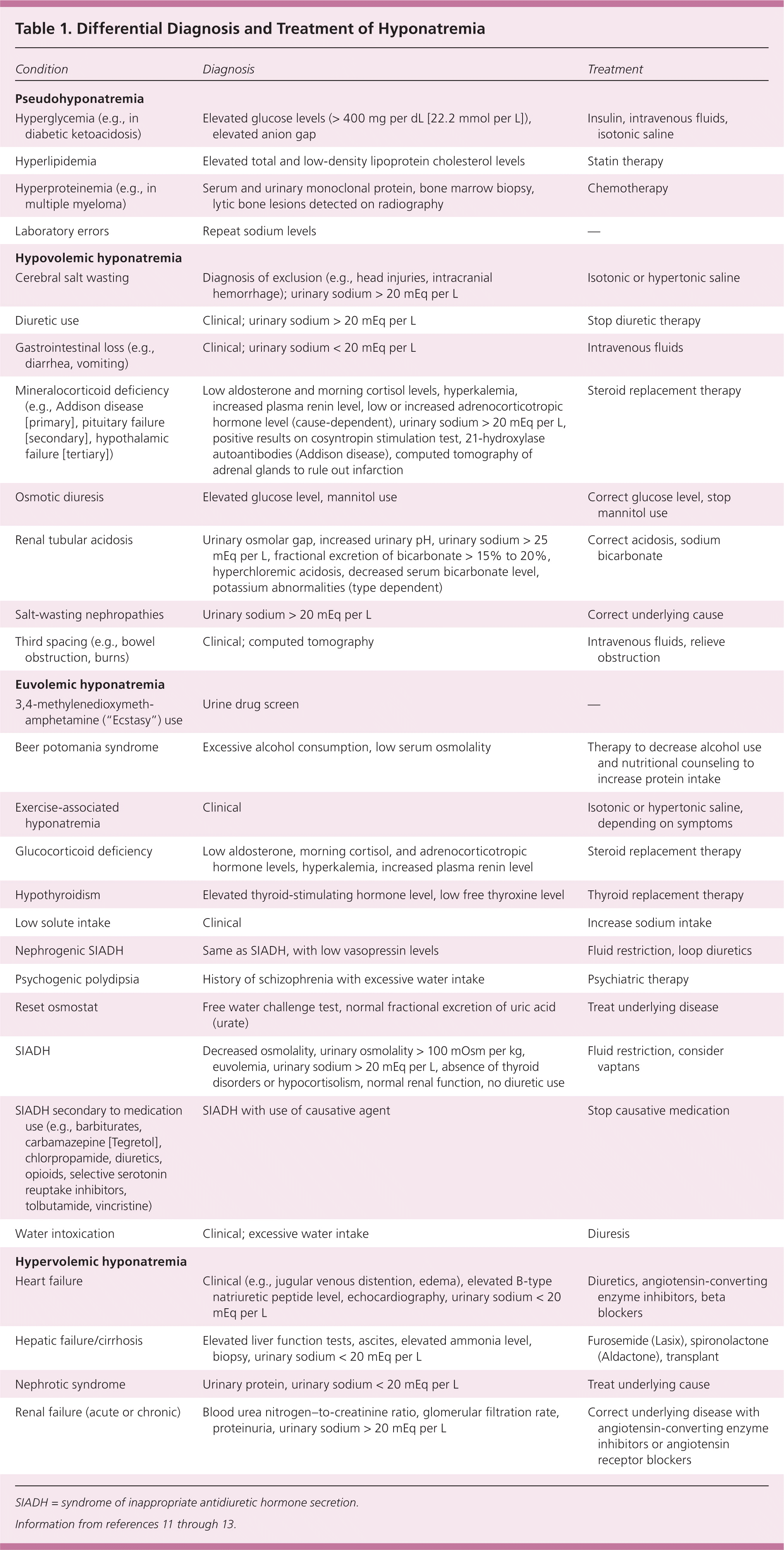
| Pseudohyponatremia |
| Hyperglycemia (e.g., in diabetic ketoacidosis) | Elevated glucose levels (> 400 mg per dL [22.2 mmol per L]), elevated anion gap | Insulin, intravenous fluids, isotonic saline |
| Hyperlipidemia | Elevated total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels | Statin therapy |
| Hyperproteinemia (e.g., in multiple myeloma) | Serum and urinary monoclonal protein, bone marrow biopsy, lytic bone lesions detected on radiography | Chemotherapy |
| Laboratory errors | Repeat sodium levels | — |
| Hypovolemic hyponatremia |
| Cerebral salt wasting | Diagnosis of exclusion (e.g., head injuries, intracranial hemorrhage); urinary sodium > 20 mEq per L | Isotonic or hypertonic saline |
| Diuretic use | Clinical; urinary sodium > 20 mEq per L | Stop diuretic therapy |
| Gastrointestinal loss (e.g., diarrhea, vomiting) | Clinical; urinary sodium < 20 mEq per L | Intravenous fluids |
| Mineralocorticoid deficiency (e.g., Addison disease [primary], pituitary failure [secondary], hypothalamic failure [tertiary]) | Low aldosterone and morning cortisol levels, hyperkalemia, increased plasma renin level, low or increased adrenocorticotropic hormone level (cause-dependent), urinary sodium > 20 mEq per L, positive results on cosyntropin stimulation test, 21-hydroxylase autoantibodies (Addison disease), computed tomography of adrenal glands to rule out infarction | Steroid replacement therapy |
| Osmotic diuresis | Elevated glucose level, mannitol use | Correct glucose level, stop mannitol use |
| Renal tubular acidosis | Urinary osmolar gap, increased urinary pH, urinary sodium > 25 mEq per L, fractional excretion of bicarbonate > 15% to 20%, hyperchloremic acidosis, decreased serum bicarbonate level, potassium abnormalities (type dependent) | Correct acidosis, sodium bicarbonate |
| Salt-wasting nephropathies | Urinary sodium > 20 mEq per L | Correct underlying cause |
| Third spacing (e.g., bowel obstruction, burns) | Clinical; computed tomography | Intravenous fluids, relieve obstruction |
| Euvolemic hyponatremia |
| 3,4-methylenedioxymeth-amphetamine (“Ecstasy”) use | Urine drug screen | — |
| Beer potomania syndrome | Excessive alcohol consumption, low serum osmolality | Therapy to decrease alcohol use and nutritional counseling to increase protein intake |
| Exercise-associated hyponatremia | Clinical | Isotonic or hypertonic saline, depending on symptoms |
| Glucocorticoid deficiency | Low aldosterone, morning cortisol, and adrenocorticotropic hormone levels, hyperkalemia, increased plasma renin level | Steroid replacement therapy |
| Hypothyroidism | Elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone level, low free thyroxine level | Thyroid replacement therapy |
| Low solute intake | Clinical | Increase sodium intake |
| Nephrogenic SIADH | Same as SIADH, with low vasopressin levels | Fluid restriction, loop diuretics |
| Psychogenic polydipsia | History of schizophrenia with excessive water intake | Psychiatric therapy |
| Reset osmostat | Free water challenge test, normal fractional excretion of uric acid (urate) | Treat underlying disease |
| SIADH | Decreased osmolality, urinary osmolality > 100 mOsm per kg, euvolemia, urinary sodium > 20 mEq per L, absence of thyroid disorders or hypocortisolism, normal renal function, no diuretic use | Fluid restriction, consider vaptans |
| SIADH secondary to medication use (e.g., barbiturates, carbamazepine [Tegretol], chlorpropamide, diuretics, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tolbutamide, vincristine) | SIADH with use of causative agent | Stop causative medication |
| Water intoxication | Clinical; excessive water intake | Diuresis |
| Hypervolemic hyponatremia |
| Heart failure | Clinical (e.g., jugular venous distention, edema), elevated B-type natriuretic peptide level, echocardiography, urinary sodium < 20 mEq per L | Diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers |
| Hepatic failure/cirrhosis | Elevated liver function tests, ascites, elevated ammonia level, biopsy, urinary sodium < 20 mEq per L | Furosemide (Lasix), spironolactone (Aldactone), transplant |
| Nephrotic syndrome | Urinary protein, urinary sodium < 20 mEq per L | Treat underlying cause |
| Renal failure (acute or chronic) | Blood urea nitrogen–to-creatinine ratio, glomerular filtration rate, proteinuria, urinary sodium > 20 mEq per L | Correct underlying disease with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers |