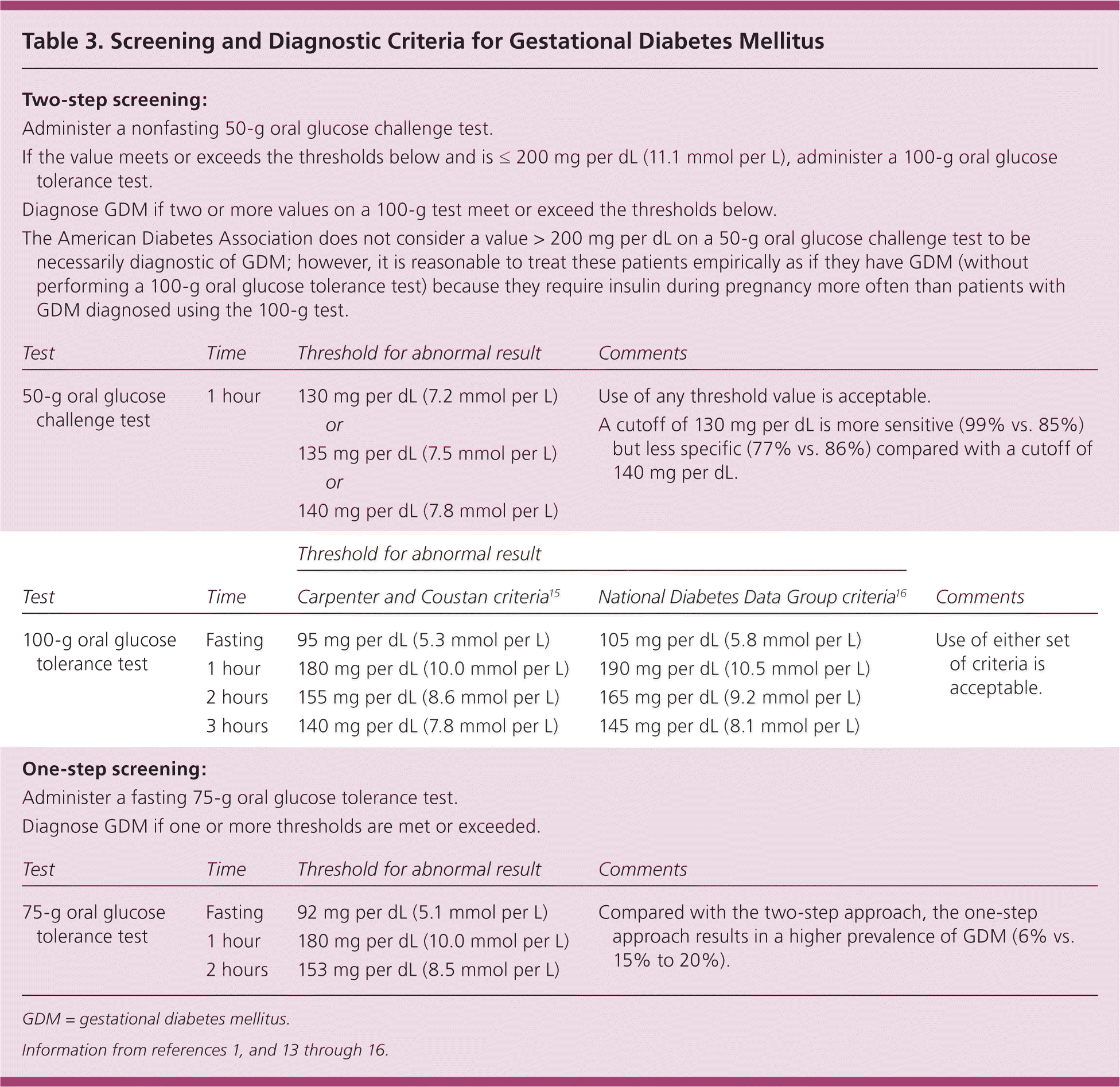
| Two-step screening: |
| Administer a nonfasting 50-g oral glucose challenge test. |
| If the value meets or exceeds the thresholds below and is ≤ 200 mg per dL (11.1 mmol per L), administer a 100-g oral glucose tolerance test. |
| Diagnose GDM if two or more values on a 100-g test meet or exceed the thresholds below. |
| The American Diabetes Association does not consider a value > 200 mg per dL on a 50-g oral glucose challenge test to be necessarily diagnostic of GDM; however, it is reasonable to treat these patients empirically as if they have GDM (without performing a 100-g oral glucose tolerance test) because they require insulin during pregnancy more often than patients with GDM diagnosed using the 100-g test. |
| Test | Time | Threshold for abnormal result | Comments |
|
| 50-g oral glucose challenge test | 1 hour | 130 mg per dL (7.2 mmol per L) | Use of any threshold value is acceptable. |
| | | or | A cutoff of 130 mg per dL is more sensitive (99% vs. 85%) but less specific (77% vs. 86%) compared with a cutoff of 140 mg per dL. |
| | 135 mg per dL (7.5 mmol per L) | |
| | | or | |
| | 140 mg per dL (7.8 mmol per L) | |
| | Threshold for abnormal result
| |
| Test | Time | Carpenter and Coustan criteria15 | National Diabetes Data Group criteria16 | Comments |
|
| 100-g oral glucose tolerance test | Fasting | 95 mg per dL (5.3 mmol per L) | 105 mg per dL (5.8 mmol per L) | Use of either set of criteria is acceptable. |
| 1 hour | 180 mg per dL (10.0 mmol per L) | 190 mg per dL (10.5 mmol per L) | |
| 2 hours | 155 mg per dL (8.6 mmol per L) | 165 mg per dL (9.2 mmol per L) | |
| 3 hours | 140 mg per dL (7.8 mmol per L) | 145 mg per dL (8.1 mmol per L) | |
| One-step screening: | | | |
| Administer a fasting 75-g oral glucose tolerance test. |
| Diagnose GDM if one or more thresholds are met or exceeded. |
| Test | Time | Threshold for abnormal result | Comments |
|
| 75-g oral glucose tolerance test | Fasting | 92 mg per dL (5.1 mmol per L) | Compared with the two-step approach, the one-step approach results in a higher prevalence of GDM (6% vs. 15% to 20%). |
| 1 hour | 180 mg per dL (10.0 mmol per L) | |
| 2 hours | 153 mg per dL (8.5 mmol per L) | |