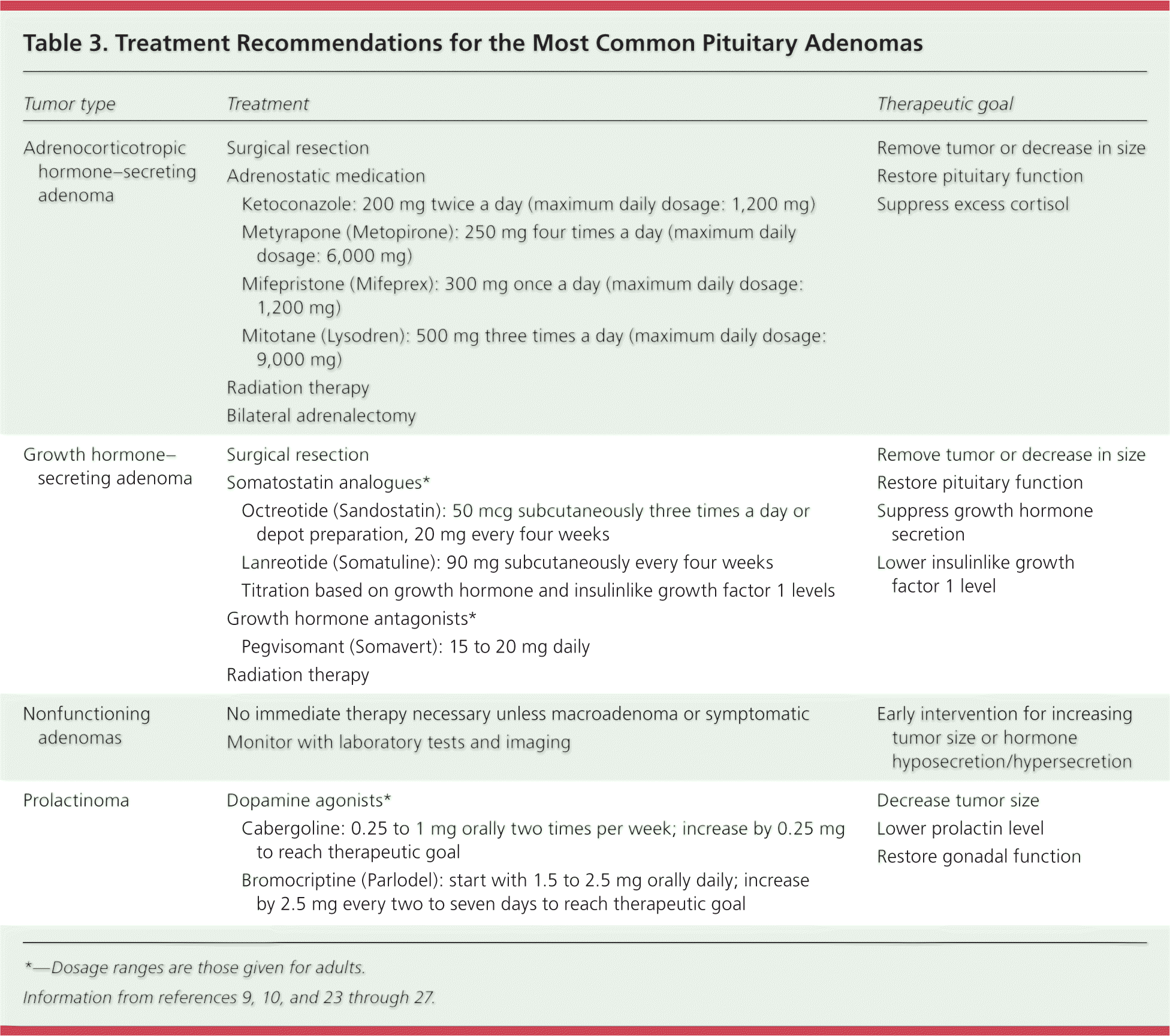
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone–secreting adenoma | Surgical resection | |
| Adrenostatic medication |
| Ketoconazole: 200 mg twice a day (maximum daily dosage: 1,200 mg) |
| Metyrapone (Metopirone): 250 mg four times a day (maximum daily dosage: 6,000 mg) |
| Mifepristone (Mifeprex): 300 mg once a day (maximum daily dosage: 1,200 mg) |
| Mitotane (Lysodren): 500 mg three times a day (maximum daily dosage: 9,000 mg) |
| Radiation therapy |
| Bilateral adrenalectomy |
| Growth hormone–secreting adenoma | Surgical resection | Remove tumor or decrease in size Restore pituitary function Suppress growth hormone secretion Lower insulinlike growth factor 1 level
|
| Somatostatin analogues* |
| Octreotide (Sandostatin): 50 mcg subcutaneously three times a day or depot preparation, 20 mg every four weeks |
| Lanreotide (Somatuline): 90 mg subcutaneously every four weeks |
| Titration based on growth hormone and insulinlike growth factor 1 levels |
| Growth hormone antagonists* |
| Pegvisomant (Somavert): 15 to 20 mg daily |
| Radiation therapy |
| Nonfunctioning adenomas | No immediate therapy necessary unless macroadenoma or symptomatic | |
| Monitor with laboratory tests and imaging |
| Prolactinoma | Dopamine agonists* | Decrease tumor size Lower prolactin level Restore gonadal function
|
| Cabergoline: 0.25 to 1 mg orally two times per week; increase by 0.25 mg to reach therapeutic goal |
| Bromocriptine (Parlodel): start with 1.5 to 2.5 mg orally daily; increase by 2.5 mg every two to seven days to reach therapeutic goal |