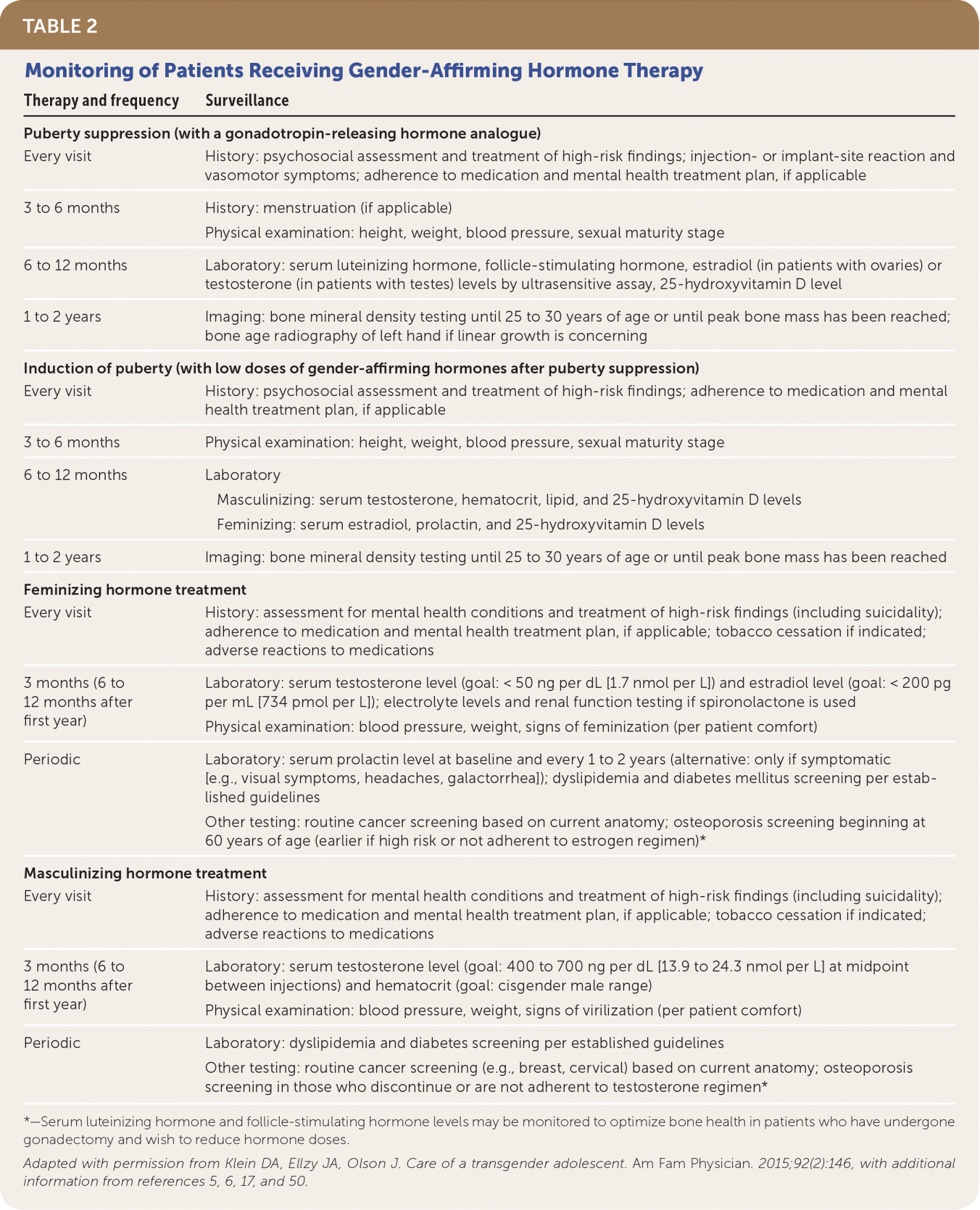
| Puberty suppression (with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue) |
| Every visit | History: psychosocial assessment and treatment of high-risk findings; injection- or implant-site reaction and vasomotor symptoms; adherence to medication and mental health treatment plan, if applicable |
| 3 to 6 months | History: menstruation (if applicable) |
| Physical examination: height, weight, blood pressure, sexual maturity stage |
| 6 to 12 months | Laboratory: serum luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, estradiol (in patients with ovaries) or testosterone (in patients with testes) levels by ultrasensitive assay, 25-hydroxyvitamin D level |
| 1 to 2 years | Imaging: bone mineral density testing until 25 to 30 years of age or until peak bone mass has been reached; bone age radiography of left hand if linear growth is concerning |
| Induction of puberty (with low doses of gender-affirming hormones after puberty suppression) |
| Every visit | History: psychosocial assessment and treatment of high-risk findings; adherence to medication and mental health treatment plan, if applicable |
| 3 to 6 months | Physical examination: height, weight, blood pressure, sexual maturity stage |
| 6 to 12 months | Laboratory Masculinizing: serum testosterone, hematocrit, lipid, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels Feminizing: serum estradiol, prolactin, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
|
| 1 to 2 years | Imaging: bone mineral density testing until 25 to 30 years of age or until peak bone mass has been reached |
| Feminizing hormone treatment |
| Every visit | History: assessment for mental health conditions and treatment of high-risk findings (including suicidality); adherence to medication and mental health treatment plan, if applicable; tobacco cessation if indicated; adverse reactions to medications |
| 3 months (6 to 12 months after first year) | Laboratory: serum testosterone level (goal: < 50 ng per dL [1.7 nmol per L]) and estradiol level (goal: < 200 pg per mL [734 pmol per L]); electrolyte levels and renal function testing if spironolactone is used |
| Physical examination: blood pressure, weight, signs of feminization (per patient comfort) |
| Periodic | Laboratory: serum prolactin level at baseline and every 1 to 2 years (alternative: only if symptomatic [e.g., visual symptoms, headaches, galactorrhea]); dyslipidemia and diabetes mellitus screening per established guidelines |
| Other testing: routine cancer screening based on current anatomy; osteoporosis screening beginning at 60 years of age (earlier if high risk or not adherent to estrogen regimen)* |
| Masculinizing hormone treatment |
| Every visit | History: assessment for mental health conditions and treatment of high-risk findings (including suicidality); adherence to medication and mental health treatment plan, if applicable; tobacco cessation if indicated; adverse reactions to medications |
| 3 months (6 to 12 months after first year) | Laboratory: serum testosterone level (goal: 400 to 700 ng per dL [13.9 to 24.3 nmol per L] at midpoint between injections) and hematocrit (goal: cisgender male range) |
| Physical examination: blood pressure, weight, signs of virilization (per patient comfort) |
| Periodic | Laboratory: dyslipidemia and diabetes screening per established guidelines |
| Other testing: routine cancer screening (e.g., breast, cervical) based on current anatomy; osteoporosis screening in those who discontinue or are not adherent to testosterone regimen* |