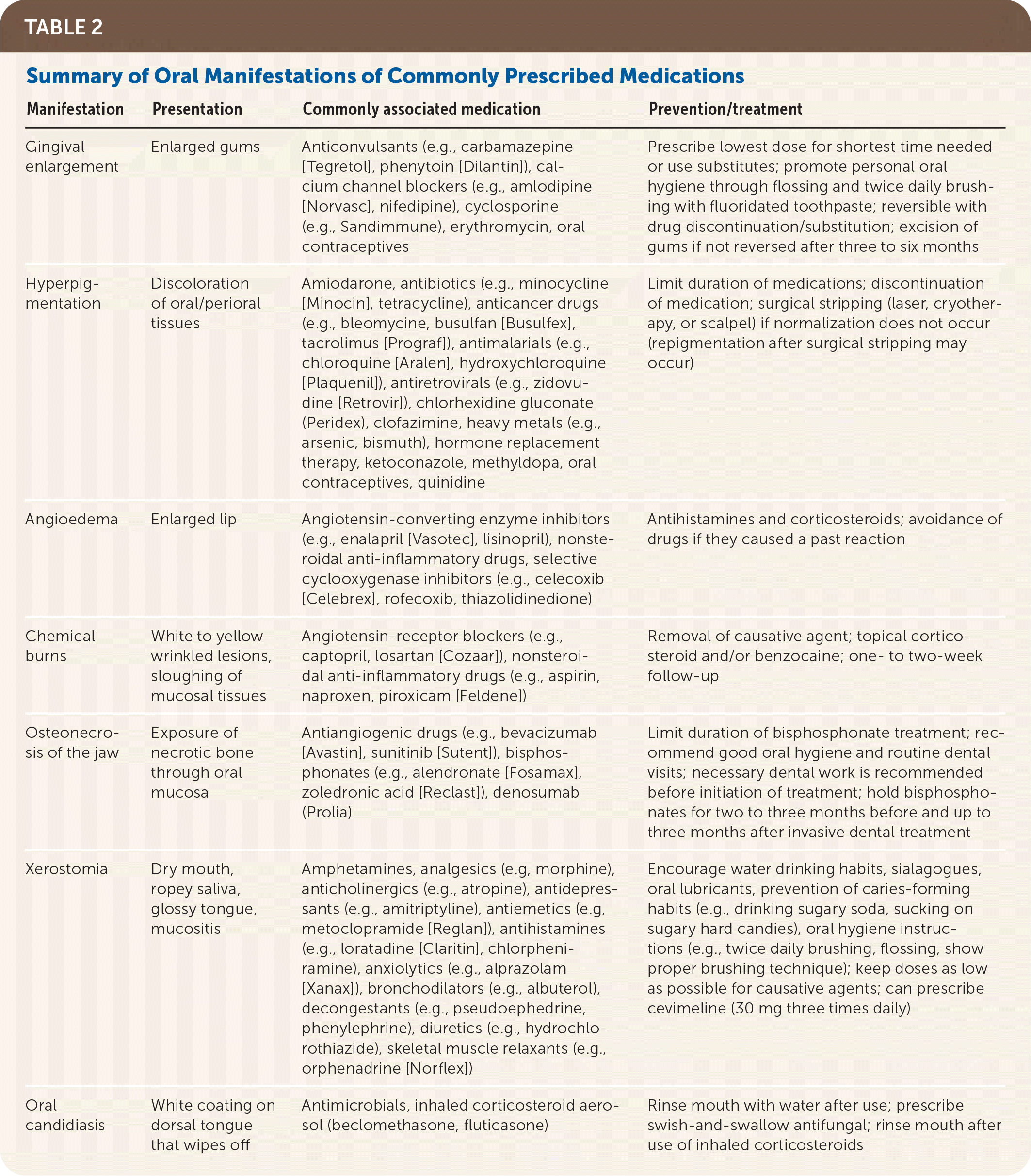
| Gingival enlargement | Enlarged gums | Anticonvulsants (e.g., carbamazepine [Tegretol], phenytoin [Dilantin]), calcium channel blockers (e.g., amlodipine [Norvasc], nifedipine), cyclosporine (e.g., Sandimmune), erythromycin, oral contraceptives | Prescribe lowest dose for shortest time needed or use substitutes; promote personal oral hygiene through flossing and twice daily brushing with fluoridated toothpaste; reversible with drug discontinuation/substitution; excision of gums if not reversed after three to six months |
| Hyperpigmentation | Discoloration of oral/perioral tissues | Amiodarone, antibiotics (e.g., minocycline [Minocin], tetracycline), anticancer drugs (e.g., bleomycine, busulfan [Busulfex], tacrolimus [Prograf]), antimalarials (e.g., chloroquine [Aralen], hydroxychloroquine [Plaquenil]), antiretrovirals (e.g., zidovudine [Retrovir]), chlorhexidine gluconate (Peridex), clofazimine, heavy metals (e.g., arsenic, bismuth), hormone replacement therapy, ketoconazole, methyldopa, oral contraceptives, quinidine | Limit duration of medications; discontinuation of medication; surgical stripping (laser, cryotherapy, or scalpel) if normalization does not occur (repigmentation after surgical stripping may occur) |
| Angioedema | Enlarged lip | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (e.g., enalapril [Vasotec], lisinopril), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, selective cyclooxygenase inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib [Celebrex], rofecoxib, thiazolidinedione) | Antihistamines and corticosteroids; avoidance of drugs if they caused a past reaction |
| Chemical burns | White to yellow wrinkled lesions, sloughing of mucosal tissues | Angiotensin-receptor blockers (e.g., captopril, losartan [Cozaar]), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., aspirin, naproxen, piroxicam [Feldene]) | Removal of causative agent; topical corticosteroid and/or benzocaine; one- to two-week follow-up |
| Osteonecrosis of the jaw | Exposure of necrotic bone through oral mucosa | Antiangiogenic drugs (e.g., bevacizumab [Avastin], sunitinib [Sutent]), bisphosphonates (e.g., alendronate [Fosamax], zoledronic acid [Reclast]), denosumab (Prolia) | Limit duration of bisphosphonate treatment; recommend good oral hygiene and routine dental visits; necessary dental work is recommended before initiation of treatment; hold bisphosphonates for two to three months before and up to three months after invasive dental treatment |
| Xerostomia | Dry mouth, ropey saliva, glossy tongue, mucositis | Amphetamines, analgesics (e.g, morphine), anticholinergics (e.g., atropine), antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline), antiemetics (e.g, metoclopramide [Reglan]), antihistamines (e.g., loratadine [Claritin], chlorpheniramine), anxiolytics (e.g., alprazolam [Xanax]), bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol), decongestants (e.g., pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine), diuretics (e.g., hydrochlorothiazide), skeletal muscle relaxants (e.g., orphenadrine [Norflex]) | Encourage water drinking habits, sialagogues, oral lubricants, prevention of caries-forming habits (e.g., drinking sugary soda, sucking on sugary hard candies), oral hygiene instructions (e.g., twice daily brushing, flossing, show proper brushing technique); keep doses as low as possible for causative agents; can prescribe cevimeline (30 mg three times daily) |
| Oral candidiasis | White coating on dorsal tongue that wipes off | Antimicrobials, inhaled corticosteroid aerosol (beclomethasone, fluticasone) | Rinse mouth with water after use; prescribe swish-and-swallow antifungal; rinse mouth after use of inhaled corticosteroids |