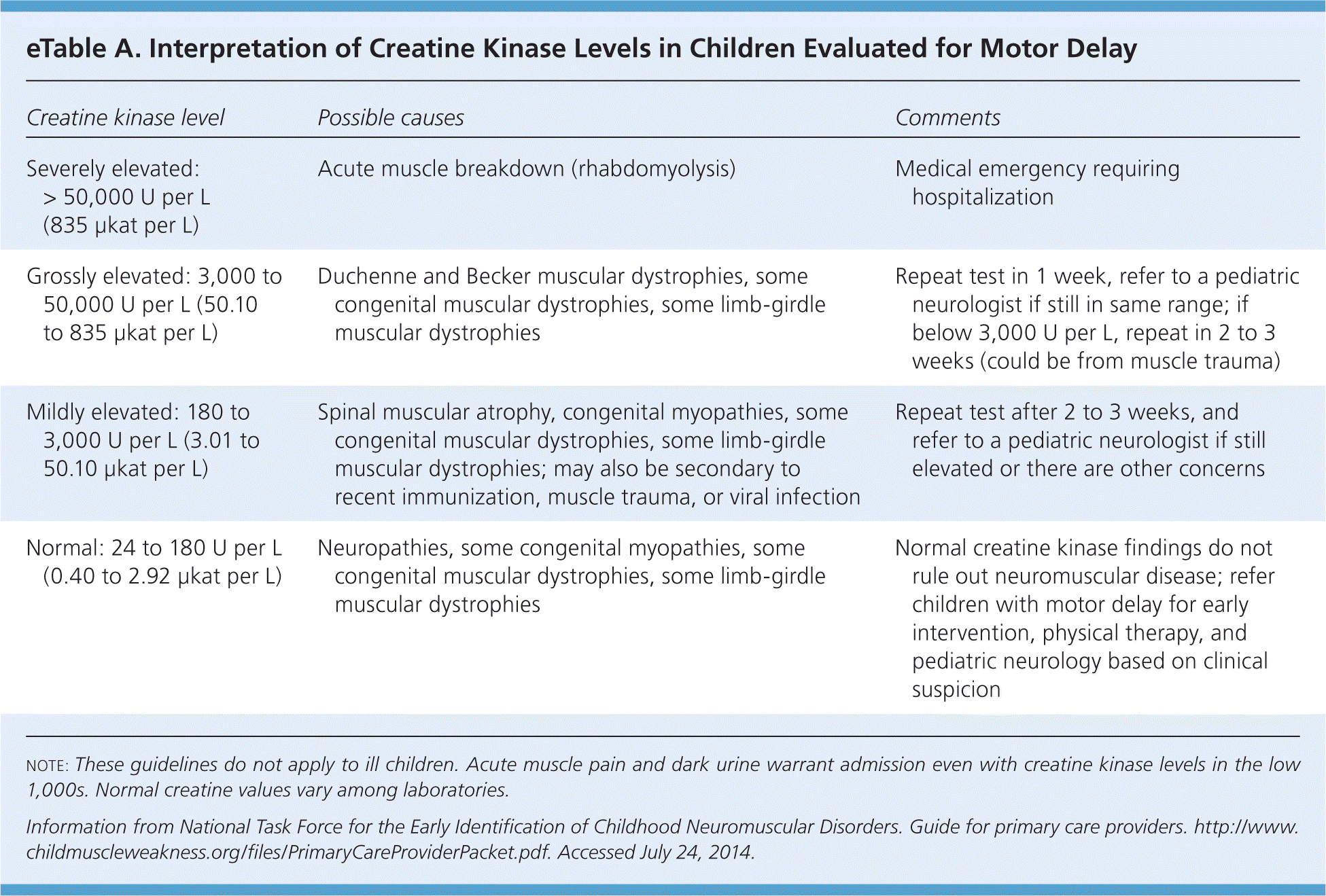
| Severely elevated: > 50,000 U per L (835 μkat per L) | Acute muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis) | Medical emergency requiring hospitalization |
| Grossly elevated: 3,000 to 50,000 U per L (50.10 to 835 μkat per L) | Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies, some congenital muscular dystrophies, some limb-girdle muscular dystrophies | Repeat test in 1 week, refer to a pediatric neurologist if still in same range; if below 3,000 U per L, repeat in 2 to 3 weeks (could be from muscle trauma) |
| Mildly elevated: 180 to 3,000 U per L (3.01 to 50.10 μkat per L) | Spinal muscular atrophy, congenital myopathies, some congenital muscular dystrophies, some limb-girdle muscular dystrophies; may also be secondary to recent immunization, muscle trauma, or viral infection | Repeat test after 2 to 3 weeks, and refer to a pediatric neurologist if still elevated or there are other concerns |
| Normal: 24 to 180 U per L (0.40 to 2.92 μkat per L) | Neuropathies, some congenital myopathies, some congenital muscular dystrophies, some limb-girdle muscular dystrophies | Normal creatine kinase findings do not rule out neuromuscular disease; refer children with motor delay for early intervention, physical therapy, and pediatric neurology based on clinical suspicion |