
Am Fam Physician. 2009;79(1):48-49
Author disclosure: Nothing to disclose.
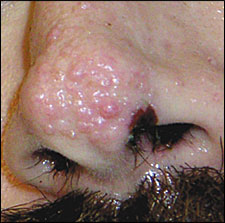
A 24-year-old man with mental retardation who was admitted to the hospital for community-acquired pneumonia presented with papulonodular lesions on his nose (see accompanying figure). The patient's guardian reported that the lesions first appeared 10 years earlier on the anterior aspect of the nose. The lesions had remained fairly stable in appearance and did not seem to bother the patient. The patient had a history of tonicclonic seizures beginning in childhood that were well controlled with phenytoin (Dilantin). He had a family history of similar lesions.
Question
Discussion
The correct answer is B: adenoma sebaceum. The term adenoma sebaceum is a misnomer because it does not represent sebaceous hyperplasia. Tuberous sclerosis is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by the development of hamartomas. These hamartomas may involve the skin, brain, heart, kidneys, and other organs in varying severity and lead to the various clinical features of this disorder. Angiofibromas (previously called adenoma sebaceum) are the most common skin lesions associated with tuberous sclerosis, and typically affect the malar region of the face. Histologically, these lesions are composed of fibrous and vascular tissue (hence, the term angiofibromas). The diagnostic triad of seizure disorder, mental retardation, and facial angiofibromas (Vogt triad) is classic for tuberous sclerosis.1 How-ever, more than one half of persons with the condition are of normal intelligence.2
The lesions of adenoma sebaceum typically occur in adolescence or young adulthood and appear on the nose, nasolabial folds, and cheeks in a malar distribution. They initially appear as freckles and progress into erythematous, papulonodular lesions. They do not produce pus and remain unchanged over time. The National Tuberous Sclerosis Association has published guide-lines for evaluating patients with suspected tuberous sclerosis.3 Facial angiofibromas are a major diagnostic feature. Other dermatologic features include hypomelanotic macules or ash leaf spots on the trunk, lower and upper extremities, head, and neck; shagreen patches (i.e., fibromas on the trunk); and periungual fibromas (i.e., flesh-colored lesions along the nail folds).
Tuberous sclerosis–related seizures begin as myoclonic jerks in early childhood, and then progress to tonicclonic seizures as the child gets older. Behavioral problems are common and include attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism. Treatment of adenoma sebaceum focuses on cosmesis and can be achieved with laser therapy, cryotherapy, electrocautery, or dermabrasion. Disfiguring lesions may improve with laser therapy and dermabrasion.
Acne vulgaris is a common inflammatory disorder beginning in adolescence, although it may also occur in adulthood. Acne lesions may be papular, nodular, or pustular. They are nonstatic and have a waxing and waning course.
Rhinophyma occurs in the late stages of rosacea and is caused by hyperplasia of sebaceous glands of the nose. The condition begins between 30 and 50 years of age and affects more men than women, primarily those of Celtic descent.4 It is associated with telangiectasia, nodules, papules, and pustules. It can be disfiguring and may require surgical treatment.
Sebaceous hyperplasia is common in older persons. It appears as small (1 to 3 mm) yellow papules with central umbilication and surface telangiectasia. Biopsy is useful in differentiating sebaceous hyperplasia from a basal cell carcinoma.5
Syringomas are benign tumors of the sweat ducts, appearing as tiny, flesh-colored, dermal papules. They typically occur on the lower eyelid in persons between 20 and 40 years of age, and have no potential for malignancy.
| Condition | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Acne vulgaris | Inflammatory process; pustular, nodular, or papular; nonstatic with a waxing and waning course; usually occurs in adolescence, but may also occur in adulthood |
| Adenoma sebaceum | Erythematous, papulonodular, static lesions in a malar distribution; associated with tuberous sclerosis, seizures, mental retardation, other skin lesions, and hamartomas in other visceral locations; appears in adolescence and young adulthood |
| Rhinophyma | Occurs in late stages of rosacea; nose is primarily affected; associated with telangiectasia, nodules, papules, and pustules; usually begins between 30 and 50 years of age |
| Sebaceous hyperplasia | Small (1 to 3 mm) yellow papules with central umbilication and surface telangiectasia; common in older persons |
| Syringoma | Benign tumors of the sweat ducts; small, flesh-colored, dermal papules, typically on the lower eyelid; occurs between 20 and 40 years of age |