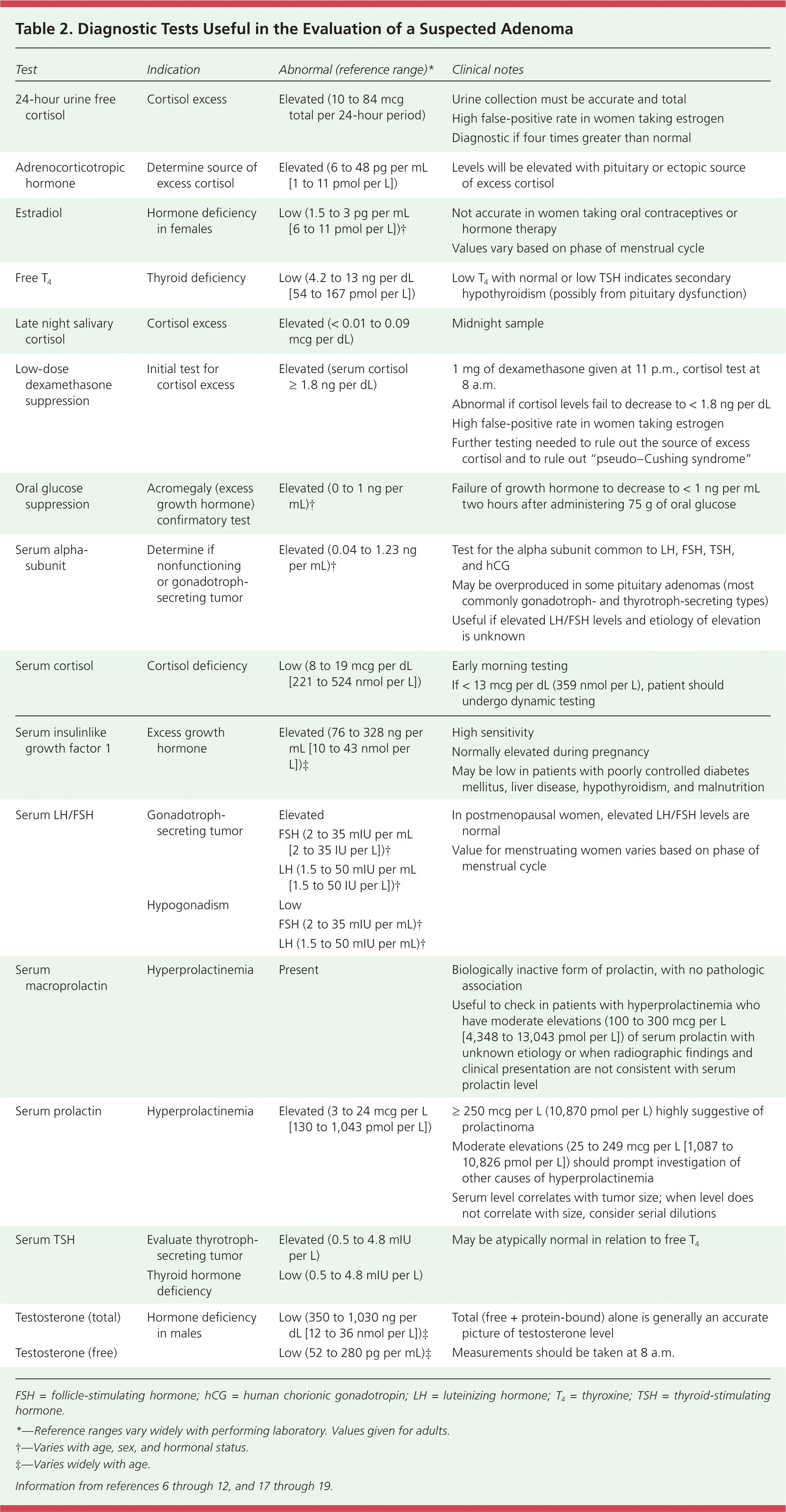
| 24-hour urine free cortisol | Cortisol excess | Elevated (10 to 84 mcg total per 24-hour period) | Urine collection must be accurate and total |
| High false-positive rate in women taking estrogen |
| Diagnostic if four times greater than normal |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone | Determine source of excess cortisol | Elevated (6 to 48 pg per mL [1 to 11 pmol per L]) | Levels will be elevated with pituitary or ectopic source of excess cortisol |
| Estradiol | Hormone deficiency in females | Low (1.5 to 3 pg per mL [6 to 11 pmol per L])† | Not accurate in women taking oral contraceptives or hormone therapy |
| Values vary based on phase of menstrual cycle |
| Free T4 | Thyroid deficiency | Low (4.2 to 13 ng per dL [54 to 167 pmol per L]) | Low T4 with normal or low TSH indicates secondary hypothyroidism (possibly from pituitary dysfunction) |
| Late night salivary cortisol | Cortisol excess | Elevated (< 0.01 to 0.09 mcg per dL) | Midnight sample |
| Low-dose dexamethasone suppression | Initial test for cortisol excess | Elevated (serum cortisol ≥ 1.8 ng per dL) | 1 mg of dexamethasone given at 11 p.m., cortisol test at 8 a.m. |
| Abnormal if cortisol levels fail to decrease to < 1.8 ng per dL |
| High false-positive rate in women taking estrogen |
| Further testing needed to rule out the source of excess cortisol and to rule out “pseudo–Cushing syndrome” |
| Oral glucose suppression | Acromegaly (excess growth hormone) confirmatory test | Elevated (0 to 1 ng per mL)† | Failure of growth hormone to decrease to < 1 ng per mL two hours after administering 75 g of oral glucose |
| Serum alpha-subunit | Determine if nonfunctioning or gonadotroph-secreting tumor | Elevated (0.04 to 1.23 ng per mL)† | Test for the alpha subunit common to LH, FSH, TSH, and hCG |
| May be overproduced in some pituitary adenomas (most commonly gonadotroph- and thyrotroph-secreting types) |
| Useful if elevated LH/FSH levels and etiology of elevation is unknown |
| Serum cortisol | Cortisol deficiency | Low (8 to 19 mcg per dL [221 to 524 nmol per L]) | Early morning testing |
| If < 13 mcg per dL (359 nmol per L), patient should undergo dynamic testing |
| Serum insulinlike growth factor 1 | Excess growth hormone | Elevated (76 to 328 ng per mL [10 to 43 nmol per L])‡ | High sensitivity |
| Normally elevated during pregnancy |
| May be low in patients with poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, liver disease, hypothyroidism, and malnutrition |
| Serum LH/FSH | Gonadotroph-secreting tumor | Elevated | In postmenopausal women, elevated LH/FSH levels are normal |
| FSH (2 to 35 mIU per mL [2 to 35 IU per L])† | Value for menstruating women varies based on phase of menstrual cycle |
| LH (1.5 to 50 mIU per mL [1.5 to 50 IU per L])† | |
| Hypogonadism | Low | |
| FSH (2 to 35 mIU per mL)† | |
| LH (1.5 to 50 mIU per mL)† | |
| Serum macroprolactin | Hyperprolactinemia | Present | Biologically inactive form of prolactin, with no pathologic association |
| Useful to check in patients with hyperprolactinemia who have moderate elevations (100 to 300 mcg per L [4,348 to 13,043 pmol per L]) of serum prolactin with unknown etiology or when radiographic findings and clinical presentation are not consistent with serum prolactin level |
| Serum prolactin | Hyperprolactinemia | Elevated (3 to 24 mcg per L [130 to 1,043 pmol per L]) | ≥ 250 mcg per L (10,870 pmol per L) highly suggestive of prolactinoma |
| Moderate elevations (25 to 249 mcg per L [1,087 to 10,826 pmol per L]) should prompt investigation of other causes of hyperprolactinemia |
| Serum level correlates with tumor size; when level does not correlate with size, consider serial dilutions |
| Serum TSH | Evaluate thyrotroph-secreting tumor | Elevated (0.5 to 4.8 mIU per L) | May be atypically normal in relation to free T4 |
| Thyroid hormone deficiency | Low (0.5 to 4.8 mIU per L) |
| Testosterone (total) | Hormone deficiency in males | Low (350 to 1,030 ng per dL [12 to 36 nmol per L])‡ | Total (free + protein-bound) alone is generally an accurate picture of testosterone level |
| Testosterone (free) | Low (52 to 280 pg per mL)‡ | Measurements should be taken at 8 a.m. |