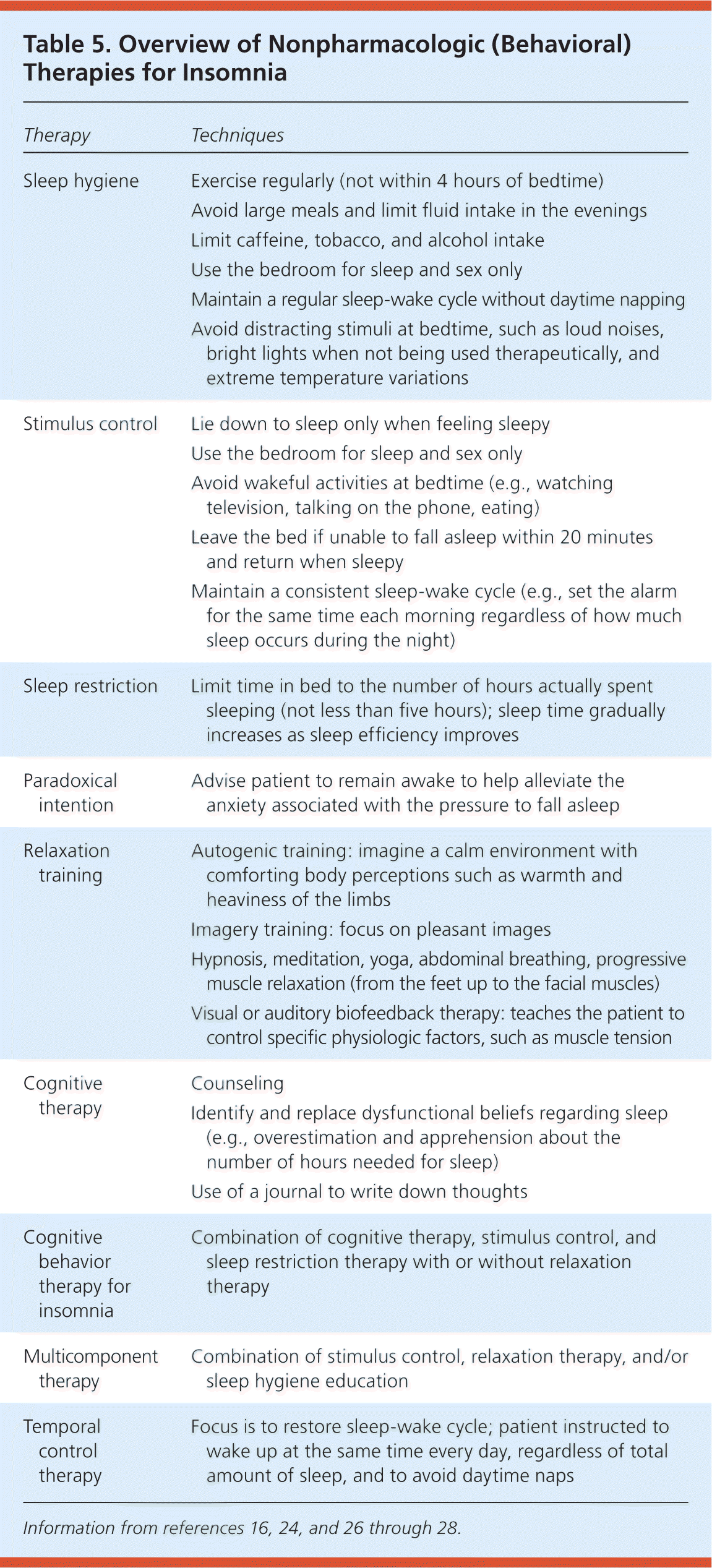
| Sleep hygiene | Exercise regularly (not within 4 hours of bedtime) |
| Avoid large meals and limit fluid intake in the evenings |
| Limit caffeine, tobacco, and alcohol intake |
| Use the bedroom for sleep and sex only |
| Maintain a regular sleep-wake cycle without daytime napping |
| Avoid distracting stimuli at bedtime, such as loud noises, bright lights when not being used therapeutically, and extreme temperature variations |
| Stimulus control | Lie down to sleep only when feeling sleepy |
| Use the bedroom for sleep and sex only |
| Avoid wakeful activities at bedtime (e.g., watching television, talking on the phone, eating) |
| Leave the bed if unable to fall asleep within 20 minutes and return when sleepy |
| Maintain a consistent sleep-wake cycle (e.g., set the alarm for the same time each morning regardless of how much sleep occurs during the night) |
| Sleep restriction | Limit time in bed to the number of hours actually spent sleeping (not less than five hours); sleep time gradually increases as sleep efficiency improves |
| Paradoxical intention | Advise patient to remain awake to help alleviate the anxiety associated with the pressure to fall asleep |
| Relaxation training | Autogenic training: imagine a calm environment with comforting body perceptions such as warmth and heaviness of the limbs |
| Imagery training: focus on pleasant images |
| Hypnosis, meditation, yoga, abdominal breathing, progressive muscle relaxation (from the feet up to the facial muscles) |
| Visual or auditory biofeedback therapy: teaches the patient to control specific physiologic factors, such as muscle tension |
| Cognitive therapy | Counseling |
| Identify and replace dysfunctional beliefs regarding sleep (e.g., overestimation and apprehension about the number of hours needed for sleep) |
| Use of a journal to write down thoughts |
| Cognitive behavior therapy for insomnia | Combination of cognitive therapy, stimulus control, and sleep restriction therapy with or without relaxation therapy |
| Multicomponent therapy | Combination of stimulus control, relaxation therapy, and/or sleep hygiene education |
| Temporal control therapy | Focus is to restore sleep-wake cycle; patient instructed to wake up at the same time every day, regardless of total amount of sleep, and to avoid daytime naps |