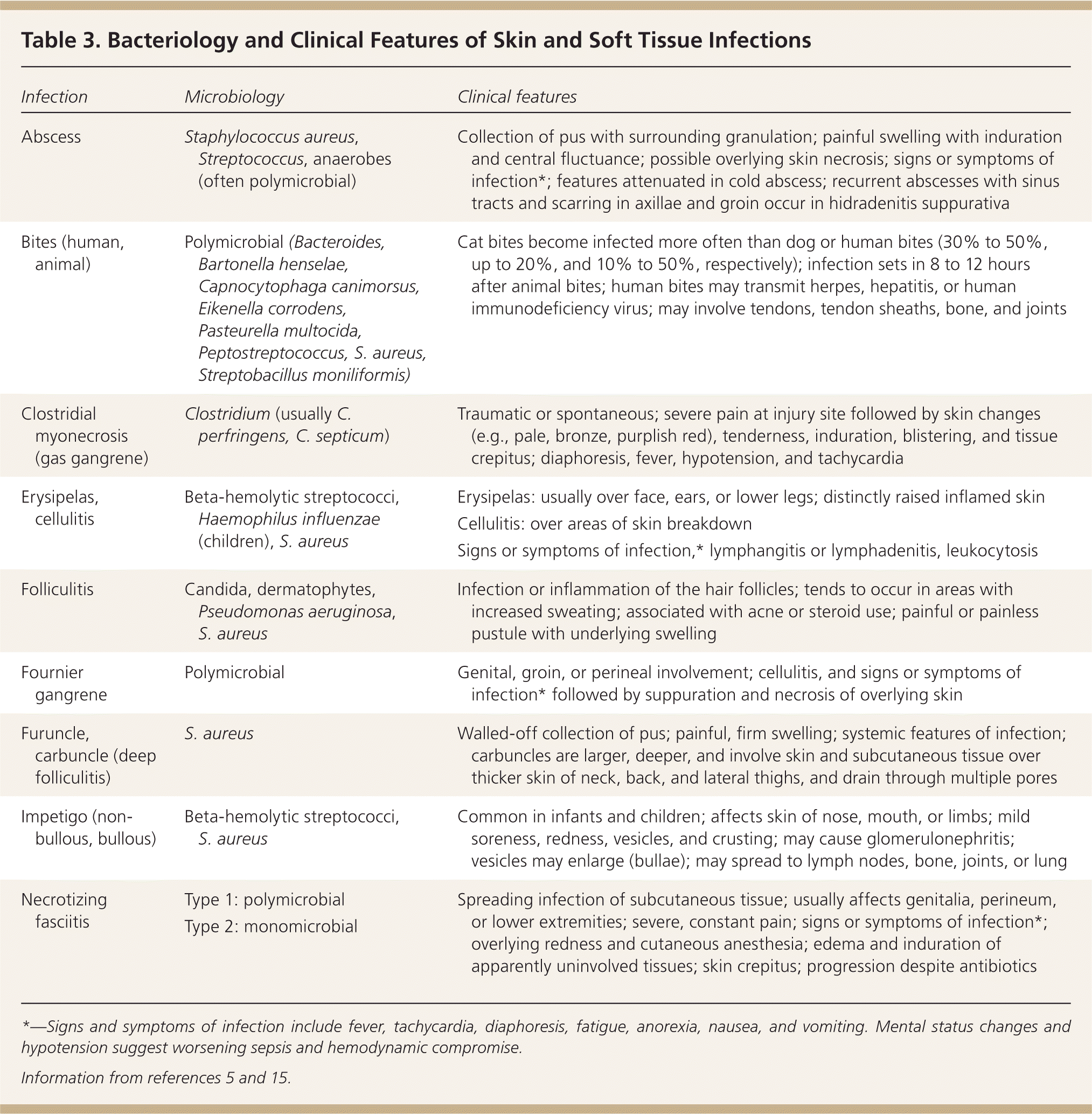
| Abscess | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, anaerobes (often polymicrobial) | Collection of pus with surrounding granulation; painful swelling with induration and central fluctuance; possible overlying skin necrosis; signs or symptoms of infection*; features attenuated in cold abscess; recurrent abscesses with sinus tracts and scarring in axillae and groin occur in hidradenitis suppurativa |
| Bites (human, animal) | Polymicrobial (Bacteroides, Bartonella henselae, Capnocytophaga canimorsus, Eikenella corrodens, Pasteurella multocida, Peptostreptococcus, S. aureus, Streptobacillus moniliformis) | Cat bites become infected more often than dog or human bites (30% to 50%, up to 20%, and 10% to 50%, respectively); infection sets in 8 to 12 hours after animal bites; human bites may transmit herpes, hepatitis, or human immunodeficiency virus; may involve tendons, tendon sheaths, bone, and joints |
| Clostridial myonecrosis (gas gangrene) | Clostridium (usually C. perfringens, C. septicum) | Traumatic or spontaneous; severe pain at injury site followed by skin changes (e.g., pale, bronze, purplish red), tenderness, induration, blistering, and tissue crepitus; diaphoresis, fever, hypotension, and tachycardia |
| Erysipelas, cellulitis | Beta-hemolytic streptococci, Haemophilus influenzae (children), S. aureus | Erysipelas: usually over face, ears, or lower legs; distinctly raised inflamed skin Cellulitis: over areas of skin breakdown Signs or symptoms of infection,* lymphangitis or lymphadenitis, leukocytosis
|
| Folliculitis | Candida, dermatophytes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, S. aureus | Infection or inflammation of the hair follicles; tends to occur in areas with increased sweating; associated with acne or steroid use; painful or painless pustule with underlying swelling |
| Fournier gangrene | Polymicrobial | Genital, groin, or perineal involvement; cellulitis, and signs or symptoms of infection* followed by suppuration and necrosis of overlying skin |
| Furuncle, carbuncle (deep folliculitis) | S. aureus | Walled-off collection of pus; painful, firm swelling; systemic features of infection; carbuncles are larger, deeper, and involve skin and subcutaneous tissue over thicker skin of neck, back, and lateral thighs, and drain through multiple pores |
| Impetigo (non-bullous, bullous) | Beta-hemolytic streptococci, S. aureus | Common in infants and children; affects skin of nose, mouth, or limbs; mild soreness, redness, vesicles, and crusting; may cause glomerulonephritis; vesicles may enlarge (bullae); may spread to lymph nodes, bone, joints, or lung |
| Necrotizing fasciitis | Type 1: polymicrobial | Spreading infection of subcutaneous tissue; usually affects genitalia, perineum, or lower extremities; severe, constant pain; signs or symptoms of infection*; overlying redness and cutaneous anesthesia; edema and induration of apparently uninvolved tissues; skin crepitus; progression despite antibiotics |
| Type 2: monomicrobial | |