ends.
Galcanezumab should be refrigerated but can be stored at room temperature for up to seven days.1
Bottom Line
In otherwise healthy adults with severe and frequent migraine or cluster headaches, galcanezumab may provide a modest reduction in debilitating headache frequency in the short term. For patients whose migraines are not responsive to oral and less expensive medications, galcanezumab may be used preventively to reduce, although not eliminate, the number of migraine episodes per month.