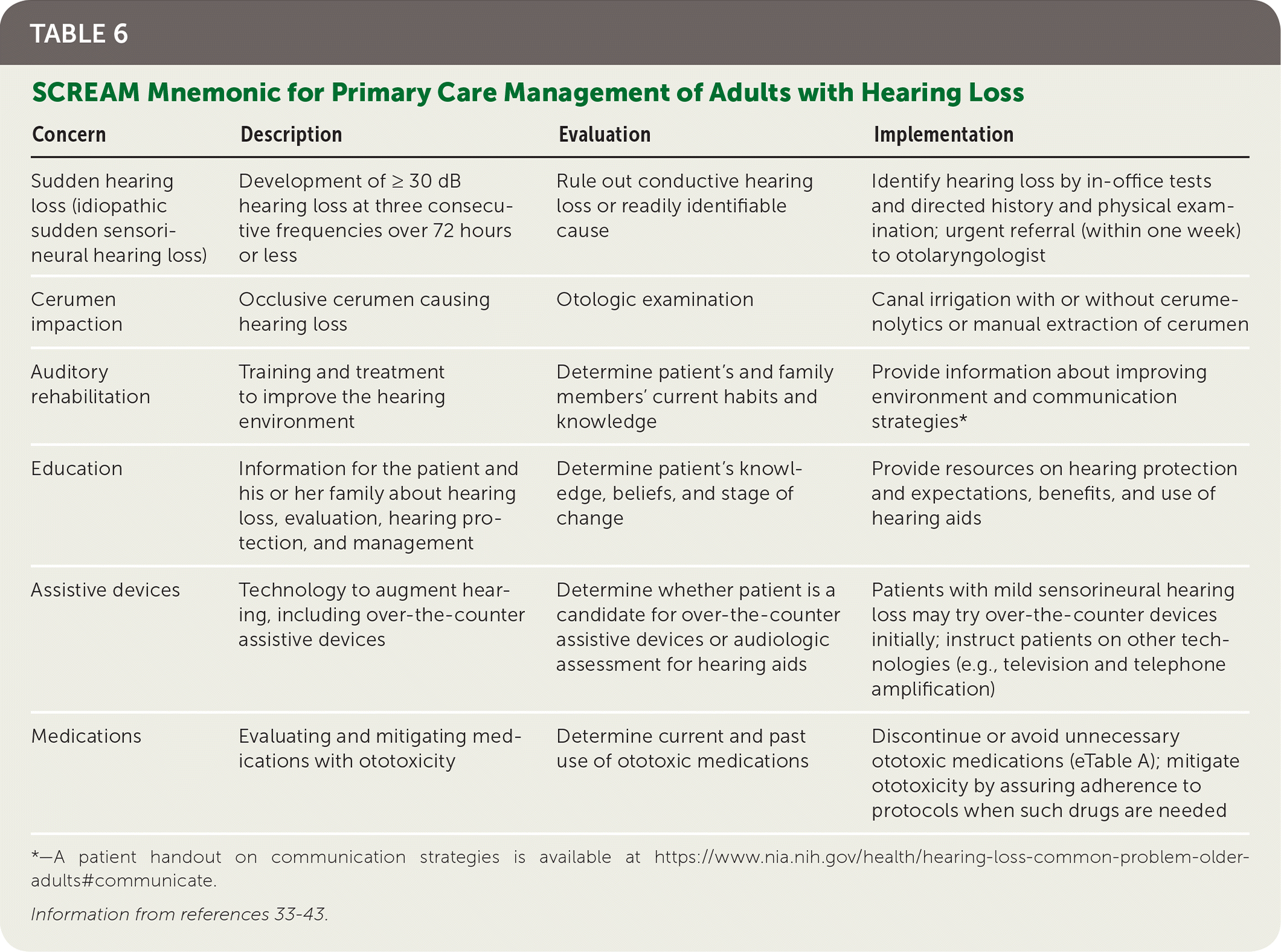
| Sudden hearing loss (idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss) | Development of ≥ 30 dB hearing loss at three consecutive frequencies over 72 hours or less | Rule out conductive hearing loss or readily identifiable cause | Identify hearing loss by in-office tests and directed history and physical examination; urgent referral (within one week) to otolaryngologist |
| Cerumen impaction | Occlusive cerumen causing hearing loss | Otologic examination | Canal irrigation with or without cerumenolytics or manual extraction of cerumen |
| Auditory rehabilitation | Training and treatment to improve the hearing environment | Determine patient's and family members' current habits and knowledge | Provide information about improving environment and communication strategies* |
| Education | Information for the patient and his or her family about hearing loss, evaluation, hearing protection, and management | Determine patient's knowledge, beliefs, and stage of change | Provide resources on hearing protection and expectations, benefits, and use of hearing aids |
| Assistive devices | Technology to augment hearing, including over-the-counter assistive devices | Determine whether patient is a candidate for over-the-counter assistive devices or audiologic assessment for hearing aids | Patients with mild sensorineural hearing loss may try over-the-counter devices initially; instruct patients on other technologies (e.g., television and telephone amplification) |
| Medications | Evaluating and mitigating medications with ototoxicity | Determine current and past use of ototoxic medications | Discontinue or avoid unnecessary ototoxic medications (eTable A); mitigate ototoxicity by assuring adherence to protocols when such drugs are needed |