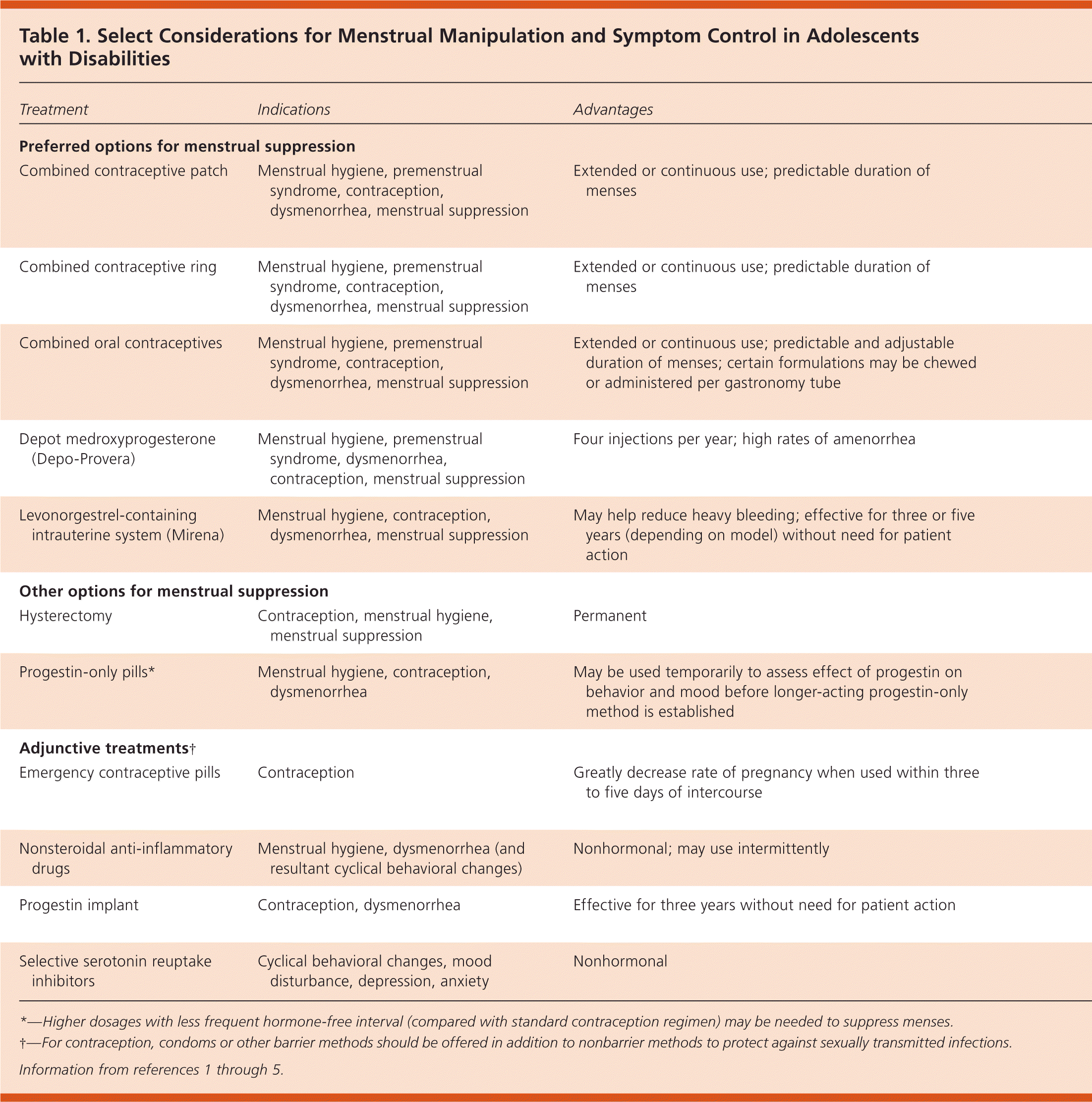
| Preferred options for menstrual suppression |
| Combined contraceptive patch | Menstrual hygiene, premenstrual syndrome, contraception, dysmenorrhea, menstrual suppression | Extended or continuous use; predictable duration of menses | Breakthrough bleeding; may be less effective at contraception in persons weighing > 198 lb (90 kg); patient may prematurely remove patch | Additional risk of thromboembolic events in patients who are immobile is unknown; estrogen exposure may be higher than with use of other estrogen-containing methods; effectiveness may decrease with use of specific antiepileptic drugs (e.g., topiramate [Topamax]) |
| Combined contraceptive ring | Menstrual hygiene, premenstrual syndrome, contraception, dysmenorrhea, menstrual suppression | Extended or continuous use; predictable duration of menses | Breakthrough bleeding; assistance often needed for placement (privacy issues) | Additional risk of thromboembolic events in patients who are immobile is unknown; effectiveness may decrease with use of specific antiepileptic drugs (e.g., topiramate) |
| Combined oral contraceptives | Menstrual hygiene, premenstrual syndrome, contraception, dysmenorrhea, menstrual suppression | Extended or continuous use; predictable and adjustable duration of menses; certain formulations may be chewed or administered per gastronomy tube | Breakthrough bleeding; may require surveillance for daily use | Additional risk of thromboembolic events in patients who are immobile is unknown; daily regimen may be advantageous in situations where other daily medications are regularly given; effectiveness may decrease with use of specific antiepileptic drugs (e.g., topiramate) |
| Depot medroxyprogesterone (Depo-Provera) | Menstrual hygiene, premenstrual syndrome, dysmenorrhea, contraception, menstrual suppression | Four injections per year; high rates of amenorrhea | May decrease bone mineral density, especially in patients who are immobile; weight gain in adolescents who are overweight or obese; irregular bleeding (tends to improve over time) | Weight gain may affect independence and mobility (e.g., patient transfers) |
| Levonorgestrel-containing intrauterine system (Mirena) | Menstrual hygiene, contraception, dysmenorrhea, menstrual suppression | May help reduce heavy bleeding; effective for three or five years (depending on model) without need for patient action | Irregular bleeding (tends to improve over time); potential need for sedation; patients may be unable to voice pain or discomfort associated with procedure or complications | Five-year model likely preferred because the three-year model has limited data on menstrual control and requires more frequent replacements |
| Other options for menstrual suppression |
| Hysterectomy | Contraception, menstrual hygiene, menstrual suppression | Permanent | Surgical complications | Legal and ethical considerations of sterilization apply; generally not a first-line treatment |
| Progestin-only pills* | Menstrual hygiene, contraception, dysmenorrhea | May be used temporarily to assess effect of progestin on behavior and mood before longer-acting progestin-only method is established | Irregular bleeding; may require surveillance for daily use | Daily regimen may be advantageous in situations where other daily medications are regularly given; effectiveness may decrease with use of specific antiepileptic drugs (e.g., topiramate) |
| Adjunctive treatments† |
| Emergency contraceptive pills | Contraception | Greatly decrease rate of pregnancy when used within three to five days of intercourse | Not typically intended for ongoing contraceptive needs | May be considered as a primary contraceptive method in persons who have infrequent and consensual intercourse, and who can remember to take pill at time of intercourse |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Menstrual hygiene, dysmenorrhea (and resultant cyclical behavioral changes) | Nonhormonal; may use intermittently | Not likely to result in complete menstrual suppression; gastrointestinal adverse effects | — |
| Progestin implant | Contraception, dysmenorrhea | Effective for three years without need for patient action | Likelihood of irregular bleeding limits its usefulness for menstrual suppression | Insertion and removal may be challenging for some patients; effectiveness may decrease with use of specific antiepileptic drugs (e.g., topiramate) |
| Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors | Cyclical behavioral changes, mood disturbance, depression, anxiety | Nonhormonal | May worsen mood | U.S. Food and Drug Administration's boxed warning on risk of suicidality applies |