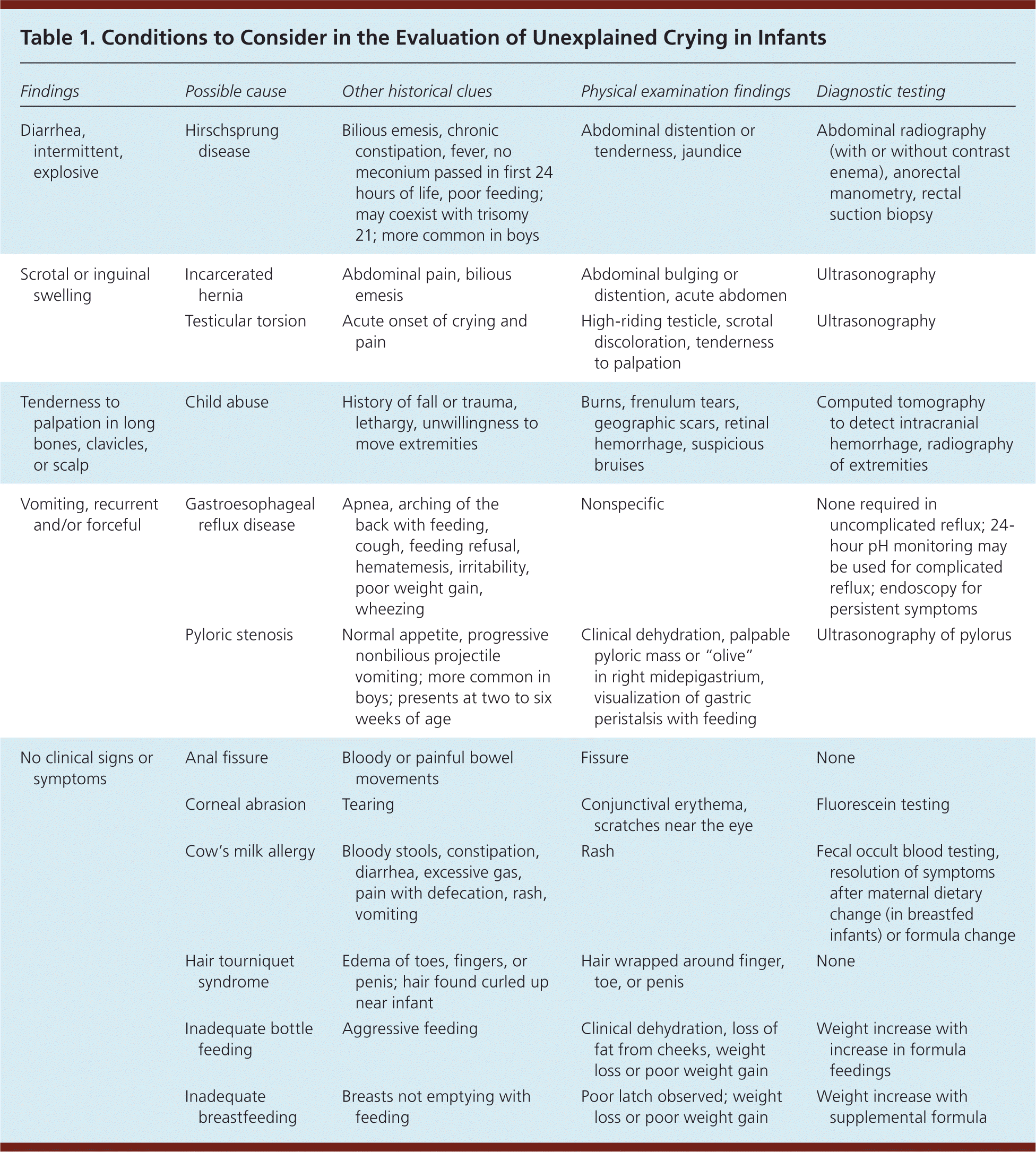
| Diarrhea, intermittent, explosive | Hirschsprung disease | Bilious emesis, chronic constipation, fever, no meconium passed in first 24 hours of life, poor feeding; may coexist with trisomy 21; more common in boys | Abdominal distention or tenderness, jaundice | Abdominal radiography (with or without contrast enema), anorectal manometry, rectal suction biopsy |
| Scrotal or inguinal swelling | Incarcerated hernia | Abdominal pain, bilious emesis | Abdominal bulging or distention, acute abdomen | Ultrasonography |
| Testicular torsion | Acute onset of crying and pain | High-riding testicle, scrotal discoloration, tenderness to palpation | Ultrasonography |
| Tenderness to palpation in long bones, clavicles, or scalp | Child abuse | History of fall or trauma, lethargy, unwillingness to move extremities | Burns, frenulum tears, geographic scars, retinal hemorrhage, suspicious bruises | Computed tomography to detect intracranial hemorrhage, radiography of extremities |
| Vomiting, recurrent and/or forceful | Gastroesophageal reflux disease | Apnea, arching of the back with feeding, cough, feeding refusal, hematemesis, irritability, poor weight gain, wheezing | Nonspecific | None required in uncomplicated reflux; 24-hour pH monitoring may be used for complicated reflux; endoscopy for persistent symptoms |
| Pyloric stenosis | Normal appetite, progressive nonbilious projectile vomiting; more common in boys; presents at two to six weeks of age | Clinical dehydration, palpable pyloric mass or “olive” in right midepigastrium, visualization of gastric peristalsis with feeding | Ultrasonography of pylorus |
| No clinical signs or symptoms | Anal fissure | Bloody or painful bowel movements | Fissure | None |
| Corneal abrasion | Tearing | Conjunctival erythema, scratches near the eye | Fluorescein testing |
| Cow's milk allergy | Bloody stools, constipation, diarrhea, excessive gas, pain with defecation, rash, vomiting | Rash | Fecal occult blood testing, resolution of symptoms after maternal dietary change (in breastfed infants) or formula change |
| Hair tourniquet syndrome | Edema of toes, fingers, or penis; hair found curled up near infant | Hair wrapped around finger, toe, or penis | None |
| Inadequate bottle feeding | Aggressive feeding | Clinical dehydration, loss of fat from cheeks, weight loss or poor weight gain | Weight increase with increase in formula feedings |
| Inadequate breastfeeding | Breasts not emptying with feeding | Poor latch observed; weight loss or poor weight gain | Weight increase with supplemental formula |