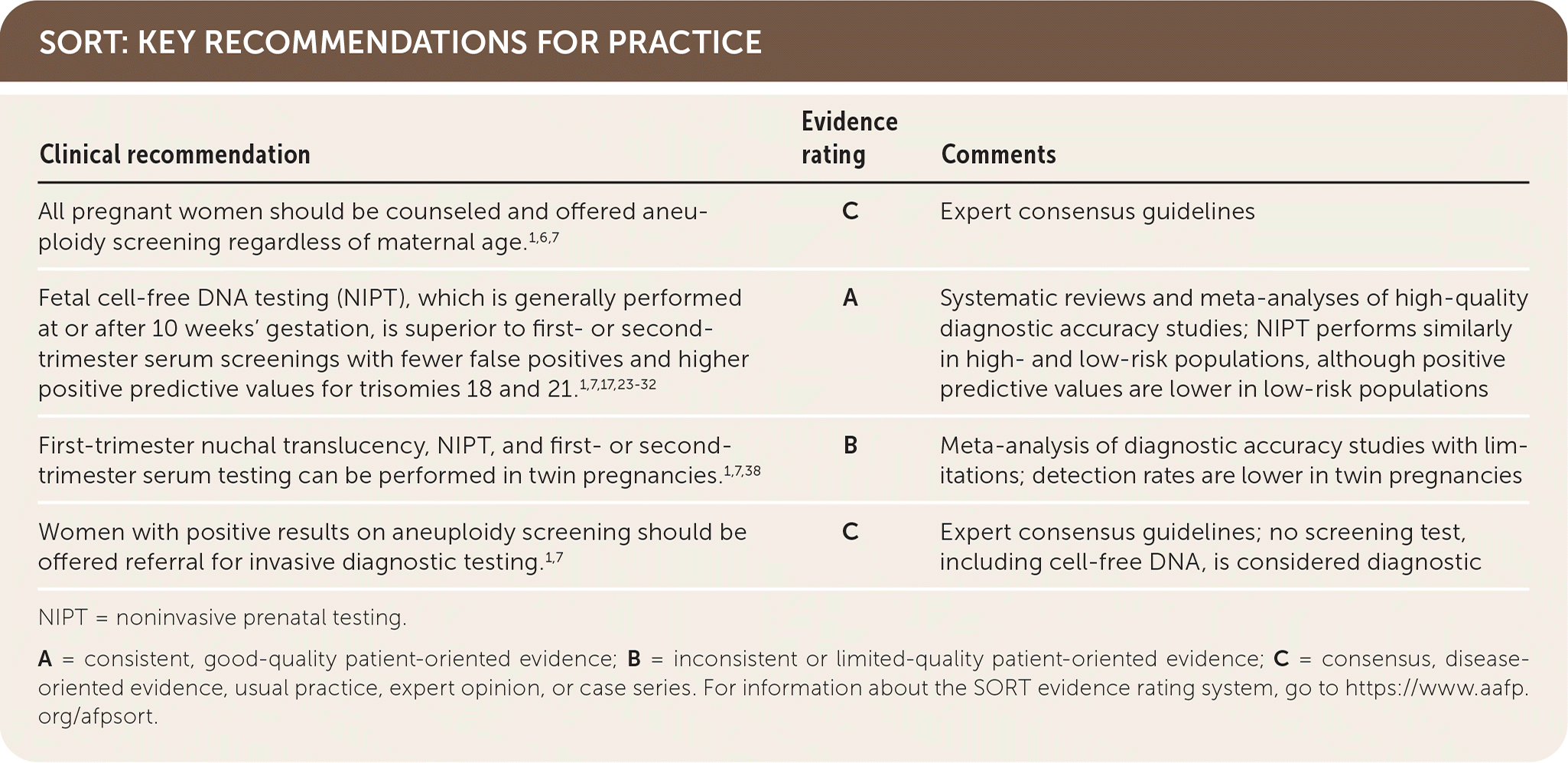
| All pregnant women should be counseled and offered aneuploidy screening regardless of maternal age.1,6,7 |
C |
Expert consensus guidelines |
| Fetal cell-free DNA testing (NIPT), which is generally performed at or after 10 weeks' gestation, is superior to first- or second-trimester serum screenings with fewer false positives and higher positive predictive values for trisomies 18 and 21.1,7,17,23–32 |
A |
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of high-quality diagnostic accuracy studies; NIPT performs similarly in high- and low-risk populations, although positive predictive values are lower in low-risk populations |
| First-trimester nuchal translucency, NIPT, and first- or second-trimester serum testing can be performed in twin pregnancies.1,7,38 |
B |
Meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies with limitations; detection rates are lower in twin pregnancies |
| Women with positive results on aneuploidy screening should be offered referral for invasive diagnostic testing.1,7 |
C |
Expert consensus guidelines; no screening test, including cell-free DNA, is considered diagnostic |