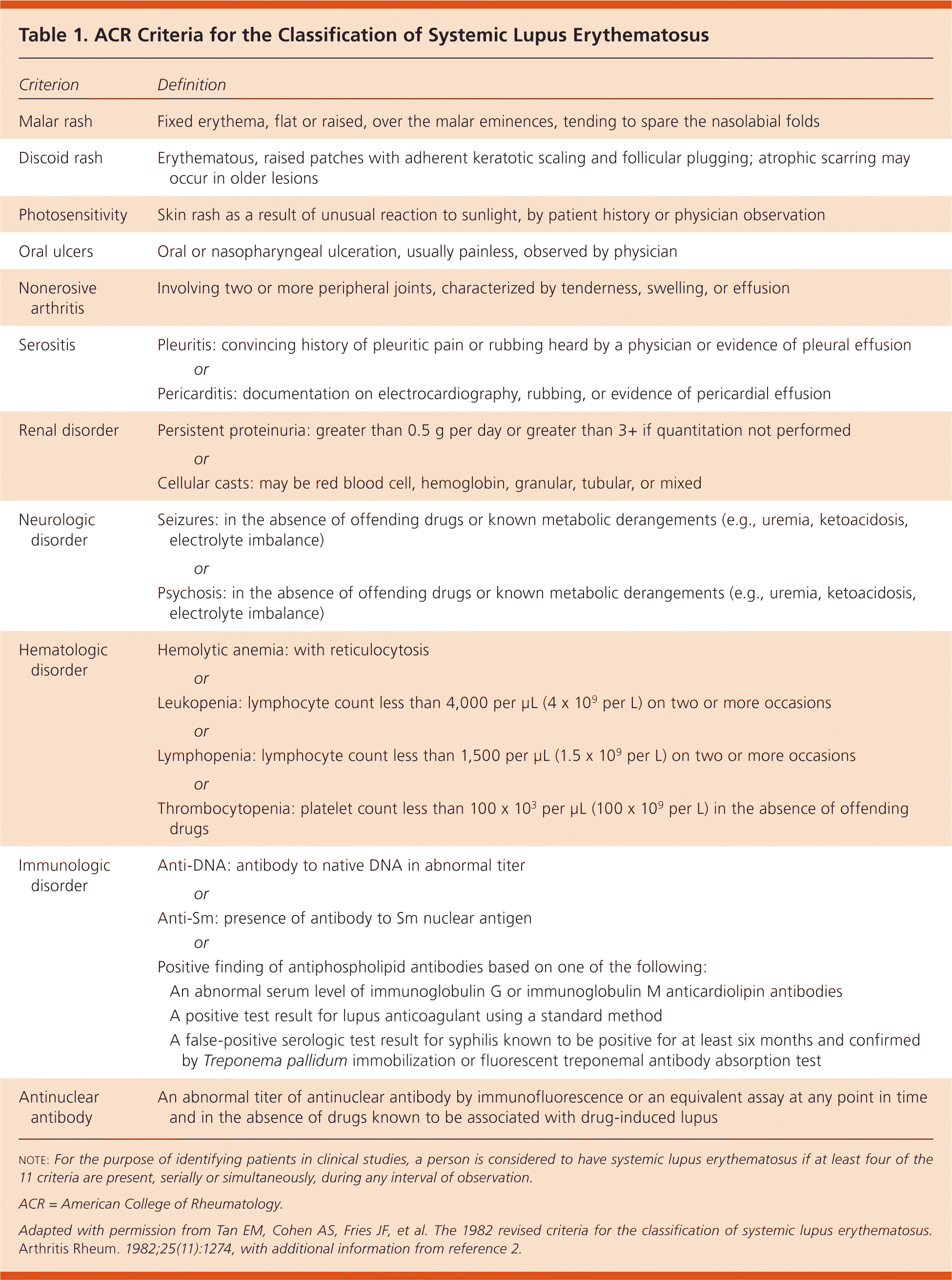
| Malar rash | Fixed erythema, flat or raised, over the malar eminences, tending to spare the nasolabial folds |
| Discoid rash | Erythematous, raised patches with adherent keratotic scaling and follicular plugging; atrophic scarring may occur in older lesions |
| Photosensitivity | Skin rash as a result of unusual reaction to sunlight, by patient history or physician observation |
| Oral ulcers | Oral or nasopharyngeal ulceration, usually painless, observed by physician |
| Nonerosive arthritis | Involving two or more peripheral joints, characterized by tenderness, swelling, or effusion |
| Serositis | Pleuritis: convincing history of pleuritic pain or rubbing heard by a physician or evidence of pleural effusion |
| or |
| Pericarditis: documentation on electrocardiography, rubbing, or evidence of pericardial effusion |
| Renal disorder | Persistent proteinuria: greater than 0.5 g per day or greater than 3+ if quantitation not performed |
| or |
| Cellular casts: may be red blood cell, hemoglobin, granular, tubular, or mixed |
| Neurologic disorder | Seizures: in the absence of offending drugs or known metabolic derangements (e.g., uremia, ketoacidosis, electrolyte imbalance) |
| or |
| Psychosis: in the absence of offending drugs or known metabolic derangements (e.g., uremia, ketoacidosis, electrolyte imbalance) |
| Hematologic disorder | Hemolytic anemia: with reticulocytosis |
| or |
| Leukopenia: lymphocyte count less than 4,000 per μL (4 × 109 per L) on two or more occasions |
| or |
| Lymphopenia: lymphocyte count less than 1,500 per μL (1.5 × 109 per L) on two or more occasions |
| or |
| Thrombocytopenia: platelet count less than 100 × 103 per μL (100 × 109 per L) in the absence of offending drugs |
| Immunologic disorder | Anti-DNA: antibody to native DNA in abnormal titer |
| or |
| Anti-Sm: presence of antibody to Sm nuclear antigen |
| or |
| Positive finding of antiphospholipid antibodies based on one of the following: |
| An abnormal serum level of immunoglobulin G or immunoglobulin M anticardiolipin antibodies |
| A positive test result for lupus anticoagulant using a standard method |
| A false-positive serologic test result for syphilis known to be positive for at least six months and confirmed by Treponema pallidum immobilization or fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test |
| Antinuclear antibody | An abnormal titer of antinuclear antibody by immunofluorescence or an equivalent assay at any point in time and in the absence of drugs known to be associated with drug-induced lupus |