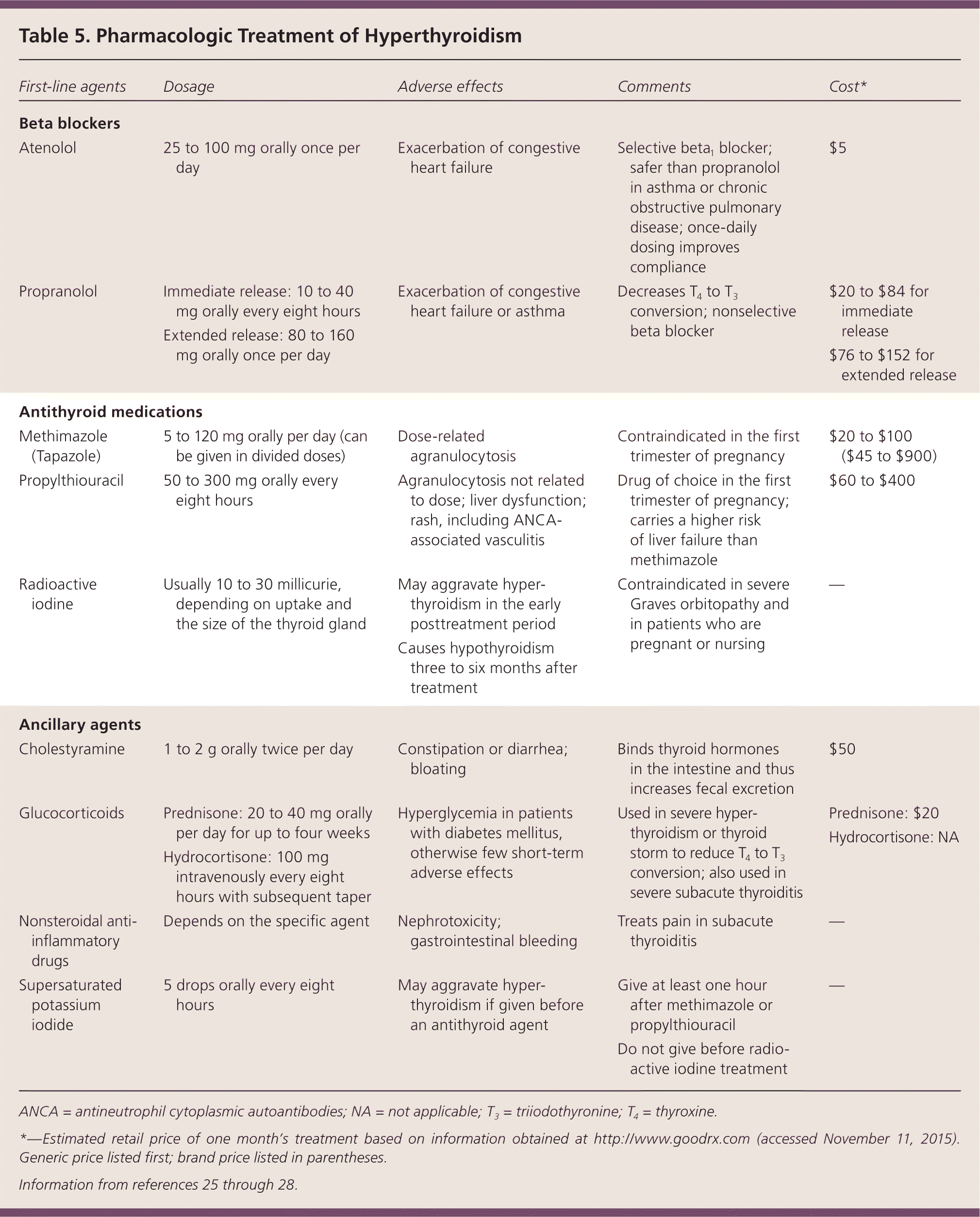
| Beta blockers |
| Atenolol | 25 to 100 mg orally once per day | Exacerbation of congestive heart failure | Selective beta1 blocker; safer than propranolol in asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; once-daily dosing improves compliance | $5 |
| Propranolol | | Exacerbation of congestive heart failure or asthma | Decreases T4 to T3 conversion; nonselective beta blocker | |
| Antithyroid medications |
| Methimazole (Tapazole) | 5 to 120 mg orally per day (can be given in divided doses) | Dose-related agranulocytosis | Contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy | $20 to $100 ($45 to $900) |
| Propylthiouracil | 50 to 300 mg orally every eight hours | Agranulocytosis not related to dose; liver dysfunction; rash, including ANCA-associated vasculitis | Drug of choice in the first trimester of pregnancy; carries a higher risk of liver failure than methimazole | $60 to $400 |
| Radioactive iodine | Usually 10 to 30 millicurie, depending on uptake and the size of the thyroid gland | | Contraindicated in severe Graves orbitopathy and in patients who are pregnant or nursing | — |
| Ancillary agents |
| Cholestyramine | 1 to 2 g orally twice per day | Constipation or diarrhea; bloating | Binds thyroid hormones in the intestine and thus increases fecal excretion | $50 |
| Glucocorticoids | | Hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus, otherwise few short-term adverse effects | Used in severe hyperthyroidism or thyroid storm to reduce T4 to T3 conversion; also used in severe subacute thyroiditis | Prednisone: $20 Hydrocortisone: NA
|
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Depends on the specific agent | Nephrotoxicity; gastrointestinal bleeding | Treats pain in subacute thyroiditis | — |
| Supersaturated potassium iodide | 5 drops orally every eight hours | May aggravate hyperthyroidism if given before an antithyroid agent | | — |