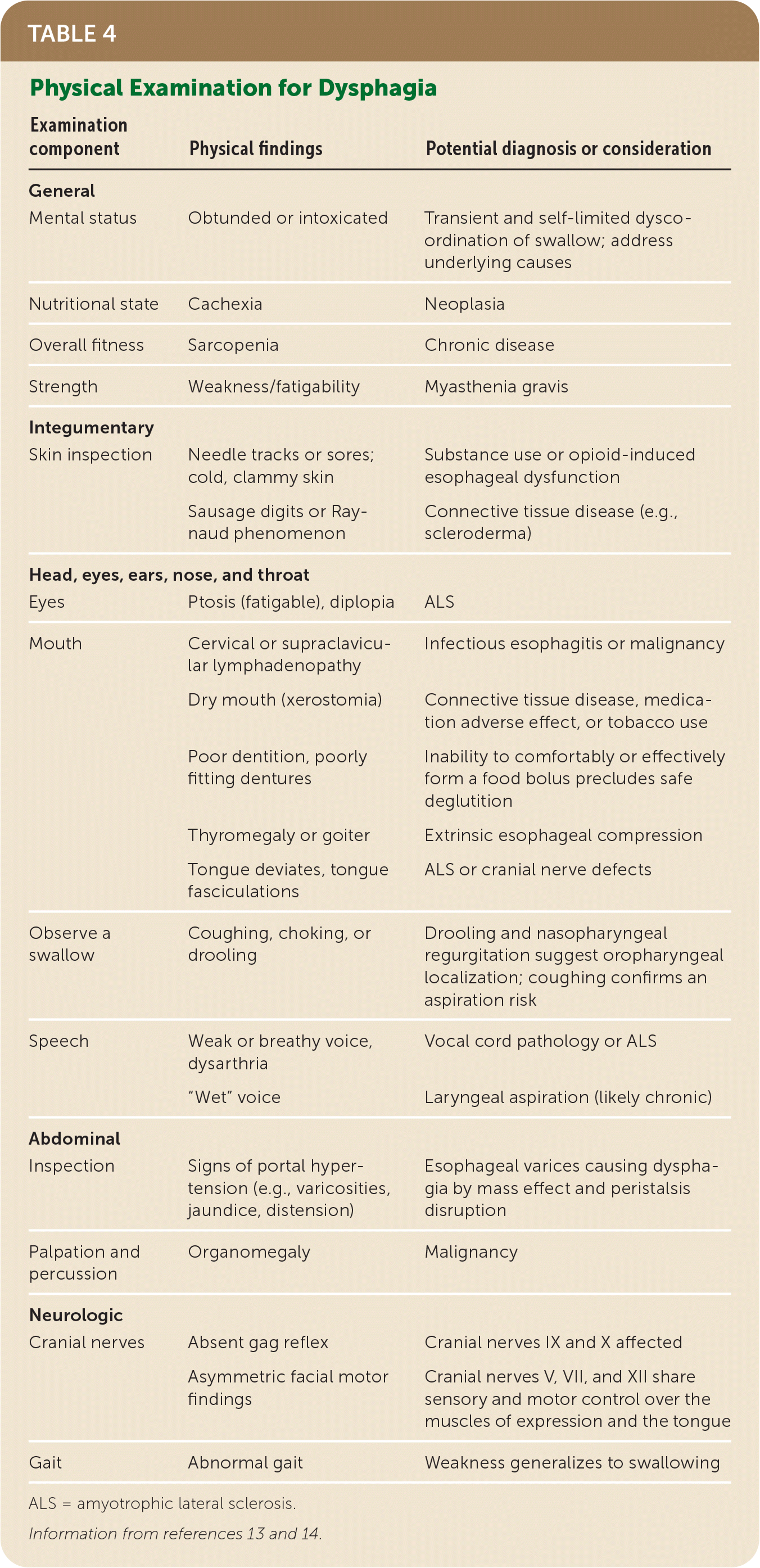
| General | | |
| Mental status | Obtunded or intoxicated | Transient and self-limited dysco-ordination of swallow; address underlying causes |
| Nutritional state | Cachexia | Neoplasia |
| Overall fitness | Sarcopenia | Chronic disease |
| Strength | Weakness/fatigability | Myasthenia gravis |
| Integumentary | | |
| Skin inspection | Needle tracks or sores; cold, clammy skin | Substance use or opioid-induced esophageal dysfunction |
| Sausage digits or Raynaud phenomenon | Connective tissue disease (e.g., scleroderma) |
| Head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat |
| Eyes | Ptosis (fatigable), diplopia | ALS |
| Mouth | Cervical or supraclavicular lymphadenopathy | Infectious esophagitis or malignancy |
| Dry mouth (xerostomia) | Connective tissue disease, medication adverse effect, or tobacco use |
| Poor dentition, poorly fitting dentures | Inability to comfortably or effectively form a food bolus precludes safe deglutition |
| Thyromegaly or goiter | Extrinsic esophageal compression |
| Tongue deviates, tongue fasciculations | ALS or cranial nerve defects |
| Observe a swallow | Coughing, choking, or drooling | Drooling and nasopharyngeal regurgitation suggest oropharyngeal localization; coughing confirms an aspiration risk |
| Speech | Weak or breathy voice, dysarthria | Vocal cord pathology or ALS |
| “Wet” voice | Laryngeal aspiration (likely chronic) |
| Abdominal | | |
| Inspection | Signs of portal hypertension (e.g., varicosities, jaundice, distension) | Esophageal varices causing dysphagia by mass effect and peristalsis disruption |
| Palpation and percussion | Organomegaly | Malignancy |
| Neurologic | | |
| Cranial nerves | Absent gag reflex | Cranial nerves IX and X affected |
| Asymmetric facial motor findings | Cranial nerves V, VII, and XII share sensory and motor control over the muscles of expression and the tongue |
| Gait | Abnormal gait | Weakness generalizes to swallowing |