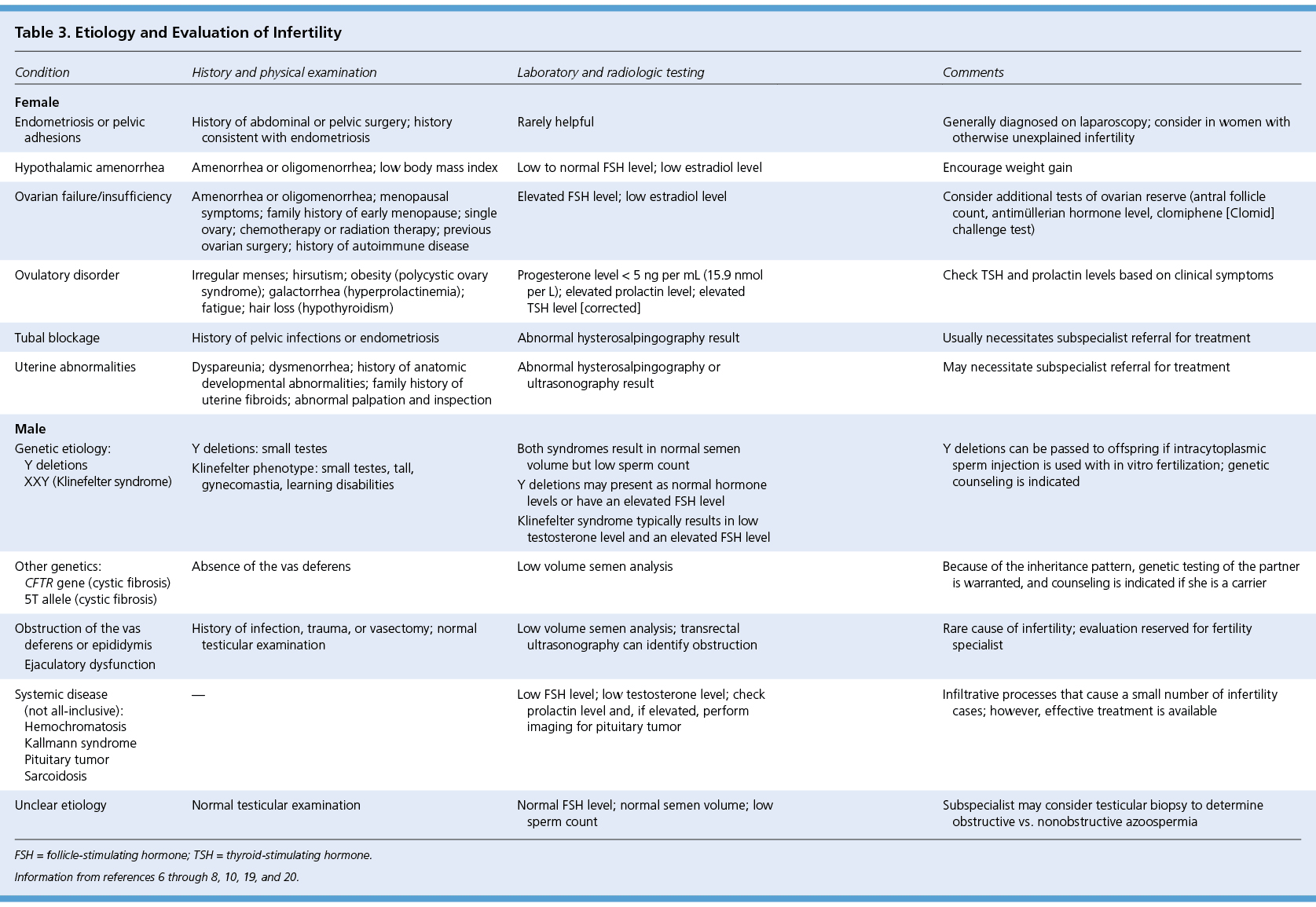
| Female |
| Endometriosis or pelvic adhesions |
History of abdominal or pelvic surgery; history consistent with endometriosis |
Rarely helpful |
Generally diagnosed on laparoscopy; consider in women with otherwise unexplained infertility |
| Hypothalamic amenorrhea |
Amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea; low body mass index |
Low to normal FSH level; low estradiol level |
Encourage weight gain |
| Ovarian failure/insufficiency |
Amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea; menopausal symptoms; family history of early menopause; single ovary; chemotherapy or radiation therapy; previous ovarian surgery; history of autoimmune disease |
Elevated FSH level; low estradiol level |
Consider additional tests of ovarian reserve (antral follicle count, antimüllerian hormone level, clomiphene [Clomid] challenge test) |
| Ovulatory disorder |
Irregular menses; hirsutism; obesity (polycystic ovary syndrome); galactorrhea (hyperprolactinemia); fatigue; hair loss (hypothyroidism) |
Progesterone level < 5 ng per mL (15.9 nmol per L); elevated prolactin level; elevated TSH level [corrected] |
Check TSH and prolactin levels based on clinical symptoms |
| Tubal blockage |
History of pelvic infections or endometriosis |
Abnormal hysterosalpingography result |
Usually necessitates subspecialist referral for treatment |
| Uterine abnormalities |
Dyspareunia; dysmenorrhea; history of anatomic developmental abnormalities; family history of uterine fibroids; abnormal palpation and inspection |
Abnormal hysterosalpingography or ultrasonography result |
May necessitate subspecialist referral for treatment |
| Male |
| Genetic etiology: |
|
Both syndromes result in normal semen volume but low sperm count |
Y deletions can be passed to offspring if intracytoplasmic sperm injection is used with in vitro fertilization; genetic counseling is indicated |
| |
Y deletions |
Y deletions: small testes |
Y deletions may present as normal hormone levels or have an elevated FSH level |
|
| |
XXY (Klinefelter syndrome) |
Klinefelter phenotype: small testes, tall, gynecomastia, learning disabilities |
Klinefelter syndrome typically results in low testosterone level and an elevated FSH level |
|
| Other genetics: |
Absence of the vas deferens |
Low volume semen analysis |
Because of the inheritance pattern, genetic testing of the partner is warranted, and counseling is indicated if she is a carrier |
| |
CFTR gene (cystic fibrosis) |
| |
5T allele (cystic fibrosis) |
| Obstruction of the vas deferens or epididymis Ejaculatory dysfunction |
History of infection, trauma, or vasectomy; normal testicular examination |
Low volume semen analysis; transrectal ultrasonography can identify obstruction |
Rare cause of infertility; evaluation reserved for fertility specialist |
| Systemic disease (not all-inclusive): |
— |
Low FSH level; low testosterone level; check prolactin level and, if elevated, perform imaging for pituitary tumor |
Infiltrative processes that cause a small number of infertility cases; however, effective treatment is available |
| |
Hemochromatosis |
| |
Kallmann syndrome |
| |
Pituitary tumor |
| |
Sarcoidosis |
| Unclear etiology |
Normal testicular examination |
Normal FSH level; normal semen volume; low sperm count |
Subspecialist may consider testicular biopsy to determine obstructive vs. nonobstructive azoospermia |