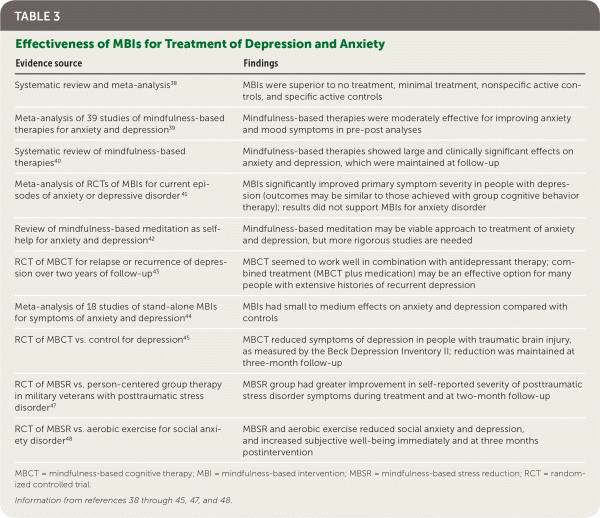
| Systematic review and meta-analysis38 | MBIs were superior to no treatment, minimal treatment, nonspecific active controls, and specific active controls |
| Meta-analysis of 39 studies of mindfulness-based therapies for anxiety and depression39 | Mindfulness-based therapies were moderately effective for improving anxiety and mood symptoms in pre-post analyses |
| Systematic review of mindfulness-based therapies40 | Mindfulness-based therapies showed large and clinically significant effects on anxiety and depression, which were maintained at follow-up |
| Meta-analysis of RCTs of MBIs for current episodes of anxiety or depressive disorder 41 | MBIs significantly improved primary symptom severity in people with depression (outcomes may be similar to those achieved with group cognitive behavior therapy); results did not support MBIs for anxiety disorder |
| Review of mindfulness-based meditation as self-help for anxiety and depression42 | Mindfulness-based meditation may be viable approach to treatment of anxiety and depression, but more rigorous studies are needed |
| RCT of MBCT for relapse or recurrence of depression over two years of follow-up43 | MBCT seemed to work well in combination with antidepressant therapy; combined treatment (MBCT plus medication) may be an effective option for many people with extensive histories of recurrent depression |
| Meta-analysis of 18 studies of stand-alone MBIs for symptoms of anxiety and depression44 | MBIs had small to medium effects on anxiety and depression compared with controls |
| RCT of MBCT vs. control for depression45 | MBCT reduced symptoms of depression in people with traumatic brain injury, as measured by the Beck Depression Inventory II; reduction was maintained at three-month follow-up |
| RCT of MBSR vs. person-centered group therapy in military veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder47 | MBSR group had greater improvement in self-reported severity of posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms during treatment and at two-month follow-up |
| RCT of MBSR vs. aerobic exercise for social anxiety disorder48 | MBSR and aerobic exercise reduced social anxiety and depression, and increased subjective well-being immediately and at three months postintervention |