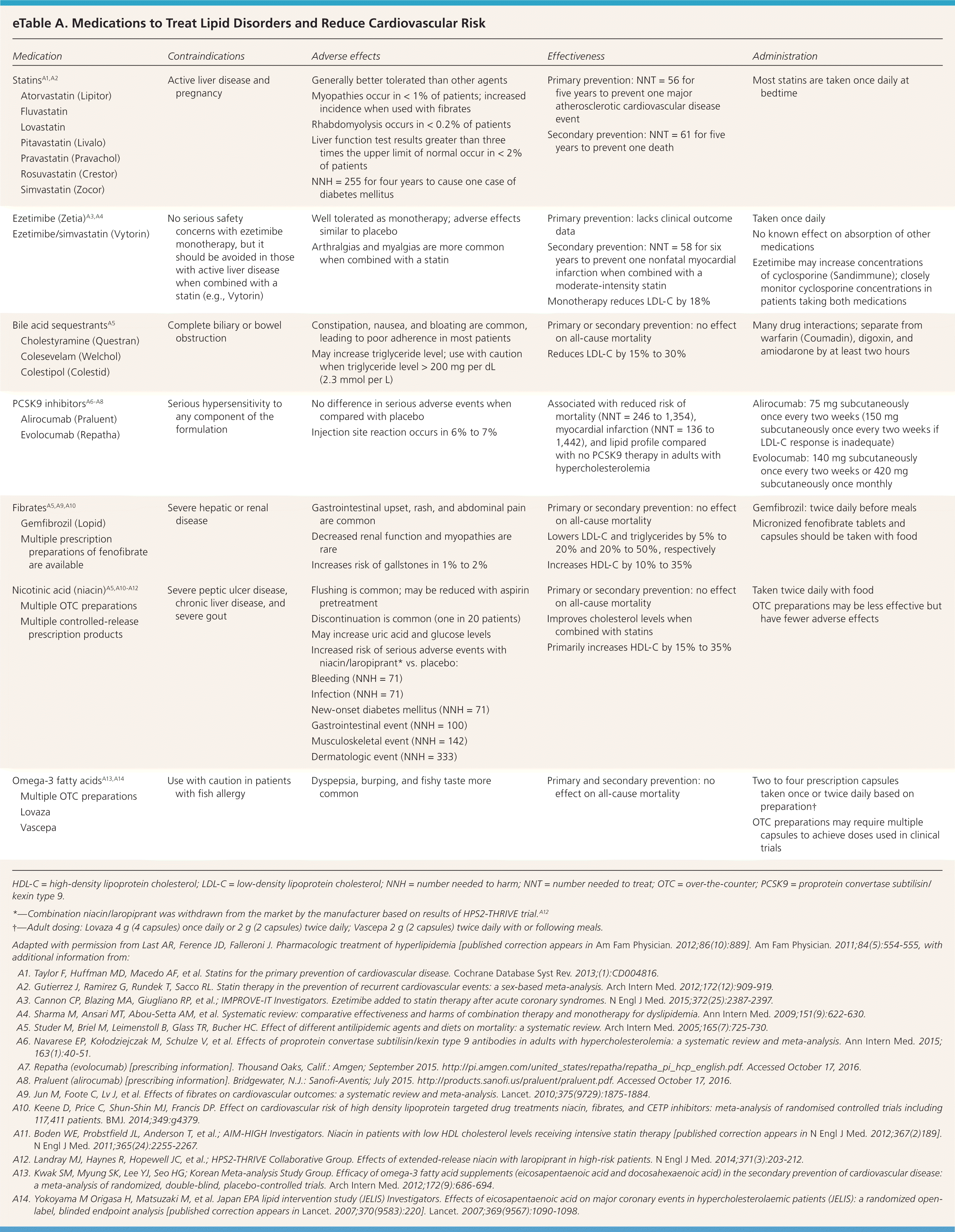
Atorvastatin (Lipitor) Fluvastatin Lovastatin Pitavastatin (Livalo) Pravastatin (Pravachol) Rosuvastatin (Crestor) Simvastatin (Zocor)
| | Generally better tolerated than other agents Myopathies occur in < 1% of patients; increased incidence when used with fibrates Rhabdomyolysis occurs in < 0.2% of patients Liver function test results greater than three times the upper limit of normal occur in < 2% of patients NNH = 255 for four years to cause one case of diabetes mellitus
| | |
| | | Primary prevention: lacks clinical outcome data Secondary prevention: NNT = 58 for six years to prevent one nonfatal myocardial infarction when combined with a moderate-intensity statin Monotherapy reduces LDL-C by 18%
| |
| | Constipation, nausea, and bloating are common, leading to poor adherence in most patients May increase triglyceride level; use with caution when triglyceride level > 200 mg per dL (2.3 mmol per L)
| | |
Alirocumab (Praluent) Evolocumab (Repatha)
| | | Associated with reduced risk of mortality (NNT = 246 to 1,354), myocardial infarction (NNT = 136 to 1,442), and lipid profile compared with no PCSK9 therapy in adults with hypercholesterolemia
| Alirocumab: 75 mg subcutaneously once every two weeks (150 mg subcutaneously once every two weeks if LDL-C response is inadequate) Evolocumab: 140 mg subcutaneously once every two weeks or 420 mg subcutaneously once monthly
|
| | Gastrointestinal upset, rash, and abdominal pain are common Decreased renal function and myopathies are rare Increases risk of gallstones in 1% to 2%
| Primary or secondary prevention: no effect on all-cause mortality Lowers LDL-C and triglycerides by 5% to 20% and 20% to 50%, respectively Increases HDL-C by 10% to 35%
| |
| | Flushing is common; may be reduced with aspirin pretreatment Discontinuation is common (one in 20 patients) May increase uric acid and glucose levels Increased risk of serious adverse events with niacin/laropiprant* vs. placebo: Bleeding (NNH = 71) Infection (NNH = 71) New-onset diabetes mellitus (NNH = 71) Gastrointestinal event (NNH = 100) Musculoskeletal event (NNH = 142) Dermatologic event (NNH = 333)
| Primary or secondary prevention: no effect on all-cause mortality Improves cholesterol levels when combined with statins Primarily increases HDL-C by 15% to 35%
| |
| | | | |