
More recent articles on injections of the hand (part I) and wrist (part II) are available.
Am Fam Physician. 2003;67(4):745-750
Joint injection of the wrist and hand region is a useful diagnostic and therapeutic tool for the family physician. In this article, the injection procedures for carpal tunnel syndrome, de Quervain's tenosynovitis, osteoarthritis of the first carpometacarpal joint, wrist ganglion cysts, and digital flexor tenosynovitis (trigger finger) are reviewed. Indications for carpal tunnel syndrome injection include median nerve compression resulting from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, repetitive use injury, and other traumatic injuries to the area. For the first carpometacarpal joint, injection may be used to treat pain secondary to osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Pain associated with de Quervain's tenosynovitis is treated effectively by therapeutic injection. If complicated by pain or paresthesias, wrist ganglion cysts respond to aspiration and injection. Painful limitation of motion occurring in trigger fingers of patients with diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis also improves with injection. The proper technique, choice and quantity of pharmaceuticals, and appropriate follow-up are essential for effective outcomes.
This article, the next in a series on diagnostic and therapeutic injections, covers the wrist and hand region. The rationale, indications, contraindications, and general approach to this technique are covered in the first article of the series.1 The wrist and hand are sites of multiple injuries and inflammatory conditions that lend themselves to diagnostic and therapeutic injection.2,3 In this article, we review the anatomy, pathology, diagnosis, and injection technique of common sites for which this skill is applicable. Specific indications include carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis of the first carpometacarpal joint, de Quervain's tenosynovitis, wrist ganglion cysts, and digital flexor tenosynovitis (trigger finger). For injection of the hand and wrist, the patient should be supine, with the wrist and hand resting comfortably at the patient's side and the targeted area facing upward.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
ANATOMY
The carpal tunnel is formed by the carpal bones dorsally, and the transverse carpal ligament (flexor retinaculum), ventrally. The contents of the tunnel include the median nerve and flexor tendons of the hand. The median nerve sensory and motor distribution includes the palmar aspect of the thumb and the index and middle fingers, and it allows opposition of the tip of the thumb with the tips of the fingers.
INDICATIONS AND DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome is clinical. Electrodiagnostic studies (nerve conduction and electromyography) may assist in confirming the diagnosis, but they have significant false-positive and negative results.4 Weakness of thumb abduction is a specific and reliable sign.5 The major indication for carpal tunnel injection is the syndrome of median nerve compression, which may result from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, repetitive use injury or other traumatic injuries to the area, and pregnancy. The use of local corticosteroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome has been shown to provide greater clinical improvement in symptoms one month after injection, compared with placebo.6,7 Long-term randomized controlled trials have not been performed, particularly comparing surgical or nonsurgical approaches with corticosteroid injection.
TIMING AND OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
Injection of the carpal tunnel is considered a later modality after appropriate nonsurgical therapeutic interventions have been undertaken. These include the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), splinting, and avoidance of precipitating activities.8
TECHNIQUE
Pharmaceuticals and equipment are described in Table 1. Essential landmarks to palpate before performing this injection include the proximal wrist crease and the palmaris longus tendon when present. The palmaris longus tendon is best identified by having the patient pinch all the fingertips together while the wrist is in a neutral position.
| Site/condition | Syringe | Needle | Anesthetic | Corticosteroid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carpal tunnel | 5 mL | 25 gauge, 1.5 inch | 2 to 3 mL of 1% lidocaine (Xylocaine) or 0.25% or 0.5% bupivacaine (Marcaine) | 1 mL of Celestone Soluspan* or 40 mg per mL methylprednisolone (Depo-Medrol) |
| First carpometacarpal joint | 3 mL | 25 gauge, 1 inch | 0.5 mL of 1% lidocaine or 0.25% or 0.5% bupivacaine | 0.25 to 0.5 mL Celestone Soluspan or methylprednisolone |
| de Quervain's tenosynovitis | 5 mL | 25 gauge, 1.5 inch | 2 mL of 1% lidocaine or 0.25% or 0.5% bupivacaine | 1 mL Celestone Soluspan or methylprednisolone |
| Ganglion cysts † | 20 to 30 mL | 18 or 22 gauge, 1 or 1.5 inch | 1 to 2 mL of 1% lidocaine or 0.25% or 0.5% bupivacaine | 1 mL Celestone Soluspan or methylprednisolone |
| Trigger finger | 3 mL | 25 gauge, 1 or 1.5 inch | 0.5 to 1 mL of 1% lidocaine or 0.25% or 0.5% bupivacaine | 0.5 mL Celestone Soluspan or methylprednisolone |
APPROACH AND NEEDLE ENTRY
The injection is performed at a site just ulnar to the palmaris longus tendon and at the proximal wrist crease. For those few patients without a palmaris longus tendon, the needle is inserted just ulnar to the midline of the wrist. The needle is inserted at a 30-degree angle and directed toward the ring finger (Figure 1). If the needle meets obstruction or if the patient experiences paresthesias, the needle should be withdrawn and redirected in a more ulnar fashion. Another injection site is at the volar side of the forearm, 4 cm proximal to the wrist crease between the tendons of the radial flexor muscle and the palmaris longus muscle.7 In this approach, the angle of insertion is between 10 and 20 degrees depending on the thickness of the wrist. As with any injection, aspirate to ensure that the needle has not been placed in a blood vessel. Inject slowly, but with consistent pressure.
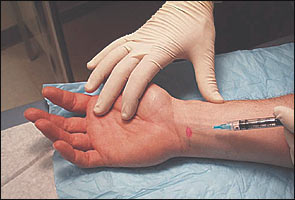
First Carpometacarpal Joint
ANATOMY
The movements of the thumb are dictated by the saddle-shaped articular surface of the base of the first metacarpal, which articulates with the trapezium.
INDICATIONS AND DIAGNOSIS
TIMING AND OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
TECHNIQUE
Pharmaceuticals and equipment are described in Table 1. Palpate the joint space between the trapezium and the first metacarpal.
APPROACH AND NEEDLE ENTRY
The needle enters just proximal to the first metacarpal on the extensor surface. Care must be taken to avoid the radial artery and the extensor pollicis tendons. To avoid the radial artery, the needle should enter toward the dorsal (ulnar) side of the extensor pollicis brevis tendon. The needle, a 25 gauge, should fall into the joint space (Figure 2). Traction can be applied to the thumb to further open the joint space.
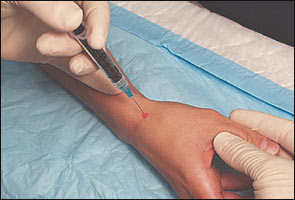
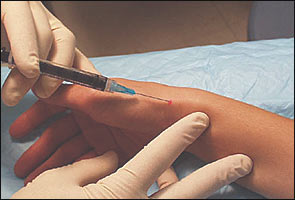
de Quervain's Disease
ANATOMY
This disorder, a stenosing tenosynovitis, involves the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons.
INDICATIONS AND DIAGNOSIS
de Quervain's disease usually occurs with repetitive use of the thumb.13 Thickening is noted, and tenderness is elicited just distal to the radial styloid process over the site of the involved tendon sheath. The Finkelstein test is performed by having the patient make a fist with the thumb inside while simultaneously ulnar deviating the hand. Pain over the affected area is elicited in de Quervain's disease.
TIMING AND OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
Immobilization and the use of NSAIDs should be tried before injection therapy is performed.2
INJECTION TECHNIQUE
Pharmaceuticals and equipment are described in Table 1. With the thumb abducted and extended, palpate the course of the tendons distal to the radial styloid process.
APPROACH AND NEEDLE ENTRY
The needle is placed into the first extensor compartment, directed proximally toward the radial styloid process and sliding in parallel to the abductor and extensor tendons (Figure 3). Do not inject directly into a tendon.
Ganglion Cysts
ANATOMY
Ganglion cysts account for approximately 60 percent of soft tissue, tumor-like swelling affecting the hand and wrist. They usually develop spontaneously in adults 20 to 50 years of age. There is a female-to-male preponderance of 3:1.14 The dorsal wrist ganglion arises from the scapholunate joint and constitutes about 65 percent of ganglia of the wrist and hand. The volar wrist ganglion arises from the distal aspect of the radius and accounts for about 20 to 25 percent of ganglia. Flexor tendon sheath ganglia make up the remaining 10 to 15 percent. The cystic structures are found near or are attached to tendon sheaths and joint capsules. The cyst is filled with soft, gelatinous, sticky, and mucoid fluid.
INDICATIONS AND DIAGNOSIS
Cysts are self evident, being soft and ballotable, and occur along the dorsal and volar aspects of the wrist. Most ganglia resolve spontaneously and do not require treatment. If the patient has symptoms, including pain or paresthesias, or is disturbed by the appearance, aspiration with or without injection of a corticosteroid is effective (no recurrence of the cyst) in 27 to 67 percent of patients.15,16
TIMING AND OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
Aspiration and injection are performed on an elective basis determined by symptoms and patient request.
INJECTION TECHNIQUE
Pharmaceuticals and equipment are described in Table 1. Boundaries of the cyst should be palpated.
APPROACH AND NEEDLE ENTRY
An 18- or 22-gauge needle inserted directly into the cyst should be used to aspirate the cyst after local anesthesia is given. A 20- or 30-mL syringe should be used to provide optimal suction for aspiration. If injecting a corticosteroid after aspiration, a hemostat is used to stabilize the needle while the syringe is changed.
Trigger Finger (Digital Flexor Tenosynovitis)
ANATOMY
All flexor tendons of the hand may develop a tenosynovitis.
INDICATIONS AND DIAGNOSIS
Symptoms develop when a tendon cannot glide within its sheath because of a thickening or nodule that catches at the site of the first annular pulley, preventing smooth extension or flexion of the finger. Patients complain of catching or locking and discomfort with grasping activity of the hand. Trigger finger occurs commonly in patients who have rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes mellitus, and repetitive use injuries.17
TIMING AND OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
INJECTION TECHNIQUE
Pharmaceuticals and equipment are described in Table 1. A nodule secondary to the tenosynovitis is usually palpable in the region of the metacarpal head of the affected tendon.
APPROACH AND NEEDLE ENTRY
A 25-gauge, 1-inch, or 1.5-inch needle is inserted over the palmar aspect distal to the metacarpal head at a 30-degree angle and then directed proximally, almost parallel to the skin, toward the nodule (Figure 4).
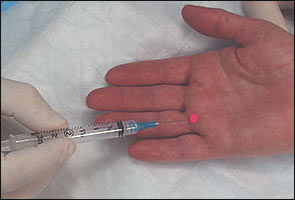
Follow-Up Care
The patient should remain in the supine position for several minutes after the injection. To ascertain whether the pharmaceuticals have been injected into the appropriate location, move the joint through passive range of motion. For tenosynovitis, stress the finger flexors to ascertain the same. A compression dressing should be applied after aspirating a ganglion cyst. To monitor for any adverse reactions, the patient should remain in the office for 30 minutes after the injection. In general, patients should avoid strenuous activity involving the injected region for 48 hours. Patients should be cautioned that they may experience worsening symptoms during the first 24 to 48 hours related to a possible steroid flare, which can be treated with ice and NSAIDs. A follow-up appointment should be arranged within three weeks.