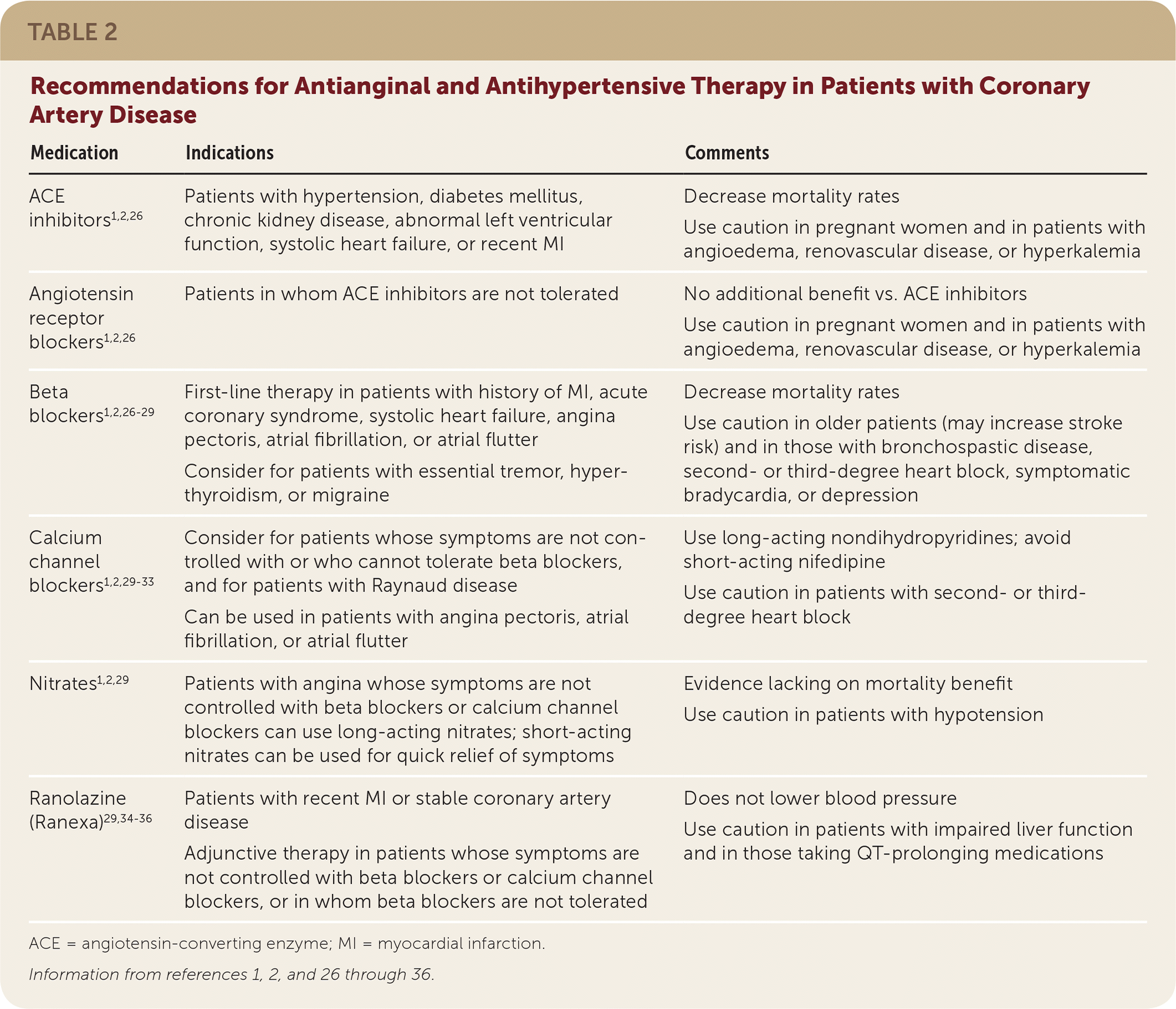
| Medication | Indications | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| ACE inhibitors1,2,26 | Patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, abnormal left ventricular function, systolic heart failure, or recent MI | Decrease mortality rates Use caution in pregnant women and in patients with angioedema, renovascular disease, or hyperkalemia |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers1,2,26 | Patients in whom ACE inhibitors are not tolerated | No additional benefit vs. ACE inhibitors Use caution in pregnant women and in patients with angioedema, renovascular disease, or hyperkalemia |
| Beta blockers1,2,26–29 | First-line therapy in patients with history of MI, acute coronary syndrome, systolic heart failure, angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation, or atrial flutter Consider for patients with essential tremor, hyperthyroidism, or migraine | Decrease mortality rates Use caution in older patients (may increase stroke risk) and in those with bronchospastic disease, second- or third-degree heart block, symptomatic bradycardia, or depression |
| Calcium channel blockers1,2,29–33 | Consider for patients whose symptoms are not controlled with or who cannot tolerate beta blockers, and for patients with Raynaud disease Can be used in patients with angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation, or atrial flutter | Use long-acting nondihydropyridines; avoid short-acting nifedipine Use caution in patients with second- or third-degree heart block |
| Nitrates1,2,29 | Patients with angina whose symptoms are not controlled with beta blockers or calcium channel blockers can use long-acting nitrates; short-acting nitrates can be used for quick relief of symptoms | Evidence lacking on mortality benefit Use caution in patients with hypotension |
| Ranolazine (Ranexa)29,34–36 | Patients with recent MI or stable coronary artery disease Adjunctive therapy in patients whose symptoms are not controlled with beta blockers or calcium channel blockers, or in whom beta blockers are not tolerated | Does not lower blood pressure Use caution in patients with impaired liver function and in those taking QT-prolonging medications |