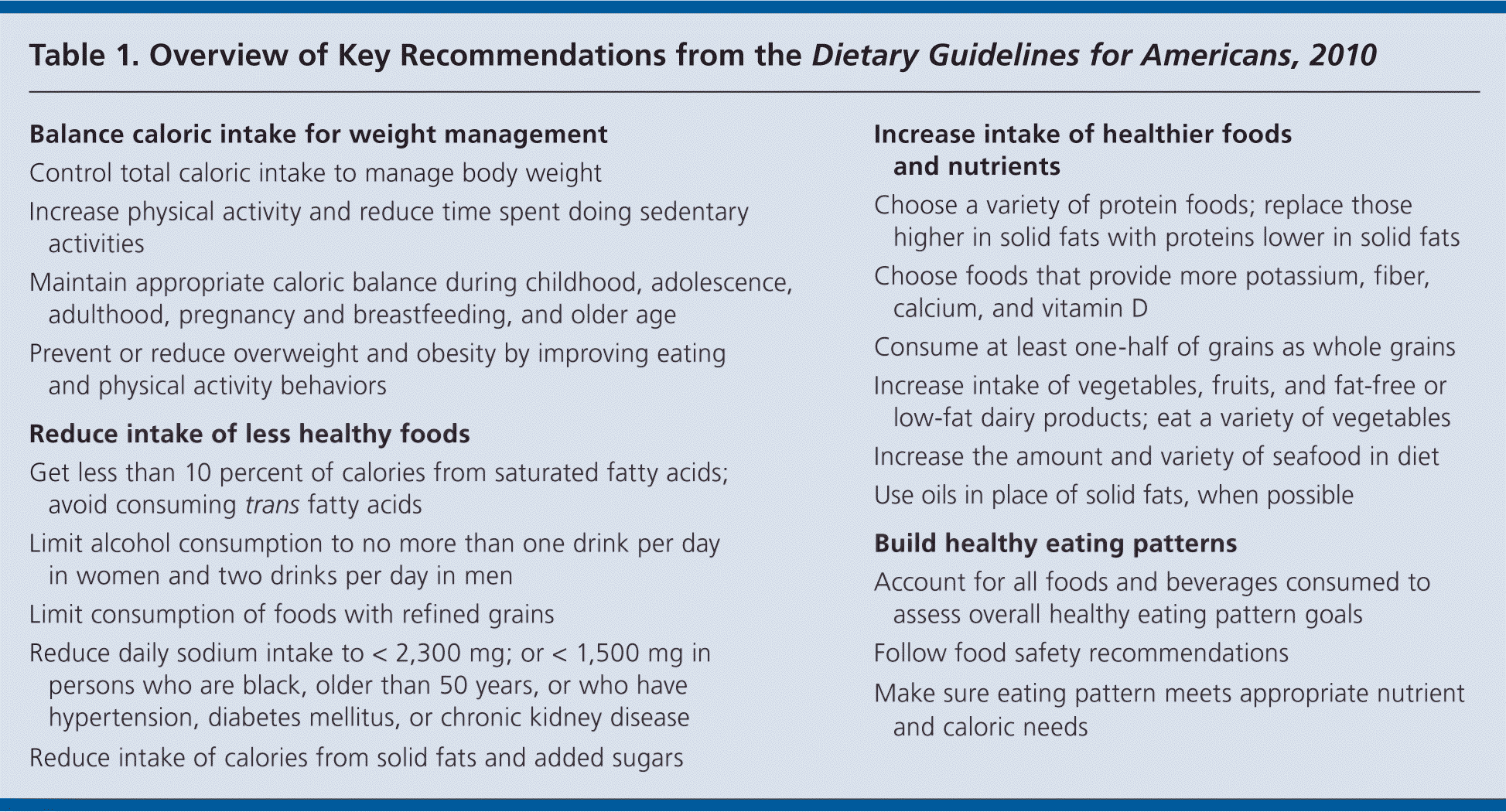
| Balance caloric intake for weight management |
| Control total caloric intake to manage body weight |
| Increase physical activity and reduce time spent doing sedentary activities |
| Maintain appropriate caloric balance during childhood, adolescence, adulthood, pregnancy and breastfeeding, and older age |
| Prevent or reduce overweight and obesity by improving eating and physical activity behaviors |
| Reduce intake of less healthy foods |
| Get less than 10 percent of calories from saturated fatty acids; avoid consuming trans fatty acids |
| Limit alcohol consumption to no more than one drink per day in women and two drinks per day in men |
| Limit consumption of foods with refined grains |
| Reduce daily sodium intake to < 2,300 mg; or < 1,500 mg in persons who are black, older than 50 years, or who have hypertension, diabetes mellitus, or chronic kidney disease |
| Reduce intake of calories from solid fats and added sugars |
| Increase intake of healthier foods and nutrients |
| Choose a variety of protein foods; replace those higher in solid fats with proteins lower in solid fats |
| Choose foods that provide more potassium, fiber, calcium, and vitamin D |
| Consume at least one-half of grains as whole grains |
| Increase intake of vegetables, fruits, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products; eat a variety of vegetables |
| Increase the amount and variety of seafood in diet |
| Use oils in place of solid fats, when possible |
| Build healthy eating patterns |
| Account for all foods and beverages consumed to assess overall healthy eating pattern goals |
| Follow food safety recommendations |
| Make sure eating pattern meets appropriate nutrient and caloric needs |