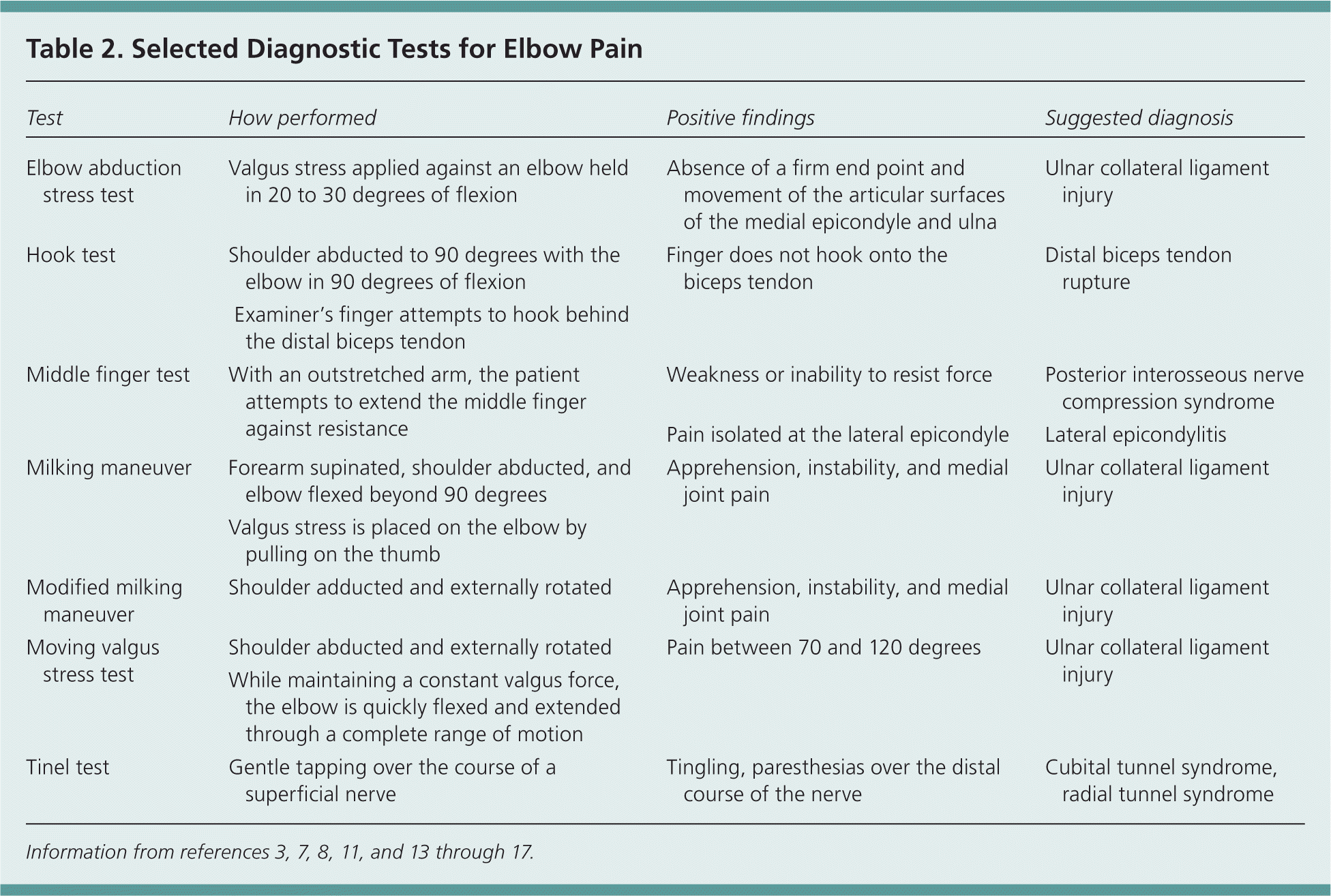
| Elbow abduction stress test | Valgus stress applied against an elbow held in 20 to 30 degrees of flexion | Absence of a firm end point and movement of the articular surfaces of the medial epicondyle and ulna | Ulnar collateral ligament injury |
| Hook test | Shoulder abducted to 90 degrees with the elbow in 90 degrees of flexion | Finger does not hook onto the biceps tendon | Distal biceps tendon rupture |
| Examiner's finger attempts to hook behind the distal biceps tendon |
| Middle finger test | With an outstretched arm, the patient attempts to extend the middle finger against resistance | Weakness or inability to resist force | Posterior interosseous nerve compression syndrome |
| Pain isolated at the lateral epicondyle | Lateral epicondylitis |
| Milking maneuver | Forearm supinated, shoulder abducted, and elbow flexed beyond 90 degrees | Apprehension, instability, and medial joint pain | Ulnar collateral ligament injury |
| Valgus stress is placed on the elbow by pulling on the thumb |
| Modified milking maneuver | Shoulder adducted and externally rotated | Apprehension, instability, and medial joint pain | Ulnar collateral ligament injury |
| Moving valgus stress test | Shoulder abducted and externally rotated | Pain between 70 and 120 degrees | Ulnar collateral ligament injury |
| While maintaining a constant valgus force, the elbow is quickly flexed and extended through a complete range of motion |
| Tinel test | Gentle tapping over the course of a superficial nerve | Tingling, paresthesias over the distal course of the nerve | Cubital tunnel syndrome, radial tunnel syndrome |