Am Fam Physician. 2015;91(2):123-124
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
An 84-year-old woman presented with a one-week history of fever, blistering lips, and progressive skin sloughing. She had diffuse muscle aches and increased facial pigmentation and edema without recent sun exposure. Her history was significant for removal of a toenail by a podiatrist three weeks earlier. The podiatrist prescribed an antibiotic.
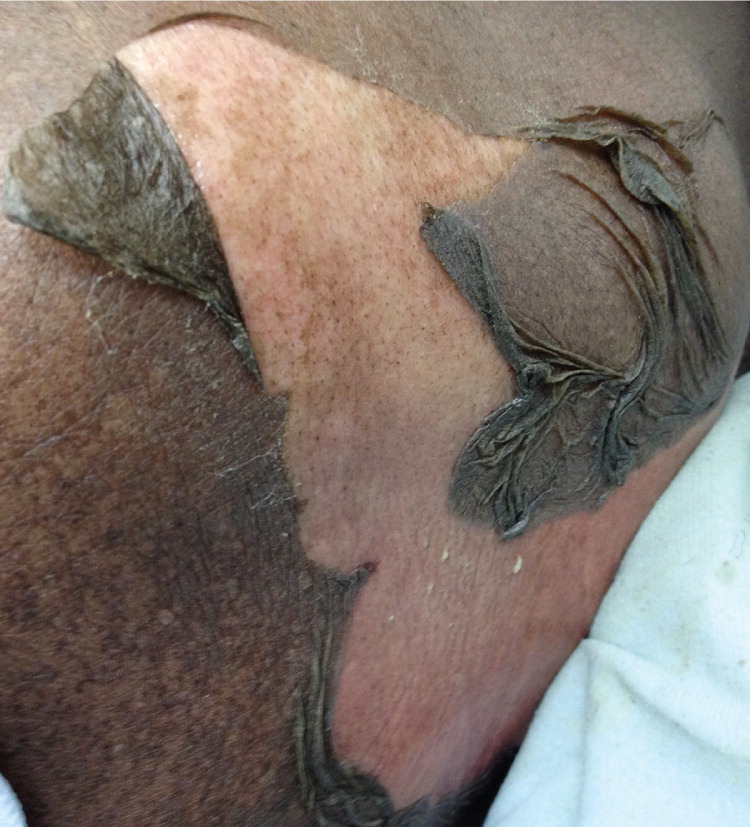
Physical examination revealed a large area of epidermal skin sloughing on her left upper back and elbows (see accompanying figure). She had hemorrhagic crusting and erosions of the oral mucosa. There were also bullae on her left inner thigh. Nikolsky sign (exfoliation of skin with application of pressure) was present. Initial laboratory tests revealed new acute renal insufficiency with a creatinine level of 3.6 mg per dL (318 μmol per L); it was 0.8 mg per dL (71 μmol per L) at last check one year prior.
Question
Discussion
The answer is D: discontinuation of medications. This patient's physical examination findings and history of recent antibiotic use suggest a diagnosis of drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome. The initial step in treatment is stopping all possible causative medications. Subsequently, the patient should be resuscitated with fluids and replacement electrolytes, and possibly transferred to the intensive care or burn unit for support.1
Patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome present with full-thickness epidermal necrosis over normal underlying dermis. Other symptoms may include confluent edema, facial edema, mucous membrane erosions and hemorrhagic crusting, skin pain and tenderness, bullae, a burning skin sensation, tongue swelling, blistering, and acute renal injury.2
Initial presentation, as shown, was consistent with Stevens-Johnson syndrome because of a smaller body surface area involvement. However, the patient eventually progressed to toxic epidermal necrolysis, which is a mucocutaneous disease usually involving two or more mucous membranes and one-third of the body surface area.2 Patients may recall a prodrome of upper respiratory tract infection, fever, and malaise. The rash typically begins on the face and progresses to other parts of the body. The rash may begin as painful erythema or target lesions, or as bullae with eventual sloughing. The initial clusters of lesions appear over one to two weeks, and may regress in four weeks in the case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome,3 or progress to full body involvement.
Although Stevens-Johnson syndrome involves less than 10% of the body surface area, it has a mortality rate of 1% to 5%.4 Toxic epidermal necrolysis is a more severe reaction that involves greater than 30% of the body surface area, with a mortality rate of 25% to 40%.2 Body surface area involvement usually differentiates the two entities. The estimated incidence of these reactions is one to two cases per 1 million persons annually.2 Medications commonly associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis include sulfonamides, allopurinol (Zyloprim), antiepileptics, antipsychotics, analgesics, and penicillins.5 Infectious triggers such as herpes viruses and mycoplasma are less likely to lead to severe reactions.
Skin biopsy will demonstrate full-thickness epidermal necrosis with normal underlying dermis or a scant lymphocytic infiltrate.3 This histologic finding helps differentiate Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis from autoimmune blistering diseases; severe photosensitivity reactions; and infectious causes, such as staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, that only involve loss of the stratum corneum.
Because of the extensive epidermal loss with Stevens-Johnson syndrome, the same precautions must be made as with severe burns (i.e., isolation, sterile environment, and repeated monitoring for sepsis).6 Supportive treatment includes pain control, fluidized air beds,7 early nasogastric tube feedings, and topical emollients for mucous membranes. Ophthalmology consultation is recommended. A thorough urogenital evaluation should be performed to assess for mucosal involvement. Intravenous immunoglobulin and systemic corticosteroids are often initiated as treatment; however, the evidence for their use is inconclusive.5,8 Patients should avoid the causative medication and structurally similar drugs.