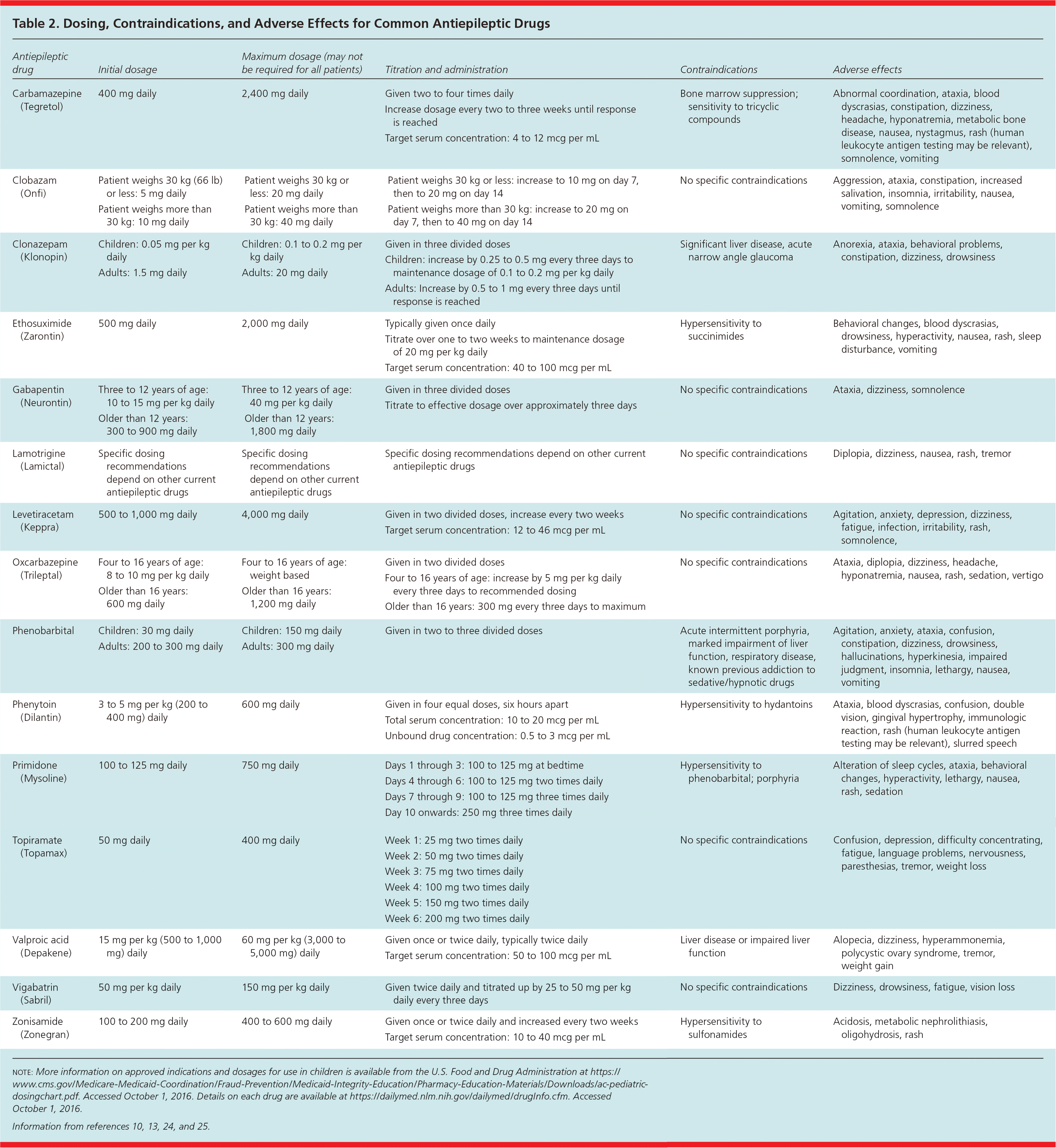
| Carbamazepine (Tegretol) | 400 mg daily | 2,400 mg daily | Given two to four times daily | Bone marrow suppression; sensitivity to tricyclic compounds | Abnormal coordination, ataxia, blood dyscrasias, constipation, dizziness, headache, hyponatremia, metabolic bone disease, nausea, nystagmus, rash (human leukocyte antigen testing may be relevant), somnolence, vomiting |
| | | Increase dosage every two to three weeks until response is reached | | |
| | | Target serum concentration: 4 to 12 mcg per mL | | |
| Clobazam (Onfi) | Patient weighs 30 kg (66 lb) or less: 5 mg daily | Patient weighs 30 kg or less: 20 mg daily | Patient weighs 30 kg or less: increase to 10 mg on day 7, then to 20 mg on day 14 | No specific contraindications | Aggression, ataxia, constipation, increased salivation, insomnia, irritability, nausea, vomiting, somnolence |
| Patient weighs more than 30 kg: 10 mg daily | Patient weighs more than 30 kg: 40 mg daily | Patient weighs more than 30 kg: increase to 20 mg on day 7, then to 40 mg on day 14 | | |
| Clonazepam (Klonopin) | Children: 0.05 mg per kg daily | Children: 0.1 to 0.2 mg per kg daily | Given in three divided doses | Significant liver disease, acute narrow angle glaucoma | Anorexia, ataxia, behavioral problems, constipation, dizziness, drowsiness |
| | | Children: increase by 0.25 to 0.5 mg every three days to maintenance dosage of 0.1 to 0.2 mg per kg daily | | |
| Adults: 1.5 mg daily | Adults: 20 mg daily | Adults: Increase by 0.5 to 1 mg every three days until response is reached | | |
| Ethosuximide (Zarontin) | 500 mg daily | 2,000 mg daily | Typically given once daily | Hypersensitivity to succinimides | Behavioral changes, blood dyscrasias, drowsiness, hyperactivity, nausea, rash, sleep disturbance, vomiting |
| | | Titrate over one to two weeks to maintenance dosage of 20 mg per kg daily | | |
| | | Target serum concentration: 40 to 100 mcg per mL | | |
| Gabapentin (Neurontin) | Three to 12 years of age: 10 to 15 mg per kg daily | Three to 12 years of age: 40 mg per kg daily | Given in three divided doses | No specific contraindications | Ataxia, dizziness, somnolence |
| Older than 12 years: 300 to 900 mg daily | Older than 12 years: 1,800 mg daily | Titrate to effective dosage over approximately three days | | |
| Lamotrigine (Lamictal) | Specific dosing recommendations depend on other current antiepileptic drugs | Specific dosing recommendations depend on other current antiepileptic drugs | Specific dosing recommendations depend on other current antiepileptic drugs | No specific contraindications | Diplopia, dizziness, nausea, rash, tremor |
| Levetiracetam (Keppra) | 500 to 1,000 mg daily | 4,000 mg daily | Given in two divided doses, increase every two weeks | No specific contraindications | Agitation, anxiety, depression, dizziness, fatigue, infection, irritability, rash, somnolence, |
| | | Target serum concentration: 12 to 46 mcg per mL | | |
| Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal) | Four to 16 years of age: 8 to 10 mg per kg daily | Four to 16 years of age: weight based | Given in two divided doses | No specific contraindications | Ataxia, diplopia, dizziness, headache, hyponatremia, nausea, rash, sedation, vertigo |
| Older than 16 years: 600 mg daily | Older than 16 years: 1,200 mg daily | Four to 16 years of age: increase by 5 mg per kg daily every three days to recommended dosing | | |
| | | Older than 16 years: 300 mg every three days to maximum | | |
| Phenobarbital | Children: 30 mg daily | Children: 150 mg daily | Given in two to three divided doses | Acute intermittent porphyria, marked impairment of liver function, respiratory disease, known previous addiction to sedative/hypnotic drugs | Agitation, anxiety, ataxia, confusion, constipation, dizziness, drowsiness, hallucinations, hyperkinesia, impaired judgment, insomnia, lethargy, nausea, vomiting |
| Adults: 200 to 300 mg daily | Adults: 300 mg daily | | | |
| Phenytoin (Dilantin) | 3 to 5 mg per kg (200 to 400 mg) daily | 600 mg daily | Given in four equal doses, six hours apart | Hypersensitivity to hydantoins | Ataxia, blood dyscrasias, confusion, double vision, gingival hypertrophy, immunologic reaction, rash (human leukocyte antigen testing may be relevant), slurred speech |
| | | Total serum concentration: 10 to 20 mcg per mL | | |
| | | Unbound drug concentration: 0.5 to 3 mcg per mL | | |
| Primidone (Mysoline) | 100 to 125 mg daily | 750 mg daily | Days 1 through 3: 100 to 125 mg at bedtime | Hypersensitivity to phenobarbital; porphyria | Alteration of sleep cycles, ataxia, behavioral changes, hyperactivity, lethargy, nausea, rash, sedation |
| | | Days 4 through 6: 100 to 125 mg two times daily | | |
| | | Days 7 through 9: 100 to 125 mg three times daily | | |
| | | Day 10 onwards: 250 mg three times daily | | |
| Topiramate (Topamax) | 50 mg daily | 400 mg daily | Week 1: 25 mg two times daily | No specific contraindications | Confusion, depression, difficulty concentrating, fatigue, language problems, nervousness, paresthesias, tremor, weight loss |
| | | Week 2: 50 mg two times daily | | |
| | | Week 3: 75 mg two times daily | | |
| | | Week 4: 100 mg two times daily | | |
| | | Week 5: 150 mg two times daily | | |
| | | Week 6: 200 mg two times daily | | |
| Valproic acid (Depakene) | 15 mg per kg (500 to 1,000 mg) daily | 60 mg per kg (3,000 to 5,000 mg) daily | Given once or twice daily, typically twice daily | Liver disease or impaired liver function | Alopecia, dizziness, hyperammonemia, polycystic ovary syndrome, tremor, weight gain |
| | | Target serum concentration: 50 to 100 mcg per mL | | |
| Vigabatrin (Sabril) | 50 mg per kg daily | 150 mg per kg daily | Given twice daily and titrated up by 25 to 50 mg per kg daily every three days | No specific contraindications | Dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, vision loss |
| Zonisamide (Zonegran) | 100 to 200 mg daily | 400 to 600 mg daily | Given once or twice daily and increased every two weeks | Hypersensitivity to sulfonamides | Acidosis, metabolic nephrolithiasis, oligohydrosis, rash |
| | | Target serum concentration: 10 to 40 mcg per mL | | |