
Am Fam Physician. 2005;71(9):1766-1767
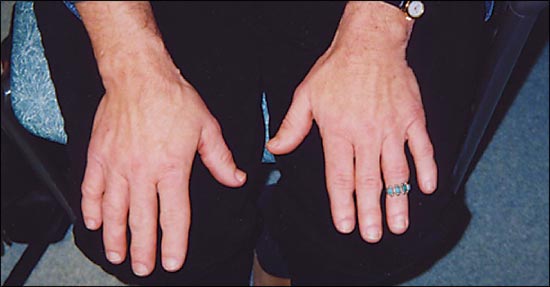
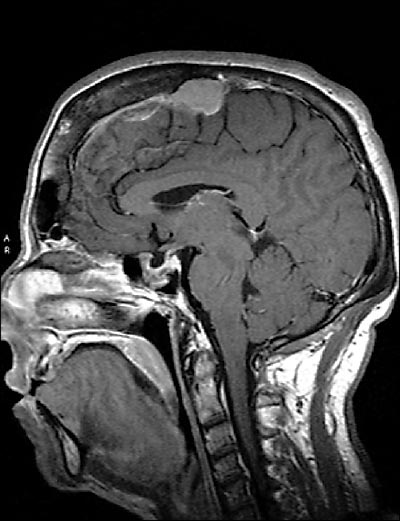
A 58-year-old woman presented to establish a primary care relationship. Her chief complaints were chronic pain of the hip and knee and excessive daytime sleepiness. Over the past few years, she felt that her body had been changing. She reported polyuria, excessive perspiration, and facial hair that she shaved once a week. She said her hands had enlarged to the point that her rings would not fit properly (Figure 1). Her medical history was significant only for hypertension and hyperlipidemia, which was well controlled with medication. She was gravida 1, para 0010 and had been postmenopausal for eight years. On physical examination, she was found to have coarse facial hair and features with a notable protruding jaw and a large fleshy nose. She also had a deep, resonant voice. The rest of her physical examination, including visual field testing, revealed no abnormalities. Magnetic resonance imaging of the head and pituitary was obtained (Figure 2).
Question
Discussion
The answer is B: ectopic growth hormone (GH)-secreting tumor. Based on the combined findings of acromegaly and an infrasellar mass (Figure 3), a GH-secreting tumor is most likely. Acromegaly is the syndrome of GH hypersecretion. Clinical features are directly attributable to excessive amounts of GH and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). Features include acral enlargement (Figure 1), osteoarthritis, hyperhidrosis, hirsutism, hypertension, cardiomyopathy, obstructive sleep apnea, and diabetes mellitus.1 Acromegaly affects three to four persons per 1 million annually, with a mean patient age of 40 to 45 years at diagnosis.1,2
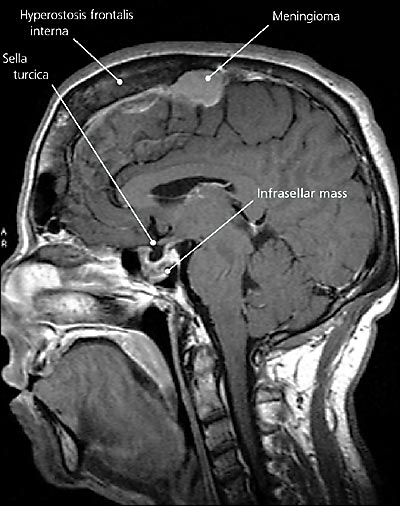
The majority of cases are caused by a somatotroph adenoma of the anterior pituitary, and most are confined to the sella. However, rare causes of acromegaly include ectopic GH-secreting tumors, hypothalamic tumors, McCune-Albright syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1, bronchial carcinoid, and small-cell lung cancer.2 Although pure monomorphic adenomas secrete GH, variant bimorphic adenomas may secrete GH and prolactin.3
This patient had a large, 1.7-cm macroadenoma located in the sphenoid sinus. On intraoperative interpretation, it was found to be ectopic in nature. All neuroendocrine hormonal levels were within normal, age-appropriate limits, except GH and IGF-1, which were extremely elevated. The patient underwent successful transsphenoidal/transseptal resection of the tumor. Immuno-histochemical staining showed isolated GH-secreting cells. Treatment included radiation and adjuvant chemotherapy,4 after which her symptoms improved dramatically and GH/IGF-1 returned to normal.
Prolactinomas are the most common pituitary adenomas. Generally, size correlates with hormonal output, and diagnosis depends on sustained hyperprolactinemia, normal or suppressed gonadotropin levels, and abnormal pituitary scanning.3 Nonsecretory or null cell pituitary adenomas are the second most common pituitary tumor. They typically present with signs and symptoms of local compression, such as bitemporal hemianopsia, headache, and symptoms from hypopituitarism.
Craniopharyngiomas are solid or cystic tumors arising from the remnants of Rathke’s pouch. Most occur within or above the sella. Typically, patients present with anterior pituitary hormonal deficiency.3
| Condition | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Prolactinoma | Most common pituitary adenoma; hypogonadism and galactorrhea |
| Ectopic growth hormone–secreting tumor | Extrapituitary acromegaly |
| Somatotroph adenoma | Pituitary acromegaly |
| Craniopharyngioma | From Rathke’s pouch, with diabetes insipidus, growth hormone deficiency, and gonadal failure |
| Meningioma | Richly vascularized nonendocrine tumor, from mesoderm cell layer, attached to dura |