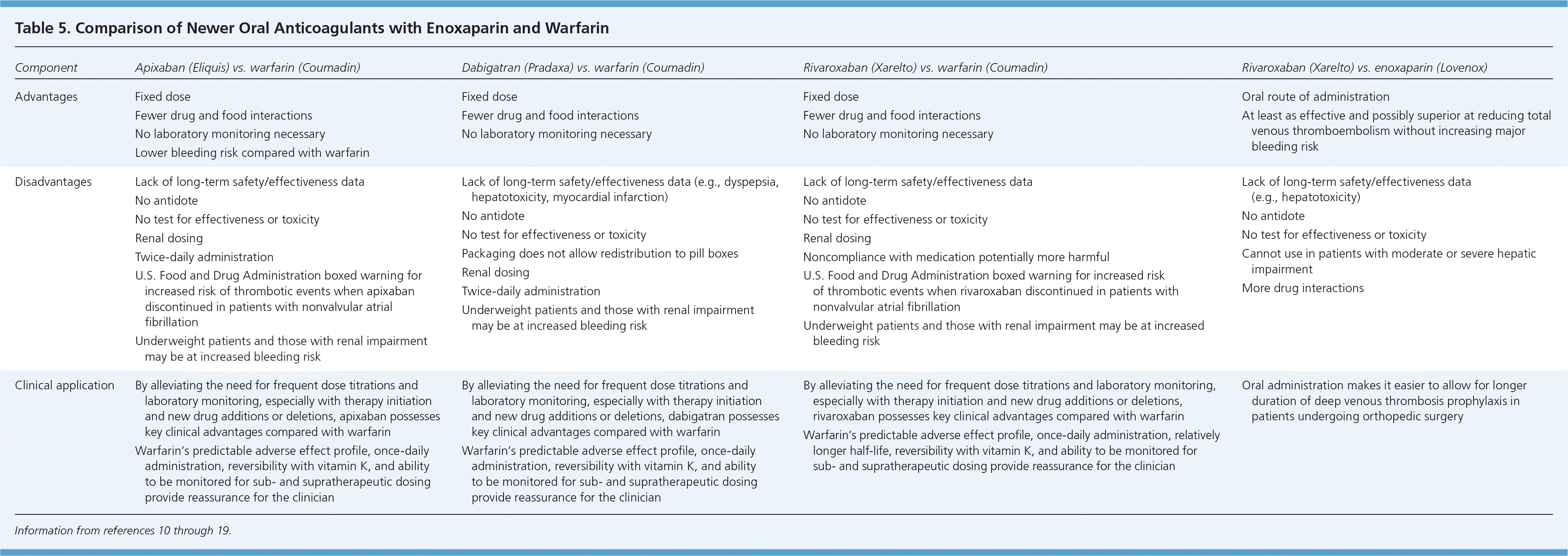
| Advantages | Fixed dose Fewer drug and food interactions No laboratory monitoring necessary Lower bleeding risk compared with warfarin
| | | |
| Disadvantages | Lack of long-term safety/effectiveness data No antidote No test for effectiveness or toxicity Renal dosing Twice-daily administration U.S. Food and Drug Administration boxed warning for increased risk of thrombotic events when apixaban discontinued in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation Underweight patients and those with renal impairment may be at increased bleeding risk
| Lack of long-term safety/effectiveness data (e.g., dyspepsia, hepatotoxicity, myocardial infarction) No antidote No test for effectiveness or toxicity Packaging does not allow redistribution to pill boxes Renal dosing Twice-daily administration Underweight patients and those with renal impairment may be at increased bleeding risk
| Lack of long-term safety/effectiveness data No antidote No test for effectiveness or toxicity Renal dosing Noncompliance with medication potentially more harmful U.S. Food and Drug Administration boxed warning for increased risk of thrombotic events when rivaroxaban discontinued in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation Underweight patients and those with renal impairment may be at increased bleeding risk
| Lack of long-term safety/effectiveness data (e.g., hepatotoxicity) No antidote No test for effectiveness or toxicity Cannot use in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment More drug interactions
|
| Clinical application | By alleviating the need for frequent dose titrations and laboratory monitoring, especially with therapy initiation and new drug additions or deletions, apixaban possesses key clinical advantages compared with warfarin Warfarin's predictable adverse effect profile, once-daily administration, reversibility with vitamin K, and ability to be monitored for sub-and supratherapeutic dosing provide reassurance for the clinician
| By alleviating the need for frequent dose titrations and laboratory monitoring, especially with therapy initiation and new drug additions or deletions, dabigatran possesses key clinical advantages compared with warfarin Warfarin's predictable adverse effect profile, once-daily administration, reversibility with vitamin K, and ability to be monitored for sub- and supratherapeutic dosing provide reassurance for the clinician
| By alleviating the need for frequent dose titrations and laboratory monitoring, especially with therapy initiation and new drug additions or deletions, rivaroxaban possesses key clinical advantages compared with warfarin Warfarin's predictable adverse effect profile, once-daily administration, relatively longer half-life, reversibility with vitamin K, and ability to be monitored for sub- and supratherapeutic dosing provide reassurance for the clinician
| |