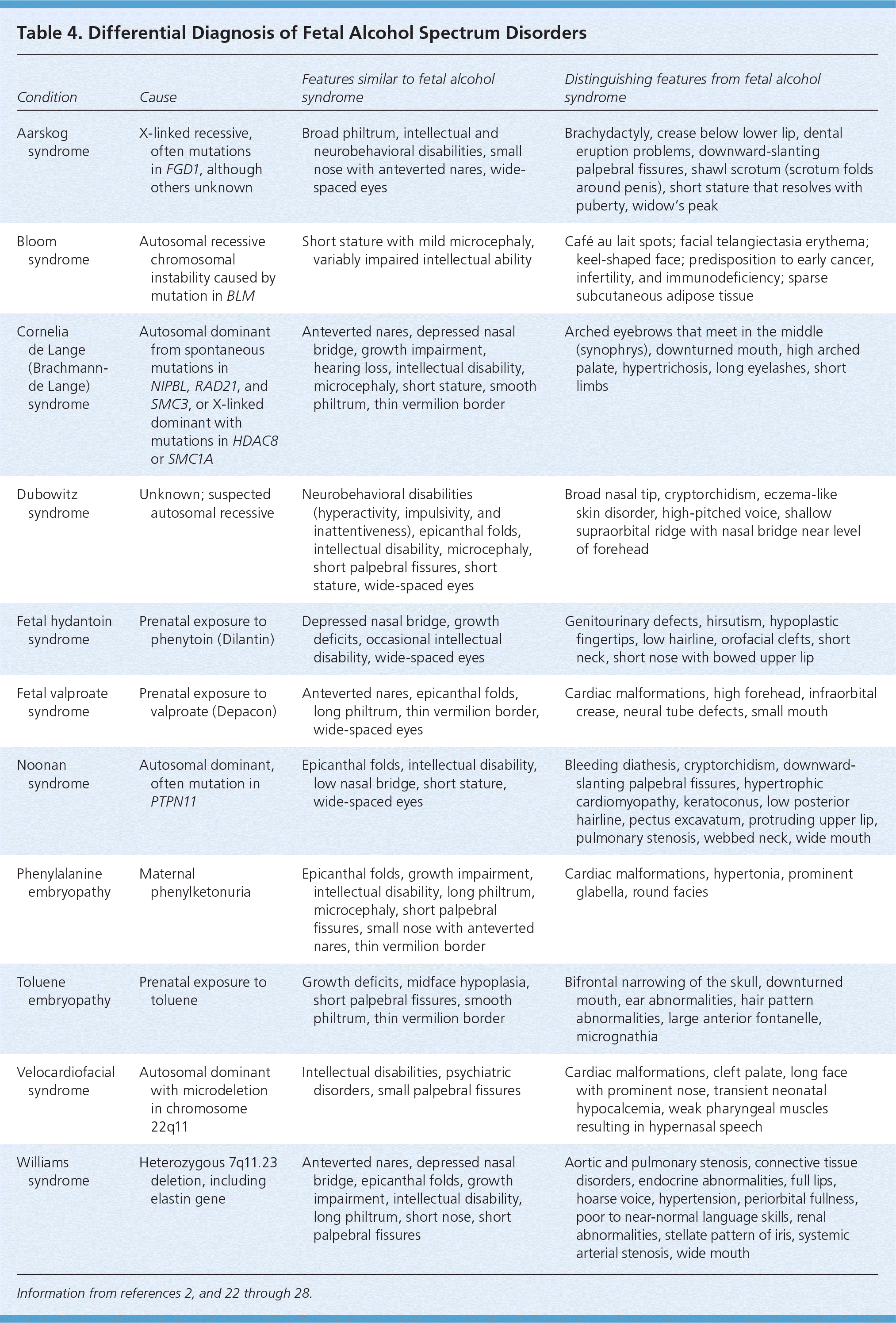
| Aarskog syndrome | X-linked recessive, often mutations in FGD1, although others unknown | Broad philtrum, intellectual and neurobehavioral disabilities, small nose with anteverted nares, wide-spaced eyes | Brachydactyly, crease below lower lip, dental eruption problems, downward-slanting palpebral fissures, shawl scrotum (scrotum folds around penis), short stature that resolves with puberty, widow's peak |
| Bloom syndrome | Autosomal recessive chromosomal instability caused by mutation in BLM | Short stature with mild microcephaly, variably impaired intellectual ability | Café au lait spots; facial telangiectasia erythema; keel-shaped face; predisposition to early cancer, infertility, and immunodeficiency; sparse subcutaneous adipose tissue |
| Cornelia de Lange (Brachmann-de Lange) syndrome | Autosomal dominant from spontaneous mutations in NIPBL, RAD21, and SMC3, or X-linked dominant with mutations in HDAC8 or SMC1A | Anteverted nares, depressed nasal bridge, growth impairment, hearing loss, intellectual disability, microcephaly, short stature, smooth philtrum, thin vermilion border | Arched eyebrows that meet in the middle (synophrys), downturned mouth, high arched palate, hypertrichosis, long eyelashes, short limbs |
| Dubowitz syndrome | Unknown; suspected autosomal recessive | Neurobehavioral disabilities (hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattentiveness), epicanthal folds, intellectual disability, microcephaly, short palpebral fissures, short stature, wide-spaced eyes | Broad nasal tip, cryptorchidism, eczema-like skin disorder, high-pitched voice, shallow supraorbital ridge with nasal bridge near level of forehead |
| Fetal hydantoin syndrome | Prenatal exposure to phenytoin (Dilantin) | Depressed nasal bridge, growth deficits, occasional intellectual disability, wide-spaced eyes | Genitourinary defects, hirsutism, hypoplastic fingertips, low hairline, orofacial clefts, short neck, short nose with bowed upper lip |
| Fetal valproate syndrome | Prenatal exposure to valproate (Depacon) | Anteverted nares, epicanthal folds, long philtrum, thin vermilion border, wide-spaced eyes | Cardiac malformations, high forehead, infraorbital crease, neural tube defects, small mouth |
| Noonan syndrome | Autosomal dominant, often mutation in PTPN11 | Epicanthal folds, intellectual disability, low nasal bridge, short stature, wide-spaced eyes | Bleeding diathesis, cryptorchidism, downward-slanting palpebral fissures, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, keratoconus, low posterior hairline, pectus excavatum, protruding upper lip, pulmonary stenosis, webbed neck, wide mouth |
| Phenylalanine embryopathy | Maternal phenylketonuria | Epicanthal folds, growth impairment, intellectual disability, long philtrum, microcephaly, short palpebral fissures, small nose with anteverted nares, thin vermilion border | Cardiac malformations, hypertonia, prominent glabella, round facies |
| Toluene embryopathy | Prenatal exposure to toluene | Growth deficits, midface hypoplasia, short palpebral fissures, smooth philtrum, thin vermilion border | Bifrontal narrowing of the skull, downturned mouth, ear abnormalities, hair pattern abnormalities, large anterior fontanelle, micrognathia |
| Velocardiofacial syndrome | Autosomal dominant with microdeletion in chromosome 22q11 | Intellectual disabilities, psychiatric disorders, small palpebral fissures | Cardiac malformations, cleft palate, long face with prominent nose, transient neonatal hypocalcemia, weak pharyngeal muscles resulting in hypernasal speech |
| Williams syndrome | Heterozygous 7q11.23 deletion, including elastin gene | Anteverted nares, depressed nasal bridge, epicanthal folds, growth impairment, intellectual disability, long philtrum, short nose, short palpebral fissures | Aortic and pulmonary stenosis, connective tissue disorders, endocrine abnormalities, full lips, hoarse voice, hypertension, periorbital fullness, poor to near-normal language skills, renal abnormalities, stellate pattern of iris, systemic arterial stenosis, wide mouth |