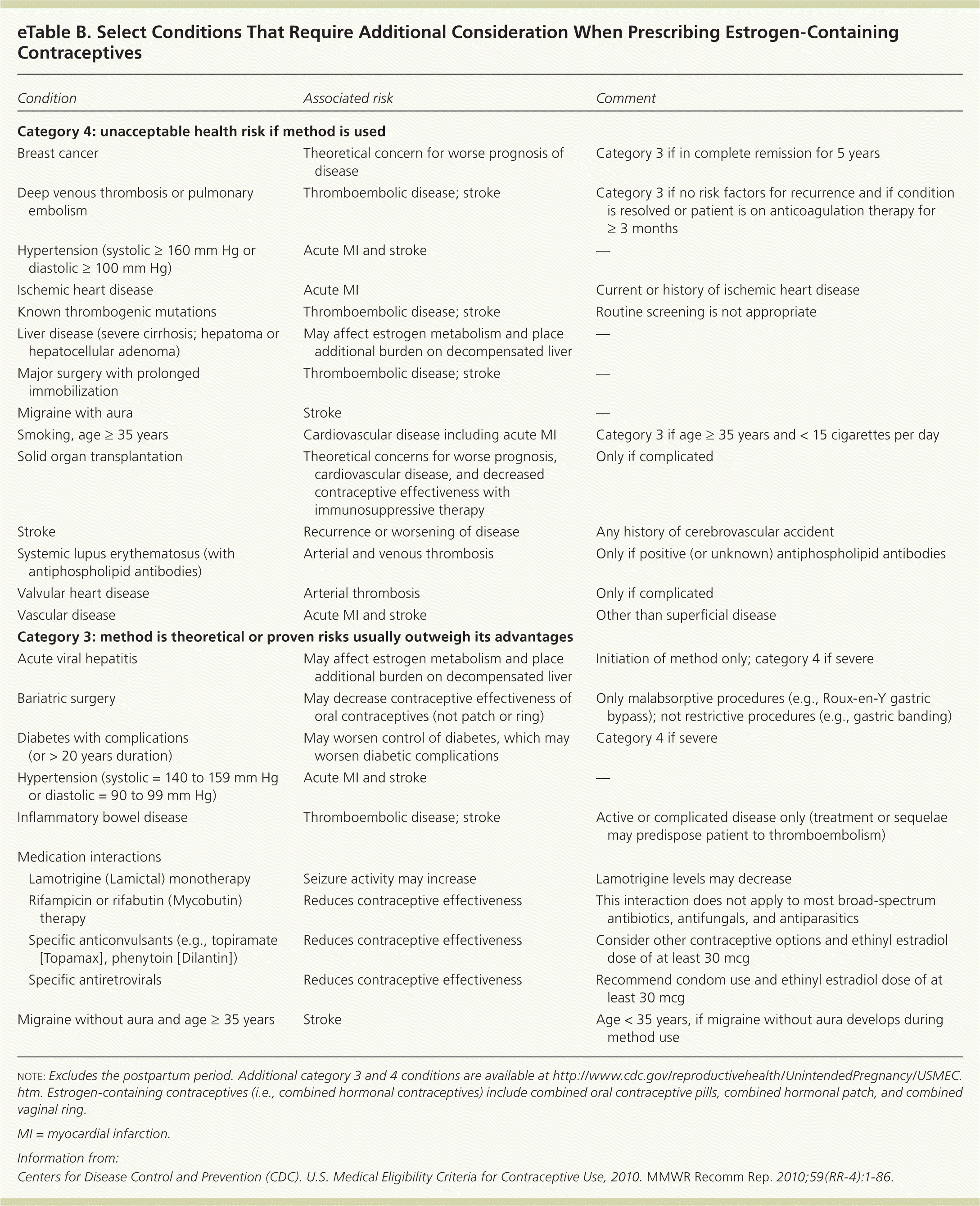
| Category 4: unacceptable health risk if method is used | |
| Breast cancer | Theoretical concern for worse prognosis of disease | Category 3 if in complete remission for 5 years |
| Deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism | Thromboembolic disease; stroke | Category 3 if no risk factors for recurrence and if condition is resolved or patient is on anticoagulation therapy for ≥ 3 months |
| Hypertension (systolic ≥ 160 mm Hg or diastolic ≥ 100 mm Hg) | Acute MI and stroke | — |
| Ischemic heart disease | Acute MI | Current or history of ischemic heart disease |
| Known thrombogenic mutations | Thromboembolic disease; stroke | Routine screening is not appropriate |
| Liver disease (severe cirrhosis; hepatoma or hepatocellular adenoma) | May affect estrogen metabolism and place additional burden on decompensated liver | — |
| Major surgery with prolonged immobilization | Thromboembolic disease; stroke | — |
| Migraine with aura | Stroke | — |
| Smoking, age ≥ 35 years | Cardiovascular disease including acute MI | Category 3 if age ≥ 35 years and < 15 cigarettes per day |
| Solid organ transplantation | Theoretical concerns for worse prognosis, cardiovascular disease, and decreased contraceptive effectiveness with immunosuppressive therapy | Only if complicated |
| Stroke | Recurrence or worsening of disease | Any history of cerebrovascular accident |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus (with antiphospholipid antibodies) | Arterial and venous thrombosis | Only if positive (or unknown) antiphospholipid antibodies |
| Valvular heart disease | Arterial thrombosis | Only if complicated |
| Vascular disease | Acute MI and stroke | Other than superficial disease |
| Category 3: method is theoretical or proven risks usually outweigh its advantages | |
| Acute viral hepatitis | May affect estrogen metabolism and place additional burden on decompensated liver | Initiation of method only; category 4 if severe |
| Bariatric surgery | May decrease contraceptive effectiveness of oral contraceptives (not patch or ring) | Only malabsorptive procedures (e.g., Roux-en-Y gastric bypass); not restrictive procedures (e.g., gastric banding) |
| Diabetes with complications (or > 20 years duration) | May worsen control of diabetes, which may worsen diabetic complications | Category 4 if severe |
| Hypertension (systolic = 140 to 159 mm Hg or diastolic = 90 to 99 mm Hg) | Acute MI and stroke | — |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | Thromboembolic disease; stroke | Active or complicated disease only (treatment or sequelae may predispose patient to thromboembolism) |
| Medication interactions | | |
| Lamotrigine (Lamictal) monotherapy | Seizure activity may increase | Lamotrigine levels may decrease |
| Rifampicin or rifabutin (Mycobutin) therapy | Reduces contraceptive effectiveness | This interaction does not apply to most broad-spectrum antibiotics, antifungals, and antiparasitics |
| Specific anticonvulsants (e.g., topiramate [Topamax], phenytoin [Dilantin]) | Reduces contraceptive effectiveness | Consider other contraceptive options and ethinyl estradiol dose of at least 30 mcg |
| Specific antiretrovirals | Reduces contraceptive effectiveness | Recommend condom use and ethinyl estradiol dose of at least 30 mcg |
| Migraine without aura and age ≥ 35 years | Stroke | Age < 35 years, if migraine without aura develops during method use |