A more recent article on diagnosing common benign skin tumors is available.
This is a corrected version of the article that appeared in print.
Am Fam Physician. 2015;92(7):601-607
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Patients will experience a wide range of skin growths and changes over their lifetime. Family physicians should be able to distinguish potentially malignant from benign skin tumors. Most lesions can be diagnosed on the basis of history and clinical examination. Lesions that are suspicious for malignancy, those with changing characteristics, symptomatic lesions, and those that cause cosmetic problems may warrant medical therapy, a simple office procedure (e.g., excision, cryosurgery, laser ablation), or referral. Acrochordons are extremely common, small, and typically pedunculated benign neoplasms. Simple scissor or shave excision, electrodesiccation, or cryosurgery can be used for treatment. Sebaceous hyperplasia presents as asymptomatic, discrete, soft, pale yellow, shiny bumps on the forehead or cheeks, or near hair follicles. Except for cosmesis, they have no clinical significance. Lipomas are soft, flesh-colored nodules that are easily moveable under the overlying skin. Keratoacanthomas are rapidly growing, squamoproliferative benign tumors that resemble squamous cell carcinomas. Early simple excision is recommended. Pyogenic granuloma is a rapidly growing nodule that bleeds easily. Treatment includes laser ablation or shave excision with electrodesiccation of the base. Dermatofibromas are an idiopathic benign proliferation of fibroblasts. No treatment is required unless there is a change in size or color, bleeding, or irritation from trauma. Epidermal inclusion cysts can be treated by simple excision with removal of the cyst and cyst wall. Seborrheic keratoses and cherry angiomas generally do not require treatment.
Skin problems are commonly encountered in primary care. One retrospective chart review of dermatology referrals at a university general medicine clinic found that approximately one-third of patients were referred during their initial visit to their primary care physician.1 However, family physicians can effectively treat most skin disorders.2 A review of diagnoses made by primary care physicians found they were correct 70% of the time (compared with 93% for dermatologists).3 Another multisite prospective cohort study found overall agreement in diagnoses and treatment between family physicians and dermatologists, with a concordance of 72% and 80%, respectively.2
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonography can aid in the diagnosis of lipomas. High-frequency ultrasonography (i.e., with probes greater than 20 MHz) provides high-resolution images of subcutaneous tumors and surrounding structures. | C | 10 |
| Diagnosis of dermatofibromas is based on the characteristic appearance and dimpling or retraction of the lesion beneath the skin with lateral compression. | C | 20 |
| Intralesional steroid injection with interval excision can hasten resolution of inflamed epidermal inclusion cysts. | C | 23 |
| The Leser-Trélat sign is the sudden onset or increase in the number of seborrheic keratosis lesions and may be the result of an underlying malignancy. | C | 26 |
Clinicians must take special precautions in evaluating skin tumors and screening for skin cancer. The use of dermoscopy to improve diagnosis has been addressed in a previous article in American Family Physician.4 However, the preferred method of diagnosing skin cancer is physical examination. This article will review some common benign skin tumors that are amenable to office procedures, as well as those that may require referral (Table 1).
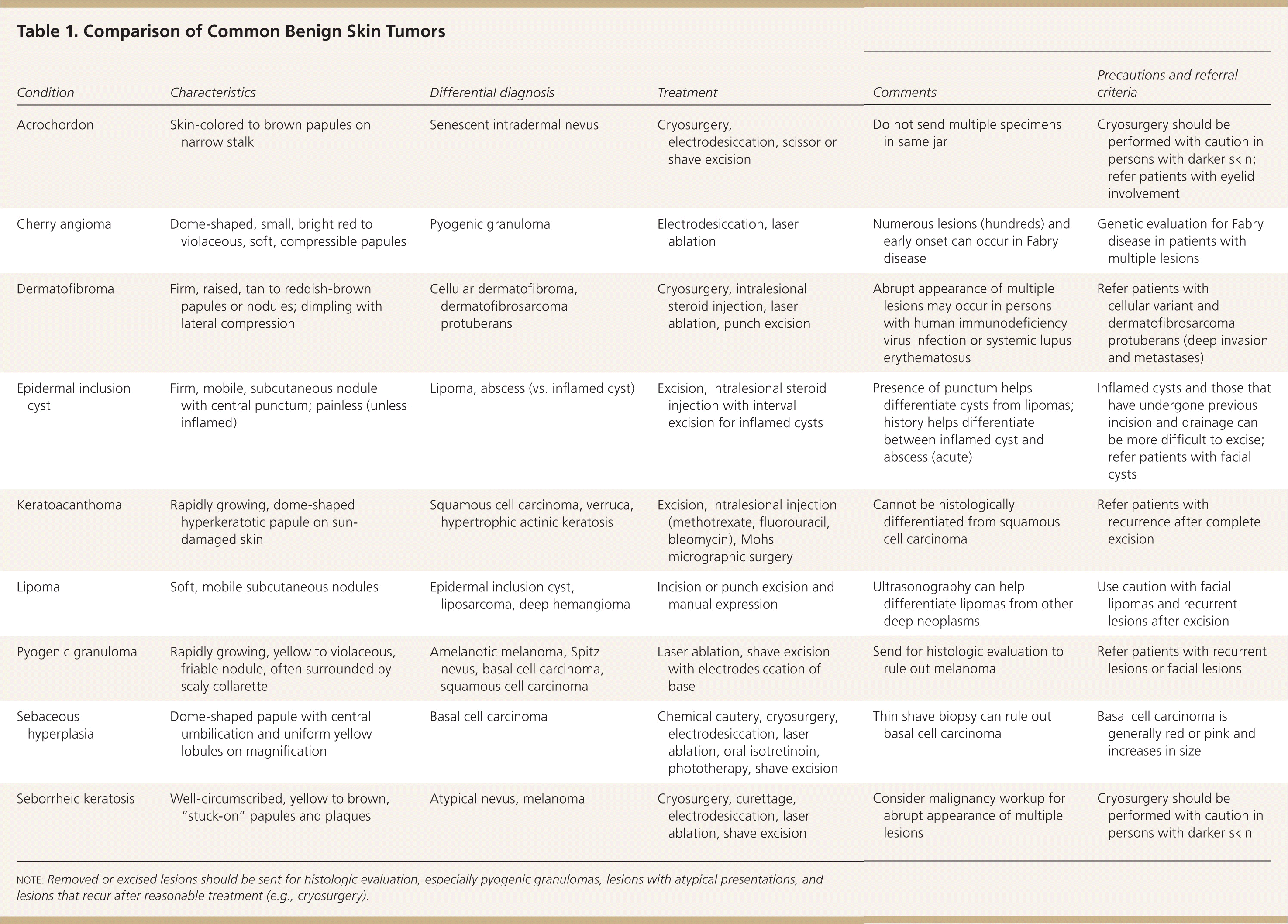
| Condition | Characteristics | Differential diagnosis | Treatment | Comments | Precautions and referral criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrochordon | Skin-colored to brown papules on narrow stalk | Senescent intradermal nevus | Cryosurgery, electrodesiccation, scissor or shave excision | Do not send multiple specimens in same jar | Cryosurgery should be performed with caution in persons with darker skin; refer patients with eyelid involvement |
| Cherry angioma | Dome-shaped, small, bright red to violaceous, soft, compressible papules | Pyogenic granuloma | Electrodesiccation, laser ablation | Numerous lesions (hundreds) and early onset can occur in Fabry disease | Genetic evaluation for Fabry disease in patients with multiple lesions |
| Dermatofibroma | Firm, raised, tan to reddish-brown papules or nodules; dimpling with lateral compression | Cellular dermatofibroma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans | Cryosurgery, intralesional steroid injection, laser ablation, punch excision | Abrupt appearance of multiple lesions may occur in persons with human immunodeficiency virus infection or systemic lupus erythematosus | Refer patients with cellular variant and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (deep invasion and metastases) |
| Epidermal inclusion cyst | Firm, mobile, subcutaneous nodule with central punctum; painless (unless inflamed) | Lipoma, abscess (vs. inflamed cyst) | Excision, intralesional steroid injection with interval excision for inflamed cysts | Presence of punctum helps differentiate cysts from lipomas; history helps differentiate between inflamed cyst and abscess (acute) | Inflamed cysts and those that have undergone previous incision and drainage can be more difficult to excise; refer patients with facial cysts |
| Keratoacanthoma | Rapidly growing, dome-shaped hyperkeratotic papule on sun-damaged skin | Squamous cell carcinoma, verruca, hypertrophic actinic keratosis | Excision, intralesional injection (methotrexate, fluorouracil, bleomycin), Mohs micrographic surgery | Cannot be histologically differentiated from squamous cell carcinoma | Refer patients with recurrence after complete excision |
| Lipoma | Soft, mobile subcutaneous nodules | Epidermal inclusion cyst, liposarcoma, deep hemangioma | Incision or punch excision and manual expression | Ultrasonography can help differentiate lipomas from other deep neoplasms | Use caution with facial lipomas and recurrent lesions after excision |
| Pyogenic granuloma | Rapidly growing, yellow to violaceous, friable nodule, often surrounded by scaly collarette | Amelanotic melanoma, Spitz nevus, basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma | Laser ablation, shave excision with electrodesiccation of base | Send for histologic evaluation to rule out melanoma | Refer patients with recurrent lesions or facial lesions |
| Sebaceous hyperplasia | Dome-shaped papule with central umbilication and uniform yellow lobules on magnification | Basal cell carcinoma | Chemical cautery, cryosurgery, electrodesiccation, laser ablation, oral isotretinoin, phototherapy, shave excision | Thin shave biopsy can rule out basal cell carcinoma | Basal cell carcinoma is generally red or pink and increases in size |
| Seborrheic keratosis | Well-circumscribed, yellow to brown, “stuck-on” papules and plaques | Atypical nevus, melanoma | Cryosurgery, curettage, electrodesiccation, laser ablation, shave excision | Consider malignancy workup for abrupt appearance of multiple lesions | Cryosurgery should be performed with caution in persons with darker skin |
Acrochordons
Acrochordons (skin tags) are extremely common, small, and typically pedunculated benign neoplasms. They consist of hyperplastic soft dermis and epidermis, and are usually skin colored or brownish (Figure 1). They are generally 2 to 5 mm in size, although they may become larger. The most common locations are in skin folds (e.g., neck, axillae, groin), where skin irritation can be a causative factor. They occur in 25% to 46% of adults and increase with age and during pregnancy.5 Studies have found that acrochordons are associated with the metabolic syndrome (obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, insulin resistance, and elevated C-reactive protein levels).6,7 This suggests they may be viewed as cutaneous clues for cardiovascular disease.
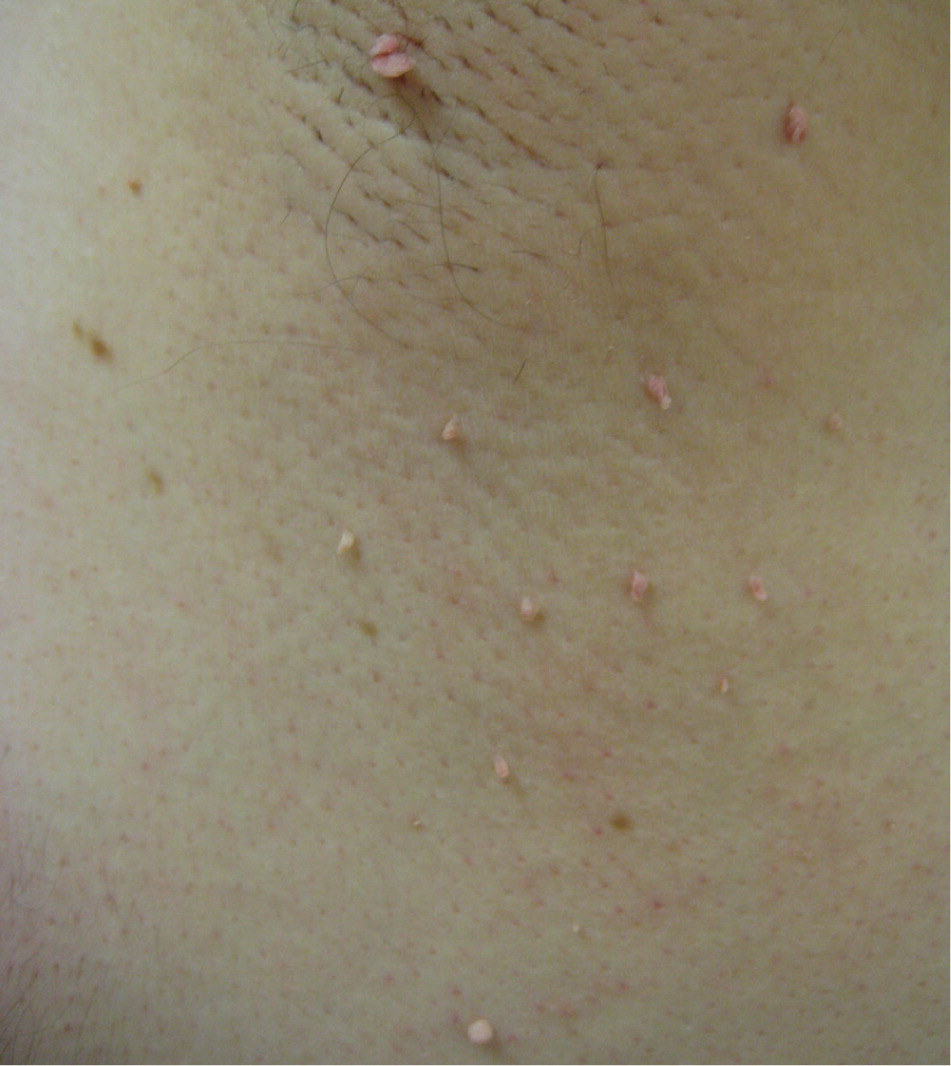
Diagnosis is based on the appearance and location of lesions. They must be differentiated from neurofibromas, seborrheic keratoses, and pedunculated nevi. There have been rare case reports of skin tags that were found to be basal or squamous cell carcinomas. Treatment consists of cryosurgery, electrodesiccation, or simple scissor or shave excision. Electrodesiccation causes less hypopigmentation than cryotherapy and is the preferred treatment in nonwhite patients. An ear speculum placed over a small lesion may be helpful in directing the freeze pattern during cryosurgery.
Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a benign disorder of the sebaceous glands that is common in middle-aged or older adults. Lesions present as asymptomatic, discrete, soft, pale yellow, shiny bumps on the forehead (Figure 2) or cheeks, or near hair follicles. They typically appear as an umbilicated dome with multiple lobules resembling a cauliflower. There may be single or multiple lesions, ranging from 1 to 4 mm in diameter. They have no clinical significance except for cosmesis. Histologically, lesions consist of enlarged mature lobules of sebocytes around a central duct. It is important to rule out basal cell carcinoma, which is generally red or pink and increasing in size. Inspection of any surface vessels will show a haphazard arrangement in basal cell carcinoma, whereas the vessels in sebaceous hyperplasia occur only between lobules.
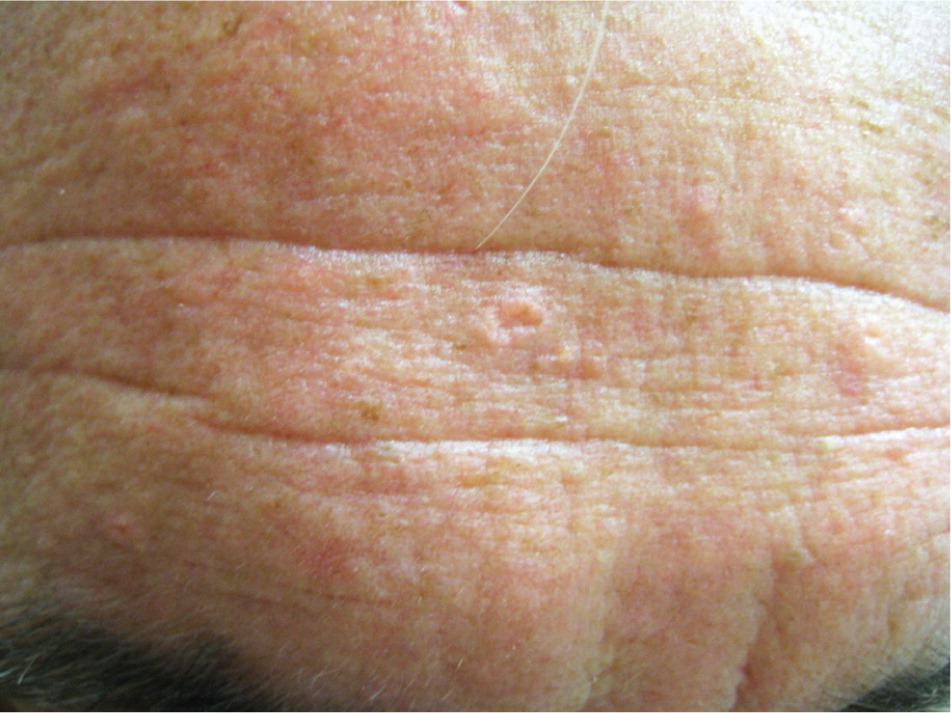
No treatment is required for sebaceous hyperplasia, although patients may request removal of lesions for cosmetic reasons or because of concerns about malignancy. Therapeutic options include cryosurgery, phototherapy, shave excision, laser ablation, electrodesiccation with curettage, chemical cautery, or oral isotretinoin for widespread lesions.8
Lipomas
Lipomas are slow-growing, benign mesenchymal tumors enclosed by a thin fibrous capsule. They closely resemble normal fat and are the most common type of soft tissue tumor. They are usually subcutaneous but may occur in any organ because they are mesenchymal. They are generally asymptomatic but may become irritated with trauma or produce local obstructive symptoms in the airway or gastrointestinal tract. Their prevalence is 1%.9
Lipomas must be clinically differentiated from other tumors. The primary differential diagnosis in a subcutaneous mass is a sebaceous cyst or abscess. Lipomas are soft, flesh-colored nodules that are easily moveable under the overlying skin. Sebaceous cysts are generally identifiable by a central punctum, and abscesses can be identified by the presence of warmth, redness, and pain. Ultrasonography is increasingly used to aid in the diagnosis of lipomas. High-frequency ultrasonography (greater than 20 MHz) can provide high-resolution images of subcutaneous tumors and surrounding structures.10 The differential diagnosis of lipomas also includes liposarcomas; risk factors for malignancy are size greater than 10 cm, older age, rapid lesion growth, location on the thigh, and invasion into deeper tissue, such as nerve or bone, leading to a firm or fixed feeling on examination. Lesions concerning for malignancy should be imaged with computed tomography or contrast magnetic resonance imaging.11
Patients commonly present with cosmetic concerns or symptoms related to compression of surrounding tissue. A single incision or punch excision (for smaller lesions) will generally allow manual expression of the lipoma without difficulty when standard excision is not required.12
Keratoacanthomas
Keratoacanthomas are rapidly growing, squamoproliferative benign tumors that resemble squamous cell carcinoma. They begin as round, firm, reddish or skin-colored papules that develop into dome-shaped nodules with a keratin-filled crater (Figure 3). They may grow to 1 to 2 cm over weeks or months. There is a slower involution phase over several months, leaving a scar if not excised early in its course. Keratoacanthomas generally occur later in life on sun-exposed areas, primarily the face, arms, and legs. They are attributed to sun exposure, cigarette smoking, human papillomavirus infection, genetic factors, trauma, and chemical carcinogens.
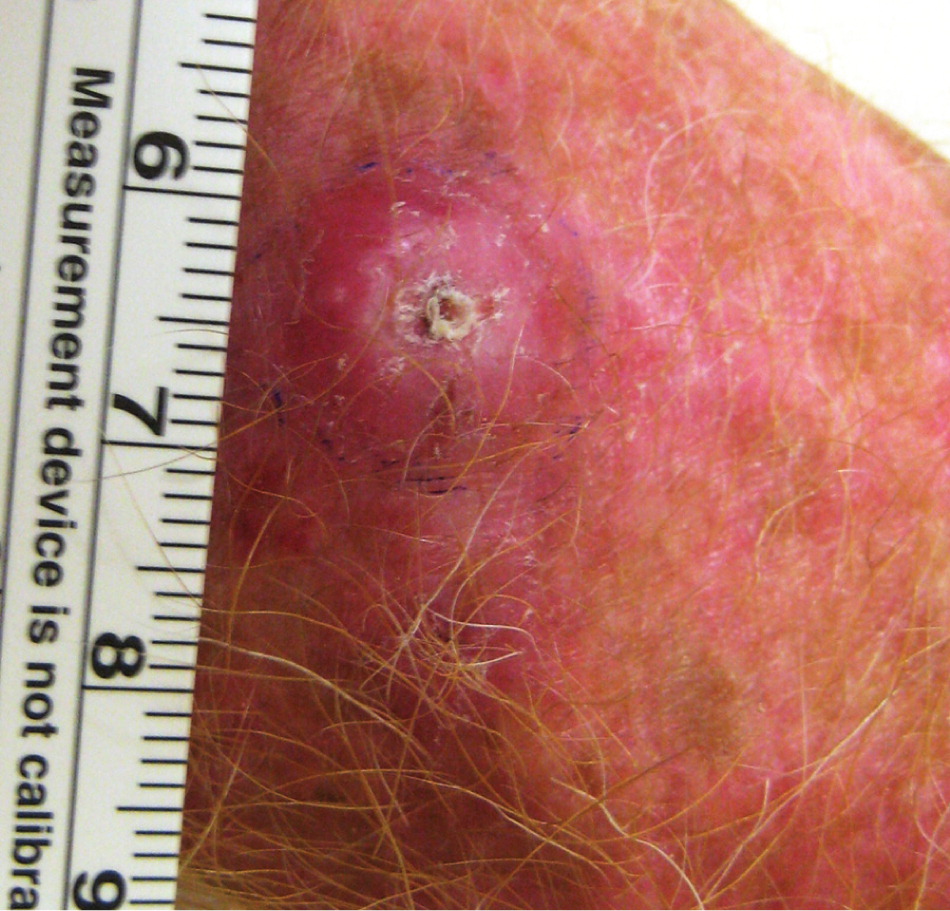
There is long-standing controversy over whether keratoacanthomas are benign, spontaneously self-limited tumors or a variant of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma that have the potential for metastasis.13 Keratoacanthomas share histopathologic characteristics that make them difficult to distinguish from squamous cell carcinoma. Shave biopsy may be inadequate to distinguish the conditions, whereas punch biopsy may be adequate because it obtains deeper tissue. Because no clinical or pathologic features can reliably differentiate keratoacanthoma from squamous cell carcinoma, early simple excision of lesions is recommended, with margins of 3 to 5 mm. Mohs micrographic surgery may be considered if tissue sparing is desired.14
Pyogenic Granulomas
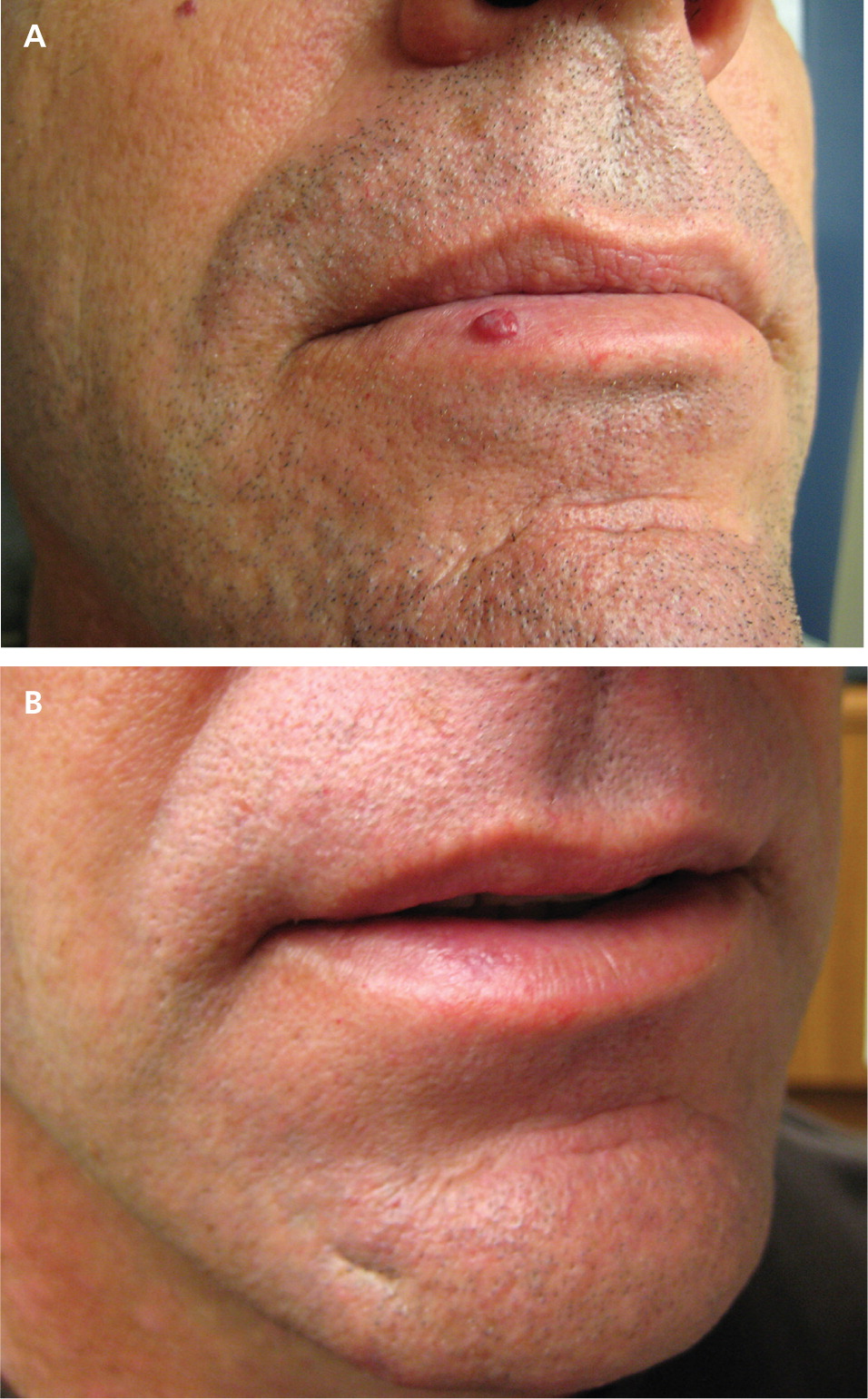
Pyogenic granulomas are rapidly growing nodules that bleed easily. Their name is a misnomer, however, as these lesions are neither pyogenic nor granulomas. They are an acquired benign tumor often found on mucous membranes. They tend to occur on the head or neck, or at sites of previous penetrating trauma. They are common in infancy and childhood, and approximately 2% of women develop a mucosal lesion in the late first to second trimester of pregnancy.17
Pyogenic granulomas are yellow to purplish, pulpy vascular lesions often surrounded by a scaly collarette. They are usually removed because of their rapid growth and tendency to bleed. The differential diagnosis includes Spitz nevi, amelanotic melanoma, and squamous or basal cell carcinoma. Treatment options include shave excision with electrodesiccation of the base, and laser ablation18 (Figure 4).
Dermatofibromas
Dermatofibromas result from idiopathic benign proliferation of fibroblasts. Generally located on the lower extremities, they may develop at any cutaneous site and range in size from 3 to 10 mm. They are four times more common in women, and most develop between 20 and 50 years of age. [corrected] They are usually asymptomatic, although pruritus and tenderness can be present. Dermatofibromas appear gradually over months and may persist for years. Although multiple dermatofibromas may be present, large numbers (15 or more) are rare. A multiple eruptive variant occurs in only 0.3% of patients, many of whom are immunocompromised (classically, those with human immunodeficiency virus infection or systemic lupus erythematosus).19
Diagnosis is based on the appearance of firm, raised, papules or nodules, ranging from tan to reddish brown. They tend to be darker at the center and fade to normal skin color at the margin. Dermatofibromas exhibit dimpling or retraction of the lesion beneath the skin with lateral compression (Figure 5).20
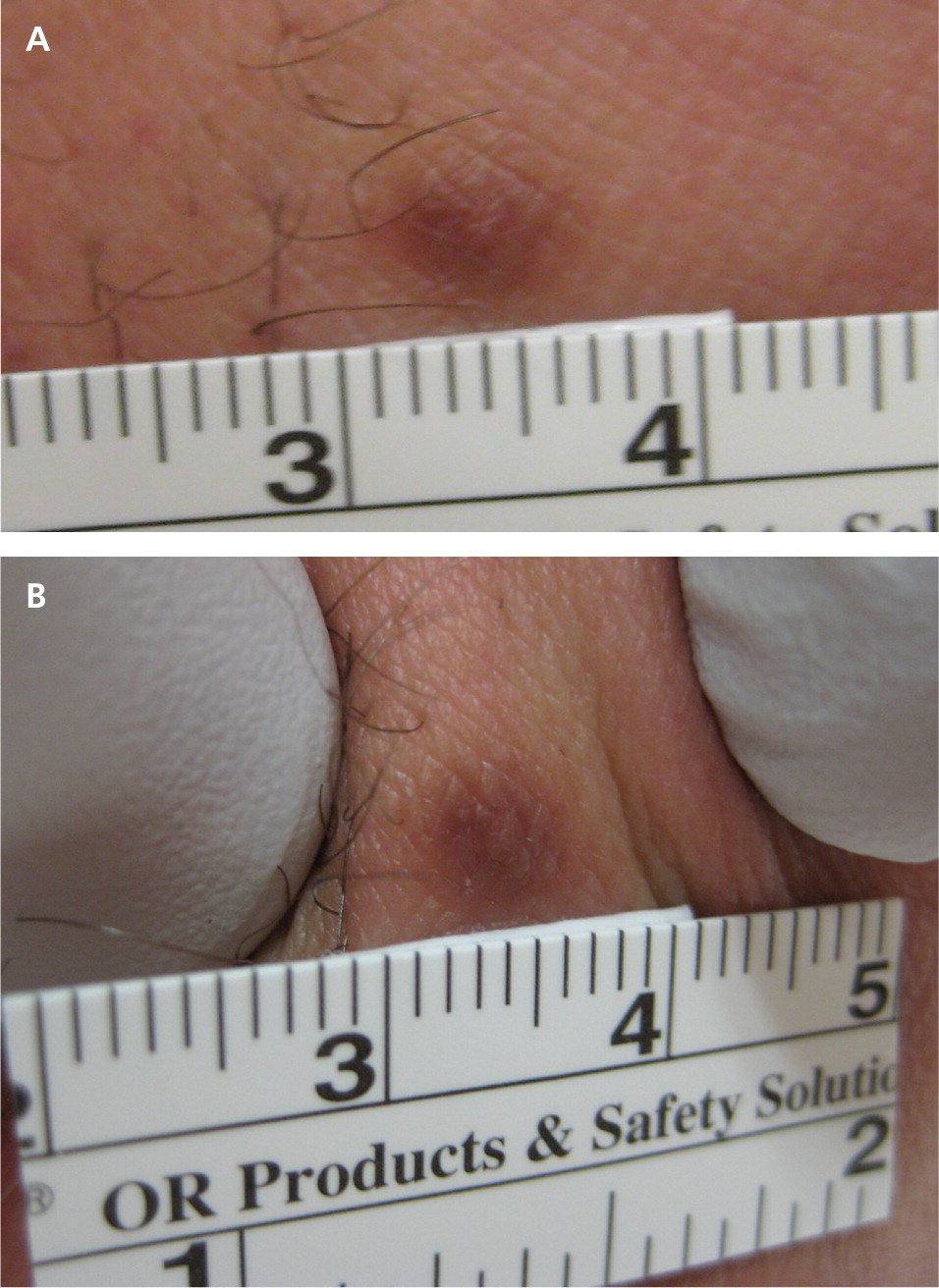
No treatment is required unless there is a change in size or color, or bleeding or irritation from trauma. A 2012 study found that 73% of patients who underwent laser ablation reported satisfaction with the results.21
Epidermal Inclusion Cysts
Epidermal inclusion cysts are the most common type of cutaneous cyst. They are discrete nodules resulting from the implantation and proliferation of epidermal elements within the dermis. However, they display no sebaceous component and are not truly sebaceous cysts. They typically present on the head, neck, or trunk, and may remain stable or enlarge over time. Spontaneous inflammation and rupture can occur, with significant involvement of surrounding tissue. There is no way to predict which lesions will remain quiescent or become larger or inflamed. Infected cysts tend to be larger, more erythematous, and more painful than sterile inflamed cysts.
Multiple epidermal inclusion cysts are associated with Gardner syndrome, an autosomal dominant condition associated with colon cancer. Cysts that are unusual in number or location (e.g., fingers, toes) warrant screening for colon cancer. Malignancies (e.g., basal cell carcinoma, Bowen disease, squamous cell carcinoma, mycosis fungoides, melanoma in situ) can develop in cysts, but this is rare.22
Diagnosis of epidermal inclusion cysts is based on appearance and palpation of a discrete, freely movable cyst or nodule. Careful inspection often reveals a central punctum (Figure 6). Treatment is unnecessary unless desired by the patient, and can be accomplished via simple excision with removal of the cyst and cyst wall. Inflamed or ruptured cysts often resolve spontaneously without therapy, although they tend to recur. Intralesional steroid injections can hasten resolution of inflamed cysts and should be followed by interval excision.23
Seborrheic Keratoses
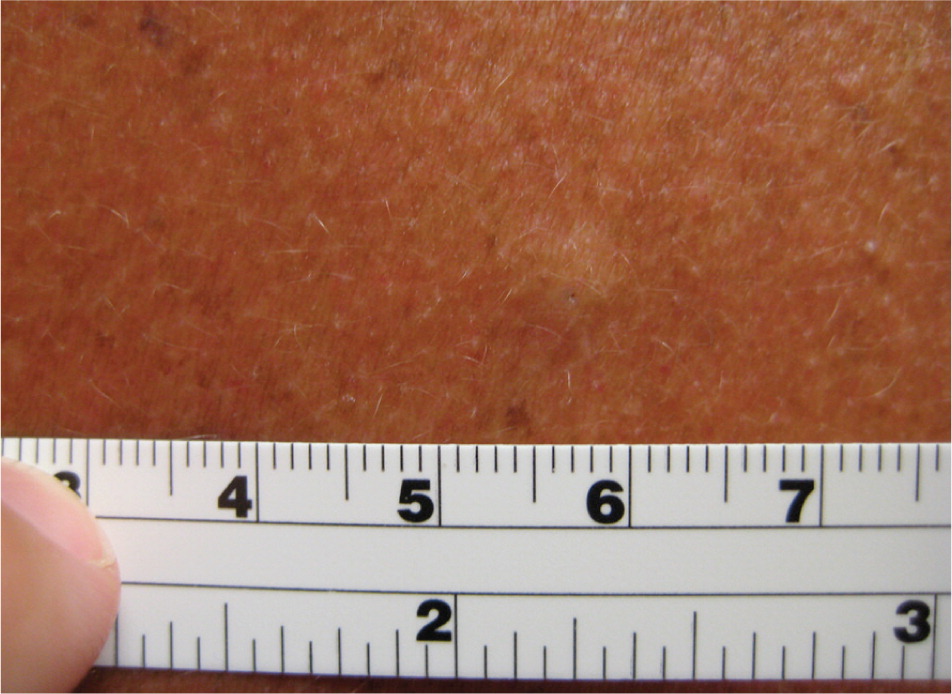
Seborrheic keratoses are the most common benign epithelial tumor. They tend to be hereditary and occur after 30 years of age.24 They present as multiple, well-circumscribed, yellow to brown, raised lesions that feel slightly greasy, velvety, or warty and are described as having a “stuck-on” appearance25 (Figure 7).
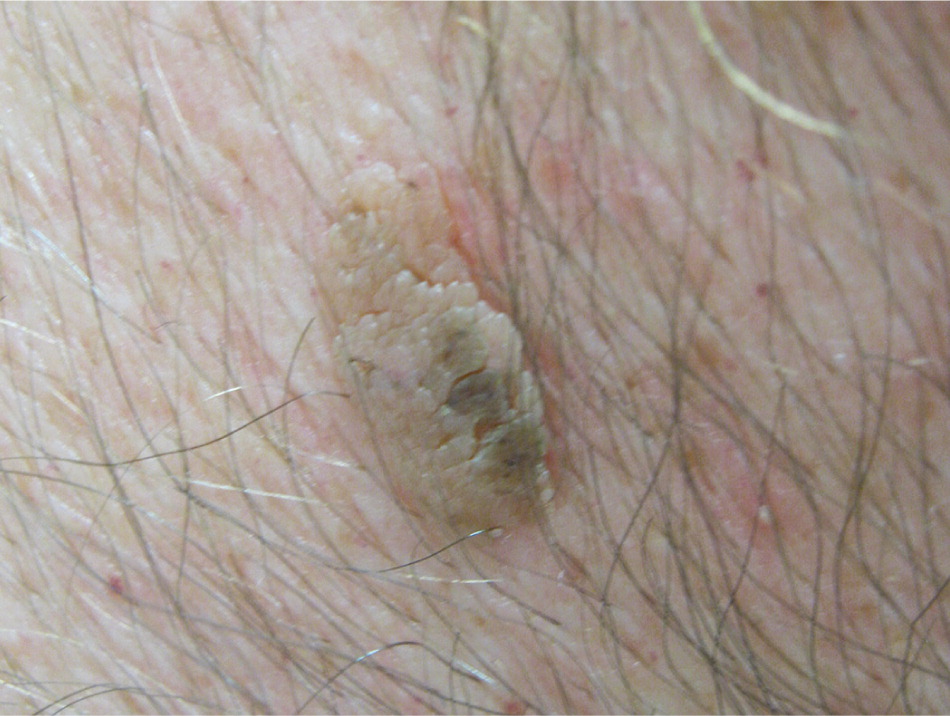
The Leser-Trélat sign is the abrupt eruption of multiple seborrheic keratosis lesions in a patient with an underlying malignancy, usually an adenocarcinoma of the stomach.26,27 This is a rare sign supported mainly by case reports, but should prompt consideration of a paraneoplastic disorder. Seborrheic keratoses may resolve with treatment of the malignancy, then reappear with its recurrence.
Seborrheic keratoses generally do not require treatment unless they become irritated or the patient has cosmetic concerns. They may be treated with electrodesiccation, laser ablation, curettage, cryosurgery, or shave excision if biopsy is required.
Cherry Angiomas
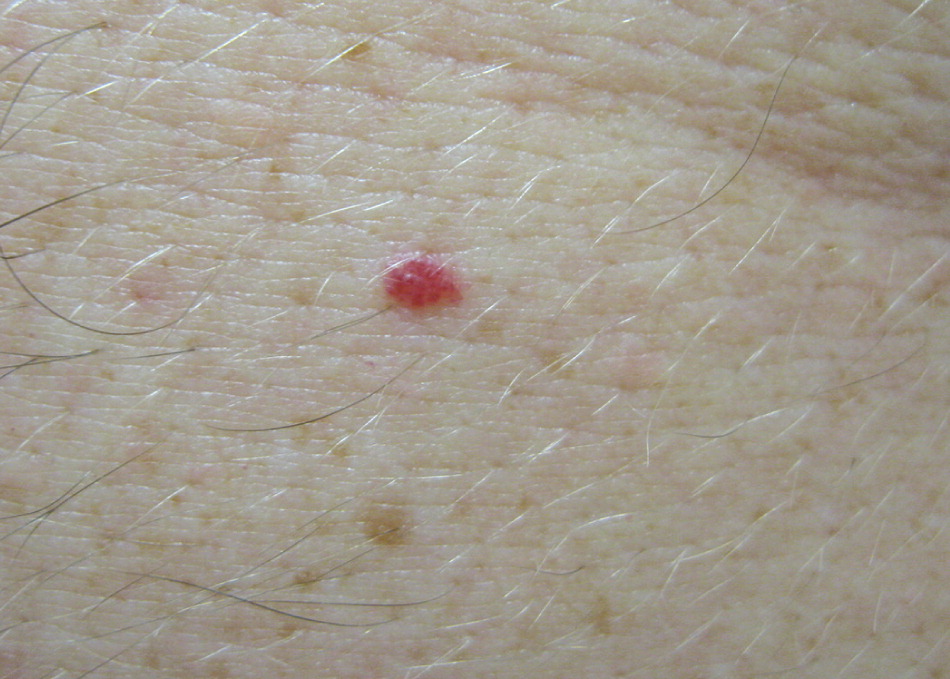
Cherry angiomas are extremely common lesions that tend to appear with increasing age. They usually occur as multiple asymptomatic lesions, most commonly on the trunk and arms. They are dome-shaped, small (0.1 to 0.5 cm in diameter), bright red to violaceous, soft, compressible papules with smooth surfaces that blanch with pressure and bleed profusely with traumatic rupture (Figure 8). They can be treated effectively with electrodesiccation or laser ablation.
Data Sources: A series of PubMed searches were completed in Clinical Queries using the key terms acrochordon, sebaceous hyperplasia, lipoma, keratoacanthoma, pyogenic granuloma, dermatofibroma, epidermal inclusion cysts, seborrheic keratosis, and cherry angiomas. The following keywords were also searched in PubMed: benign skin lesions, benign skin tumors, skin diseases, diagnosis, and treatment. The search included reviews, meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, and clinical trials. We also searched the National Guideline Clearinghouse, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, UpToDate, and Pepid. Search date: April 30, 2014.
The opinions and assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of the U.S. Navy.