
Am Fam Physician. 2003;68(12):2401-2409
Although post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a debilitating anxiety disorder that may cause significant distress and increased use of health resources, the condition often goes undiagnosed. The lifetime prevalence of PTSD in the United States is 8 to 9 percent, and approximately 25 to 30 percent of victims of significant trauma develop PTSD. The emotional and physical symptoms of PTSD occur in three clusters: re-experiencing the trauma, marked avoidance of usual activities, and increased symptoms of arousal. Before a diagnosis of PTSD can be made, the patient's symptoms must significantly disrupt normal activities and last for more than one month. Approximately 80 percent of patients with PTSD have at least one comorbid psychiatric disorder. The most common comorbid disorders include depression, alcohol and drug abuse, and other anxiety disorders. Treatment relies on a multidimensional approach, including supportive patient education, cognitive behavior therapy, and psychopharmacology. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are the mainstay of pharmacologic treatment.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an anxiety disorder that occurs following exposure to a traumatic event. The disorder has not been extensively studied in primary care; however, the events of September 11, 2001, raised both public and professional awareness of PTSD. Many more cases may now be diagnosed in family practice patients, because they are more apt to disclose information to their physicians and because physicians are more aware of the diagnosis. One study1 estimated that 11.8 percent of patients presenting to a primary care clinic met the diagnostic criteria for PTSD.
Patients with PTSD use health care resources more often than patients without PTSD, including those who have other anxiety disorders.1,2 Because of frustrations in diagnosing and managing their patient's recurrent medical complaints, some physicians characterize patients with PTSD as “difficult” or “heart-sink” patients—that is, patients who evoke “an overwhelming mixture of exasperation, defeat, and sometimes plain dislike.”3 Prompt recognition and effective treatment of PTSD can greatly benefit these patients, their families, and those who work with them.
Background
The psychologic effects of trauma have been described throughout military history. Da Costa syndrome (“soldier's heart”), which is characterized by cardiac symptoms associated with irritability and increased arousal, was described in veterans of the American Civil War. During World War I, it was hypothesized that “shell shock” resulted from brain trauma caused by exploding shells. During World War II, terms such as “combat neurosis” and “operational fatigue” were used to describe combat-related symptoms.
The Vietnam War significantly influenced the current concept of PTSD. In 1980, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 3d ed. (DSM-III)4 established criteria for the diagnosis of PTSD. Modifications were made in subsequent editions.5,6 This article reviews the current diagnostic criteria for PTSD as contained in the 4th edition, text revision (DSM-IV-TR)7 and focuses on diagnosis and management, including the detection and treatment of comorbidities.
Diagnosis
A precipitating traumatic event is necessary, but not sufficient, to make the diagnosis of PTSD. The criteria for diagnosis specify factors concerning the victim's perception of the trauma as well as the duration and impact of associated symptoms, including persistent re-experiencing of the traumatic event, marked avoidance of usual activities, and symptoms of increased arousal (Table 1).7
| A. The person has been exposed to a traumatic event in which both of the following were present: | ||
| 1. The person experienced, witnessed, or was confronted with an event or events that involved actual or threatened death or serious injury, or a threat to the physical integrity of self or others. | ||
| 2. The person's response involved intense fear, helplessness, or horror. note: In children, this may be expressed instead by disorganized or agitated behavior. | ||
| B. The traumatic event is persistently re-experienced in one (or more) of the following ways: | ||
| 1. Recurrent and intrusive distressing recollections of the event, including images, thoughts, or perceptions. note: In young children, repetitive play may occur in which themes or aspects of the trauma are expressed. | ||
| 2. Recurrent distressing dreams of the event. note: In children, there may be frightening dreams without recognizable content. | ||
| 3. Acting or feeling as if the traumatic event were recurring (includes a sense of reliving the experi ence, illusions, hallucinations, and dissociative flashback episodes, including those that occur on awakening or when intoxicated). note: In young children, trauma-specific reenactment may occur. | ||
| 4. Intense psychologic distress at exposure to internal or external cues that symbolize or resemble an aspect of the traumatic event. | ||
| 5. Physiologic reactivity on exposure to internal or external cues that symbolize or resemble an aspect of the traumatic event. | ||
| C. Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the trauma and numbing of general responsiveness (not present before the trauma), as indicated by three (or more) of the following: | ||
| 1. Effort to avoid thoughts, feelings, or conversations associated with the trauma. | ||
| 2. Effort to avoid activities, places, or people that arouse recollections of the trauma. | ||
| 3. Inability to recall an important aspect of the trauma. | ||
| 4. Markedly diminished interest or participation in significant activities. | ||
| 5. Feeling of detachment or estrangement from others. | ||
| 6. Restricted range of affect (e.g., unable to have loving feelings). | ||
| 7. Sense of a foreshortened future (e.g., does not expect to have a career, marriage, children, or a normal life span). | ||
| D. Persistent symptoms of increased arousal (not present before the trauma), as indicated by two (or more) of the following: | ||
| 1. Difficulty falling or staying asleep. | ||
| 2. Irritability or outbursts of anger. | ||
| 3. Difficulty concentrating. | ||
| 4. Hypervigilance. | ||
| 5. Exaggerated startle response. | ||
| E. Duration of the disturbance (symptoms in Criteria B, C, and D) is more than one month. | ||
| F. The disturbance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of function. | ||
| Specify if: | ||
| Acute: If duration of symptoms is less than three months. | ||
| Chronic: If duration of symptoms is three months or more. | ||
| Specify if: | ||
| With delayed onset: If onset of symptoms is at least six months after the stressor. | ||
Before a diagnosis of PTSD can be made, symptoms must last for at least one month and must significantly disrupt normal activities. In persons who have survived a traumatic event, an anxiety syndrome that lasts for less than one month is termed “acute stress disorder”; this condition requires three or more dissociative symptoms in addition to the persistent symptoms associated with PTSD. Symptoms of PTSD that last less than three months indicate an acute condition. A delayed picture occurs in patients who begin experiencing symptoms six months or more after the traumatic event.7
The diagnosis of PTSD may be difficult to make for many reasons. Patients may not recognize the link between their symptoms and an experienced traumatic event; patients may be unwilling to disclose the event; or the presentation may be obscured by depression, substance abuse, or other comorbidities.8 Direct, empathic, and nonjudgmental questioning is recommended when physicians take a patient history. For example, the physician might ask, “Have you ever been attacked or threatened?” or, “Have you ever been in a severe accident or natural disaster?”8
Making a connection between a patient's symptoms and a trauma that occurred in childhood may be particularly difficult to establish. An appropriate question to establish this connection is, “Many people are troubled by frightening events that occurred in their childhood. Do you have this problem?”9
A screening questionnaire for PTSD reportedly has a sensitivity of 80 percent and a specificity of 97 percent for the diagnosis of PTSD.10 Examples of the questions include: “Do you have diminished interest in activities”; “Do you have problems sleeping?”; and “Do you find it hard to feel or show affection for others?”10
Epidemiology
PREVALENCE
The overall lifetime prevalence of PTSD in the United States is approximately 8 to 9 percent, and the condition is twice as common in women.7,11,12 Symptoms that do not meet the full criteria for PTSD appear to be common in the general population and can be quite common in groups at high risk of PTSD.13 For example, although the lifetime prevalence of PTSD in veterans of the Vietnam War is around 30 percent, about 50 percent of Vietnam veterans had some clinically significant symptoms of PTSD.14
RISK FACTORS
The epidemiology of PTSD is directly linked to the epidemiology of trauma.11 The likelihood of developing PTSD varies with severity, duration, and proximity of the experienced trauma.4 Approximately 25 to 30 percent of victims of traumatic events develop symptoms of PTSD; however, response to trauma varies with the severity and the subjective experience associated with the trauma.12,15,16 In men, exposure to military combat and witnessing someone being badly injured or killed are the types of trauma most commonly associated with a diagnosis of PTSD. The most common traumatic events associated with PTSD in women are rape and sexual molestation.11
Persons who have been victimized previously are at greater risk of being victimized again. A history of childhood abuse increases the risk for victimization and PTSD in adults.17 Because there is a strong relationship between mental disorders and victimization by assault, patients with mental health problems have a high risk of PTSD. One study18 noted that 72.2 percent of patients in community mental health centers had been exposed to physical or sexual assault or were family members of homicide victims.18 Similarly, persons who abuse alcohol or drugs are approximately 1.5 times more likely to experience traumatic events than nondrug users and have, therefore, an increased risk of developing PTSD. A history of behavior problems before the age of 15 years, as occurs in patients with antisocial personality disorder, also increases the risk of PTSD.18
Etiology
Although the etiology of PTSD is unknown, most investigators believe that a personal predisposition is necessary for symptoms to develop after a traumatic event. Clinically significant symptoms following a traumatic event occur in a minority of persons. Those likely to develop PTSD tend to have a pre-existing depression or anxiety disorder, or a family history of anxiety and neuroticism.20
From a biologic perspective, the body's failure to return to its pretraumatic state differentiates PTSD from a simple fear response. In a normal fear response, the immediate sympathetic discharge activates the “fight-or-flight” reaction. Increases in both catecholamines and cortisol occur relative to the severity of the stressor. Cortisol release stimulated by corticotropin-releasing factor via the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis acts in a negative feedback loop to suppress sympathetic activation and cause further release of cortisol.
In patients with PTSD, ambient cortisol levels are lower than normal; this state has been attributed to chronic “adrenal exhaustion” from inhibition of the HPA axis by persistent severe anxiety. However, recent data21 note that cortisol levels in the immediate aftermath of a motor vehicle wreck were significantly lower in persons who went on to develop PTSD. In a related study,22 cortisol levels immediately after rape were lower in women with a previous history of rape. Some investigators have hypothesized that the HPA axis and the sympathetic nervous system are disassociated in persons who develop PTSD, which may allow for an uncontrolled catecholamine release that affects formation of memories during the trauma and perhaps exacerbates symptoms when that person is exposed to cues after the trauma.15
Comorbidities
PTSD is associated with increased rates of affective disorders, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse. Data from the National Comorbidity Survey12 indicate that at least one additional psychiatric disorder is present in 88.3 percent of men and 79.0 percent of women who have a history of PTSD. In addition, 59 percent of men and 44 percent of women who have PTSD meet the criteria for three or more psychiatric diagnoses. Women who have PTSD are 4.1 times as likely to develop a major depression and 4.5 times as likely to develop mania as women who do not have PTSD. Men who have PTSD are 6.9 times as likely to develop depression and 10.4 times as likely to develop mania as men who do not have PTSD.23
More than one half of men with PTSD also have a comorbid alcohol problem, and a significant portion of men and women who have PTSD have a comorbid illicit-substance use problem.12 In patients who have PTSD, phobias tend to be more prevalent than generalized anxiety disorder or panic disorder; the risk of almost all anxiety disorders is increased markedly in these patients23 (Table 2).12 The rate of attempted suicide in patients who have PTSD is estimated at 20 percent.24
| Comorbidity | Men (%) | Women (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Major depressive disorder | 47.9 | 48.5 |
| Alcohol abuse or dependence | 51.9 | 27.9 |
| Drug abuse or dependence | 34.5 | 26.9 |
| Simple phobias | 31.4 | 29.0 |
| Social phobia | 27.6 | 28.4 |
| Dysthymia | 21.4 | 23.3 |
Disease Course and Prognosis
PTSD may occur at any age, even in childhood. Symptom duration is variable and is affected by the proximity, duration, and intensity of the trauma, as well as comorbidity with other psychiatric disorders.7,20 The patient's subjective interpretation of the trauma also influences symptoms.18 In patients who are receiving treatment, the average duration of symptoms is approximately 36 months. In patients who are not receiving treatment, the average duration of symptoms rises to 64 months. More than one third of patients who have PTSD never fully recover.12
Treatment
The treatment of patients with PTSD relies on a multidimensional approach.26 Treatment options include patient education, social support, and anxiety management through psychotherapy and psychopharmacologic intervention. Patient education and social support are important initial interventions to engage the patient and mitigate the impact of the traumatic event. Local and national support groups may help to destigmatize the mental health diagnosis and reaffirm that symptoms of PTSD involve more than just a reaction to stress and require treatment. Support from family and friends encourages understanding and acceptance that may alleviate survivor guilt. However, the mainstay of treatment is psychopharmacologic and psychotherapeutic intervention (Figure 1).
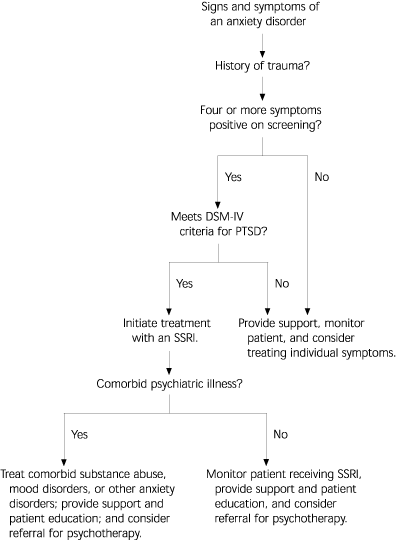
PSYCHOTHERAPY
Studies demonstrate that cognitive-behavior treatment is effective in ameliorating the symptoms of PTSD. In a study27 of patients receiving various forms of cognitive-behavior treatment in nine sessions over a six-week period, the percentage of patients who attained positive end-state function (defined as a 50 percent reduction in severity of PTSD symptoms) ranged from 21 to 46 percent. A similar study showed that 32 to 53 percent of patients receiving 10 sessions of cognitive-behavior treatment over a 16-week period achieved positive end-state function.27
Specific types of cognitive-behavior treatment include cognition therapy, exposure therapy, and stress inoculation training. These therapies focus on ways for patients to confront fear and develop anxiety-management tools. The different forms of cognitive-behavior treatment tend to be equally efficacious when used individually and in combination. Other therapies, such as group therapy, eye movement desensitization, and reprocessing therapy, may have some role in the treatment of PTSD; however, because their efficacy has not been substantially demonstrated, cognitive-behavior treatment remains the primary mode of therapy.26–28
Approximately 14 percent of patients with PTSD discontinue psychotherapy. The highest drop-out rates (up to 50 percent) occur with exposure therapy, indicating that many patients have difficulty with re-experiencing the trauma.26,27 The attending physician can provide solid therapeutic intervention with good listening skills and empathic support. If resolution of PTSD symptoms does not occur with initial support and medication, referring the patient to a therapist may be warranted.
Because PTSD can have devastating effects on family members and those close to the patient, family and other group therapies may be indicated as adjuncts to individual treatment of the patient with PTSD.29
PHARMACOLOGY
Recent interest in the treatment of PTSD has stimulated large, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials of the efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) in the treatment of the symptoms of PTSD. Currently, paroxetine (Paxil) and sertraline (Zoloft) are the only medications that have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of PTSD. In two separate 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials,30,31 both paroxetine and sertraline were found to be effective in the acute treatment of symptoms of PTSD. Of the patients who received 20 mg or 40 mg of paroxetine, 62 percent and 54 percent, respectively, responded positively compared with 37 percent of patients who received placebo.30 [Evidence level A, randomized controlled trial] Patients who received a mean daily dosage of 146 mg of sertraline had a 60 percent positive response rate compared with a 38 percent positive response rate in patients receiving placebo.31
Another study32 showed that sertraline was effective in preventing relapse of symptoms of PTSD during a 28-week maintenance phase following 24 weeks of acute therapy. This study also showed that continued treatment with sertraline at a mean daily dosage of 137 mg yielded a 5 percent relapse rate compared with a 26 percent relapse rate in those receiving placebo.32 Other trials33 have been conducted, including four open trials and two controlled trials of fluoxetine, and five open trials of fluvoxamine. These studies suggest that several SSRIs are helpful in the amelioration of acute symptoms of PTSD.33
Research into the use of neuroleptic medications in patients who have PTSD is limited for the most part to case studies. Approximately 10 percent of patients with PTSD are treated with an antipsychotic medication; these patients tend to have symptoms of PTSD that are more intrusive and severe.34 Case reports note a reduction in flashbacks and nightmares with the use of risperidone. Clozapine was reported to be effective in a patient with concomitant psychosis who was a veteran of the Vietnam War. Results of an open-label trial of olanzapine in 46 patients with combat-induced PTSD suggest possible efficacy in the treatment of PTSD.34
Previous studies33 indicate that the use of tricyclic antidepressants and monoamine oxidase inhibitors are moderately effective in the treatment of PTSD and are superior to placebo; however, because of their side effect profiles, these medications are currently considered second- or third-line agents. Open-label investigations33 of the use of the mood stabilizers lamotrigine, valproate, and carbamazepine show promise in reducing the symptoms of PTSD. Furthermore, buspirone and clonazepam have shown some benefit in reducing anxiety in patients with PTSD.33 A recent pilot study suggests that propranolol, administered after an acute traumatic event, may have a preventive effect on the subsequent development of PTSD.35