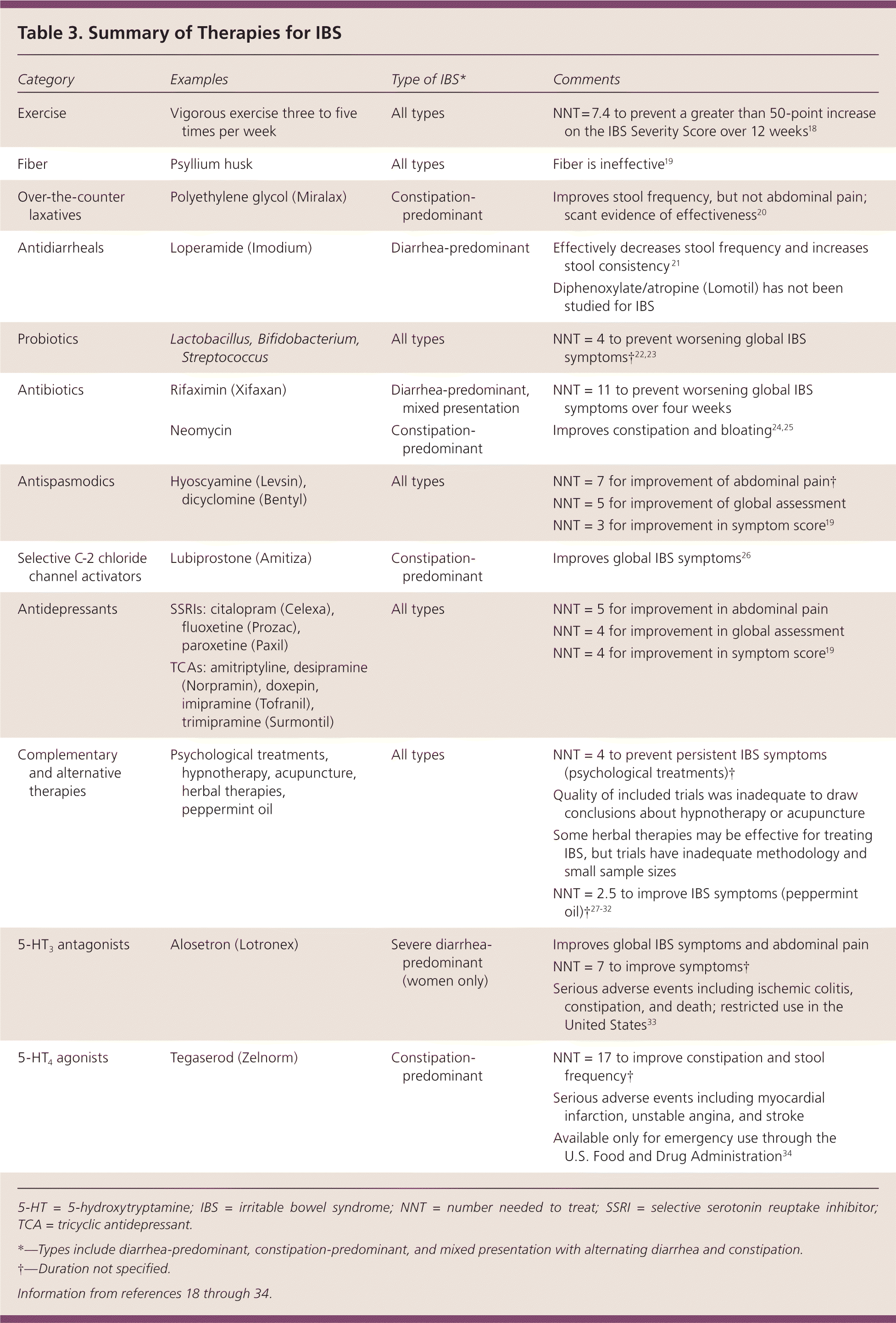
| Exercise | | All types | |
| Fiber | | All types | |
| Over-the-counter laxatives | | Constipation-predominant | |
| Antidiarrheals | | Diarrhea-predominant | |
| Probiotics | | All types | |
| Antibiotics | | Diarrhea-predominant, mixed presentation | |
| Constipation-predominant | |
| Antispasmodics | | All types | NNT = 7 for improvement of abdominal pain† NNT = 5 for improvement of global assessment NNT = 3 for improvement in symptom score19
|
| Selective C-2 chloride channel activators | | Constipation-predominant | |
| Antidepressants | SSRIs: citalopram (Celexa), fluoxetine (Prozac), paroxetine (Paxil) TCAs: amitriptyline, desipramine (Norpramin), doxepin, imipramine (Tofranil), trimipramine (Surmontil)
| All types | NNT = 5 for improvement in abdominal pain NNT = 4 for improvement in global assessment NNT = 4 for improvement in symptom score19
|
| Complementary and alternative therapies | Psychological treatments, hypnotherapy, acupuncture, herbal therapies, peppermint oil
| All types | NNT = 4 to prevent persistent IBS symptoms (psychological treatments)† Quality of included trials was inadequate to draw conclusions about hypnotherapy or acupuncture Some herbal therapies may be effective for treating IBS, but trials have inadequate methodology and small sample sizes NNT = 2.5 to improve IBS symptoms (peppermint oil)†27–32
|
| 5-HT3 antagonists | | Severe diarrhea-predominant (women only) | Improves global IBS symptoms and abdominal pain NNT = 7 to improve symptoms† Serious adverse events including ischemic colitis, constipation, and death; restricted use in the United States33
|
| 5-HT4 agonists | | Constipation-predominant | NNT = 17 to improve constipation and stool frequency† Serious adverse events including myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and stroke Available only for emergency use through the U.S. Food and Drug Administration34
|