
Am Fam Physician. 2020;102(11):online
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Details for This Review
Study Population: 1,151 patients with pericolonic abscesses
Efficacy End Points: Requiring additional treatment or intervention during initial episode
Harm End Points: Antibiotic-related morbidity
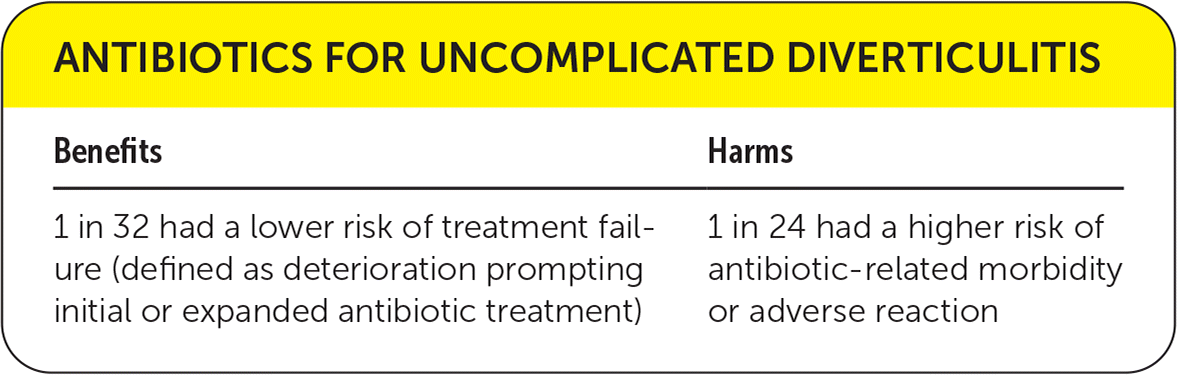
| Benefits | Harms |
|---|---|
| 1 in 32 had a lower risk of treatment failure (defined as deterioration prompting initial or expanded antibiotic treatment) | 1 in 24 had a higher risk of antibiotic-related morbidity or adverse reaction |
Narrative: Each year in the United States, there are more than 2.6 million outpatient visits and 200,000 inpatient admissions for diverticulitis.1 Diverticulitis can be divided into uncomplicated and complicated forms. Complicated diverticulitis is associated with abscess formation, fistula, and bowel obstruction or perforation. Approximately 5% to 15% of patients with diverticulitis develop an abscess or fistula, whereas bowel obstruction and frank perforation are rare.2 The mainstay of treatment for uncomplicated diverticulitis has been antibiotic therapy with bowel rest. However, recent studies have questioned the role of antibiotics.3,4 Systematic reviews have examined outcomes of acute uncomplicated diverticulitis treated with or without antibiotics.5–8
The reviews included randomized trials and observational studies. Because of the high risk of bias and confounding in observational studies, only results from the two randomized trials were considered.3,4 End points included treatment failure, recurrence of diverticulitis, complications, readmission, and mortality. Follow-up was at one month and 50 months, respectively.3,4
The difference between groups was not significant for any major end points, including recurrence rate (56 of 571 patients in the nonantibiotic group vs. 54 of 580 patients in the antibiotic group, P = .77, respectively), complications (18 of 571 patients vs. 10 of 580 patients, P = .12, respectively), readmission (113 of 571 patients vs. 81 of 580 patients, P = .26, respectively), or mortality (3 of 571 patients vs. 1 of 580 patients, P = .4, respectively).3,4
A secondary outcome reported in one of the systematic reviews was treatment failure (defined as deterioration prompting initial or expanded antibiotic treatment), which was lower in the antibiotic group (odds ratio = 0.6; 95% CI, 0.3 to 0.97; absolute risk reduction = 3.1%; number needed to treat = 32, n = 1,151).5
Although harms were not reported in the systematic review because of inconsistent reporting, the two randomized trials briefly mention adverse events. In one study, only three patients in the antibiotic group experienced adverse events (allergic reactions).3 Another study reported 22 adverse events in the antibiotic group (all were “antibiotic-related” without specification), and one adverse event in the control group (odds ratio = 25.68; 95% CI, 3.47 to 190.14; absolute risk reduction = 4.1%; number needed to harm = 24).4
Caveats: The data had several limitations, including having only two studies, and important variations in outcomes and definitions (e.g., treatment failure). The study by Daniels and colleagues included patients with small pericolonic abscesses,4 whereas the study by Chabok and colleagues included patients with any sized pericolonic abscesses,3 which may have contributed to a higher treatment failure rate in the Daniels study 4 (10.7% vs. 3.2%). In the Chabok study, antibiotic usage was guided by C-reactive protein levels, whereas the Daniels study did not describe a defined protocol or guidance for the use of antibiotics in the control group. Antibiotic treatments also differed between studies. Both studies were unblinded, and enrollment rates varied by center, leading to a risk of selection bias. However, concealment and randomization may have decreased this risk.
Conclusion: Based on limited data with high potential for bias, we have chosen a recommendation of yellow (unclear benefits). Ongoing studies and future efforts should be more rigorous and better standardized to allow for more reliable pooling and comparison.
