
Am Fam Physician. 1999;59(2):331-342
Significant cervical spine injury is very unlikely in a case of trauma if the patient has normal mental status (including no drug or alcohol use) and no neck pain, no tenderness on neck palpation, no neurologic signs or symptoms referable to the neck (such as numbness or weakness in the extremities), no other distracting injury and no history of loss of consciousness. Views required to radiographically exclude a cervical spine fracture include a posteroanterior view, a lateral view and an odontoid view. The lateral view must include all seven cervical vertebrae as well as the C7-T1 interspace, allowing visualization of the alignment of C7 and T1. The most common reason for a missed cervical spine injury is a cervical spine radiographic series that is technically inadequate. The “SCIWORA” syndrome (spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormality) is common in children. Once an injury to the spinal cord is diagnosed, methylprednisolone should be administered as soon as possible in an attempt to limit neurologic injury.
Although cervical spine radiographs are almost routine in many emergency departments, not all trauma patients with a significant injury must have radiographs, even if they arrive at the emergency department on a backboard and wearing a cervical collar. This article reviews the proper use of cervical spine radiographs in the trauma patient.
Low-risk criteria have been defined that can be used to exclude cervical spine fractures, based on the patient's history and physical examination.1–6 Patients who meet these criteria (Table 1) do not require radiographs to rule out cervical fractures. However, the criteria apply only to adults and to patients without mental status changes, including drug or alcohol intoxication. Although studies suggest that these criteria may also be used in the management of verbal children,7–9 caution is in order, since the study series are small, and the ability of children to complain about pain or sensory changes is variable. An 18-year-old patient can give a more reliable history than a five-year-old child.
Some concern has been expressed about case reports suggesting that “occult” cervical spine fractures will be missed if asymptomatic trauma patients do not undergo radiography of the cervical spine.10 On review, however, most of the reported cases did not meet the low-risk criteria in Table 1. Attention to these criteria can substantially reduce the use of cervical spine radiographs.
| Patient does not complain of neck pain when asked | |
| and | |
| Patient does not have neck tenderness on palpation | |
| and | |
| Patient does not have any history of loss of consciousness | |
| and | |
| Patient does not have any mental status changes resulting from trauma, alcohol, drugs, etc. | |
| and | |
| Patient has no symptoms referable to a neck injury, such as paralysis, sensory changes (including transitory symptoms now resolved), etc. | |
| and | |
| Patient has no other distracting painful injuries, such as fractured ankle, fractured ribs, etc. | |
Cervical Spine Series and Computed Tomography
Once the decision is made to proceed with a radiographic evaluation, the proper views must be obtained. The single portable cross-table lateral radiograph, which is sometimes obtained in the trauma room, should be abandoned. This view is insufficient to exclude a cervical spine fracture and frequently must be repeated in the radiographic department.11,12 The patient's neck should remain immobilized until a full cervical spine series can be obtained in the radiographic department. Initial films may be taken through the cervical collar, which is generally radiolucent. An adequate cervical spine series includes three views: a true lateral view, which must include all seven cervical vertebrae as well as the C7-T1 junction, an anteroposterior view and an open-mouth odontoid view.13
If no arm injury is present, traction on the arms may facilitate visualization of all seven cervical vertebrae on the lateral film. If all seven vertebrae and the C7-T1 junction are not visible, a swimmer's view, taken with one arm extended over the head, may allow adequate visualization of the cervical spine. Any film series that does not include these three views and that does not visualize all seven cervical vertebrae and the junction of C7-T1 is inadequate. The patient should be maintained in cervical immobilization, and plain films should be repeated or computed tomographic (CT) scans obtained until all vertebrae are clearly visible. The importance of obtaining all of these views and visualizing all of the vertebrae cannot be overemphasized. While some missed cervical fractures, subluxations and dislocations are the result of film misinterpretation, the most frequent cause of overlooked injury is an inadequate film series.14,15
In addition to the views listed above, some authors suggest adding two lateral oblique views.16,17 Others would obtain these views only if there is a question of a fracture on the other three films or if the films are inadequate because the cervicothoracic junction is not visualized.18 The decision to take oblique views is best made by the clinician and the radiologist who will be reviewing the films.
Besides identifying fractures, plain radiographs can also be useful in identifying ligamentous injuries. These injuries frequently present as a malalignment of the cervical vertebrae on lateral views. Unfortunately, not all ligamentous injuries are obvious. If there is a question of ligamentous injury (focal neck pain and minimal malalignment of the lateral cervical x-ray [meeting the criteria in Table 2]) and the cervical films show no evidence of instability or fracture, flexion-extension views should be obtained.17,19 These radiographs should only be obtained in conscious patients who are able to cooperate. Only active motion should be allowed, with the patient limiting the motion of the neck based on the occurrence of pain. Under no circumstance should cervical spine flexion and extension be forced, since force may result in cord injury.
| Parameter | Adults | Children |
|---|---|---|
| Predental space | 3 mm or less | 4 to 5 mm or less |
| C2-C3 pseudosubluxation | 3 mm or less | 4 to 5 mm or less |
| Retropharyngeal space | Less than 6 mm at C2, less than 22 mm at C6* | ⅓ to ⅔ vertebral body distance anteroposteriorly |
| Angulation of spinal column at any single interspace level | Less than 11 degrees | Less than 11 degrees |
| Cord dimension | 10 to 13 mm | Adult size by 6 years of age |
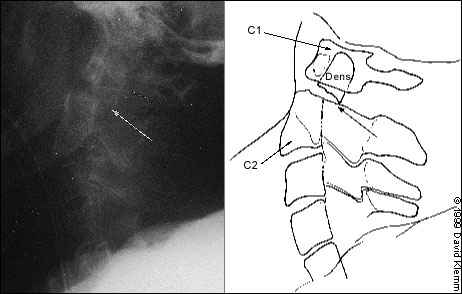
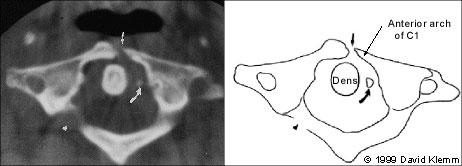
Although they may be considered adequate to rule out a fracture, cervical spine radiographs have limitations. Up to 20 percent11,20,21 of fractures are missed on plain radiographs. If there is any question of an abnormality on the plain radiograph or if the patient has neck pain that seems to be disproportionate to the findings on plain films, a CT scan of the area in question should be obtained. The CT is excellent for identifying fractures, but its ability to show ligamentous injuries is limited.22 Occasionally, plain film tomography may be in order if there is a concern about a type II dens fracture (Figure 1).
While some studies have used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as an adjunct to plain films and CT scanning,23,24 the lack of wide availability and the relatively prolonged time required for MRI scanning limits its usefulness in the acute setting. Another constraint is that resuscitation equipment with metal parts may not be able to function properly within the magnetic field generated by the MRI.
Cervical Spine Radiography
Figure 2 summarizes the approach to reading cervical spine radiographs.
LATERAL VIEW
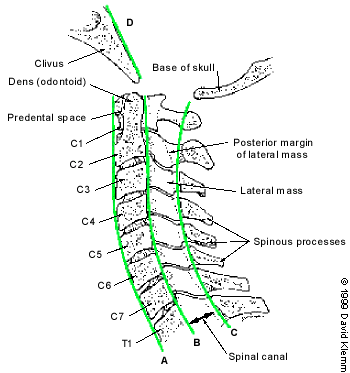
Alignment of the vertebrae on the lateral film is the first aspect to note (Figure 3). The anterior margin of the vertebral bodies, the posterior margin of the vertebral bodies, the spinolaminar line and the tips of the spinous processes (C2-C7) should all be aligned. Any malalignment (Figures 4 and 5) should be considered evidence of ligamentous injury or occult fracture, and cervical spine immobilization should be maintained until a definitive diagnosis is made.
Confusion can sometimes result from pseudosubluxation, a physiologic misalignment that is due to ligamentous laxity, which can occur at the C2-C3 level and, less commonly, at the C3-C4 level. While pseudosubluxation usually occurs in children, it also may occur in adults. If the degree of subluxation is within the normal limits listed in Table 2 and the neck is not tender at that level, flexion-extension views may clarify the situation. Pseudosubluxation should disappear with an extension view. However, flexion-extension views should not be obtained until the entire cervical spine is otherwise cleared radiographically.
After ensuring that the alignment is correct, the spinous processes are examined to be sure that there is no widening of the space between them. If widening is present, a ligamentous injury or fracture should be considered. In addition, if angulation is more than 11 degrees at any level of the cervical spine, a ligamentous injury or fracture should be assumed. The spinal canal (Figure 2) should be more than 13 mm wide on the lateral view. Anything less than this suggests that spinal cord compromise may be impending.
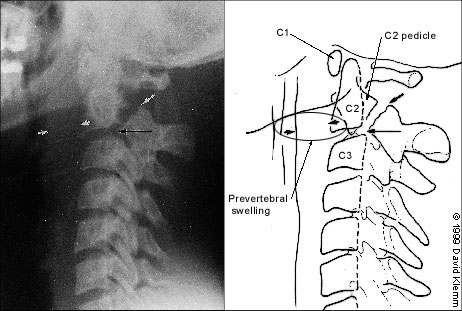
Next, the predental space—the space between the odontoid process and the anterior portion of the ring of C1 (Figure 2)—is examined. This space should be less than 3 mm in adults and less than 4 mm in children (Table 2). An increase in this space is presumptive evidence of a fracture of C1 or of the odontoid process, although it may also represent ligamentous injury at this level. If a fracture is not found on plain radiographs, a CT scan should be obtained for further investigation. The bony structures of the neck should be examined, with particular attention to the vertebral bodies and spinous processes.
The retropharyngeal space (Figure 2) is now examined. The classic advice is that an enlarged retropharyngeal space (Table 2) indicates a spinous fracture. However, the normal and abnormal ranges overlap significantly.25 Retropharyngeal soft tissue swelling (more than 6 mm at C2, more than 22 mm at C6) is highly specific for a fracture but is not very sensitive.26 Soft tissue swelling in symptomatic patients should be considered an indication for further radiographic evaluation. Finally, the craniocervical relationship is checked.
ODONTOID VIEW
The dens is next examined for fractures. Artifacts may give the appearance of a fracture (either longitudinal or horizontal) through the dens. These artifacts are often radiographic lines caused by the teeth overlying the dens. However, fractures of the dens are unlikely to be longitudinally oriented. If there is any question of a fracture, the view should be repeated to try to get the teeth out of the field. If it is not possible to exclude a fracture of the dens, thin-section CT scans or plain film tomography is indicated.
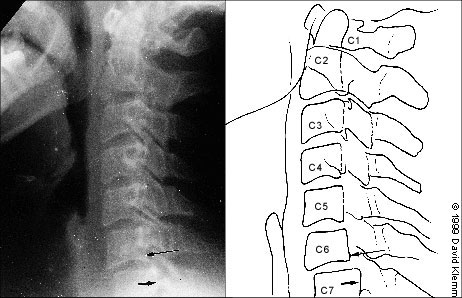
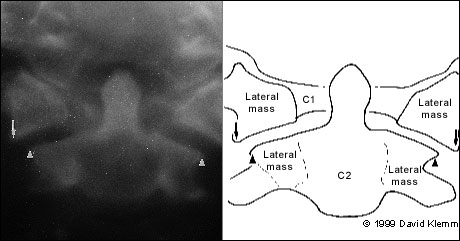
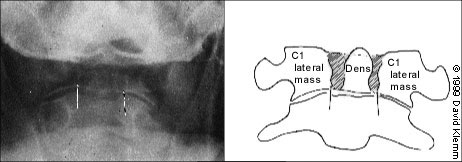
Next, the lateral aspects of C1 are examined. These aspects should be symmetric, with an equal amount of space on each side of the dens. Any asymmetry is suggestive of a fracture. Finally, the lateral aspects of C1 should line up with the lateral aspects of C2. If they do not line up, there may be a fracture of C1. Figure 6 demonstrates asymmetry in the space between the dens and C1, as well as displacement of the lateral aspects of C1 laterally.
ANTEROPOSTERIOR VIEW
The height of the cervical spines should be approximately equal on the anteroposterior view. The spinous processes should be in midline and in good alignment. If one of the spinous processes is off to one side, a facet dislocation may be present.
Common Cervical Abnormalities
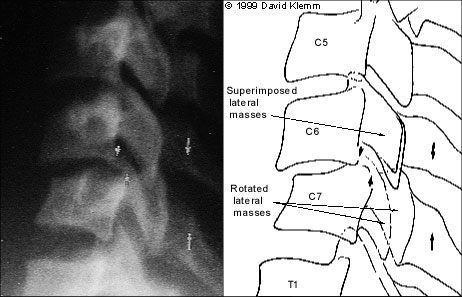
The most common types of cervical abnormalities and their radiographic findings are listed in Table 3. Except for the clay shoveler's fracture, they should be assumed to be unstable and warrant continued immobilization until definitive therapy can be arranged. Any patient found to have one spinal fracture should have an entire spine series, including views of the cervical spine, the thoracic spine and the lumbosacral spine. The incidence of noncontiguous spine fractures ranges up to 17 percent.27,28 Figures 7 through 9 demonstrate aspects of common cervical spine fractures.
| Spine level | Fracture name | Stable or Unstable | Mechanism/clinical setting | Radiologic findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | Jefferson fracture (Figures 6 and 7) | Moderately unstable | Burst fracture; occurs with axial load or vertebral compression | Displaced lateral aspects of C1 on odontoid view, predental space more than 3 mm |
| Atlantoaxial subluxation | Highly unstable | Occurs in patients with Down syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and other destructive processes | Asymmetric lateral bodies on odontoid view, increased predental space | |
| C2 | Odontoid fracture (Figures 1 and 9) | Highly unstable | Mechanism poorly understood | May be difficult to see on plain films; high clinical suspicion requires CT scanning |
| Hangman's fracture (Figure 8) | Unstable | Occurs with sudden deceleration (hanging) and with hyperextension, as in motor vehicle accidents | Bilateral pedicle fracture of C2 with or without anterior subluxation; lateral view required | |
| Any level | Flexion teardrop injury | Highly unstable | Sudden and forceful flexion | Large wedge off the anterior aspect of affected vertebra; ligamentous instability causes alignment abnormalities |
| Bilateral facet dislocations | Highly unstable | Flexion or combined flexion/rotation | Anterior displacement of 50% or more of one cervical vertebra on lateral views | |
| Unilateral facet dislocations (Figure 5) | Unstable | Flexion or combined flexion/rotation | Anterior dislocation of 25 to 33% of one cervical vertebra on lateral views; an abrupt transition in rotation so that lateral view of affected vertebra is rotated; lateral displacement of spinous process on anteroposterior view | |
| Lower cervical or upper thoracic | Clay shoveler's fracture | Very stable | Flexion, such as when picking up and throwing heavy loads (such as snow or clay) | Avulsion of posterior aspect of spinous process; frequently an incidental finding |
Initial Treatment of Cervical Spine and Cord
If a cervical fracture or dislocation is found, orthopedic or neurosurgical consultation should be obtained immediately. Any patient with a spinal cord injury should begin therapy with methylprednisolone within the first eight hours after the injury, with continued administration for up to 24 hours. Patients should receive methylprednisolone in a dosage of 30 mg per kg given intravenously over one hour. Over the next 23 hours, intravenous methylprednisolone in a dosage of 5.4 mg per kg per hour should be administered. This therapy has been shown to improve outcomes and minimize cord injury,29 although it is not without its problems. The incidence of pneumonia is increased in patients treated with high dosages of methylprednisolone.30
‘SCIWORA’ SYNDROME: UNIQUE IN CHILDREN
A special situation involving children deserves mention. In children, it is not uncommon for a spinal cord injury to show no radiographic abnormalities. This situation has been named “SCIWORA” (spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormality) syndrome. SCIWORA syndrome occurs when the elastic ligaments of a child's neck stretch during trauma. As a result, the spinal cord also undergoes stretching, leading to neuronal injury or, in some cases, complete severing of the cord.31 This situation may account for up to 70 percent of spinal cord injuries in children and is most common in children younger than eight years. Paralysis may be present on the patient's arrival in the emergency department. However, up to 30 percent of patients have a delayed onset of neurologic abnormalities, which may not occur until up to four or five days after the injury. In patients with delayed symptoms, many have neurologic symptoms at the time of the injury, such as paresthesias or weakness, that have subsequently resolved.32
It is important to inform the parents of young patients with neck trauma about this possibility so that they will be alert for any developing symptoms or signs. Fortunately, most children with SCIWORA syndrome have a complete recovery, especially if the onset is delayed.33 It is possible to evaluate these injuries with MRI, which will show the abnormality and help determine the prognosis: a patient with complete cord transection is unlikely to recover.3
The treatment of SCIWORA syndrome has not been well studied. However, the general consensus is that steroid therapy should be used.34 In addition, any child who has sustained a significant degree of trauma but has recovered completely should be restricted from physical activities for several weeks.34