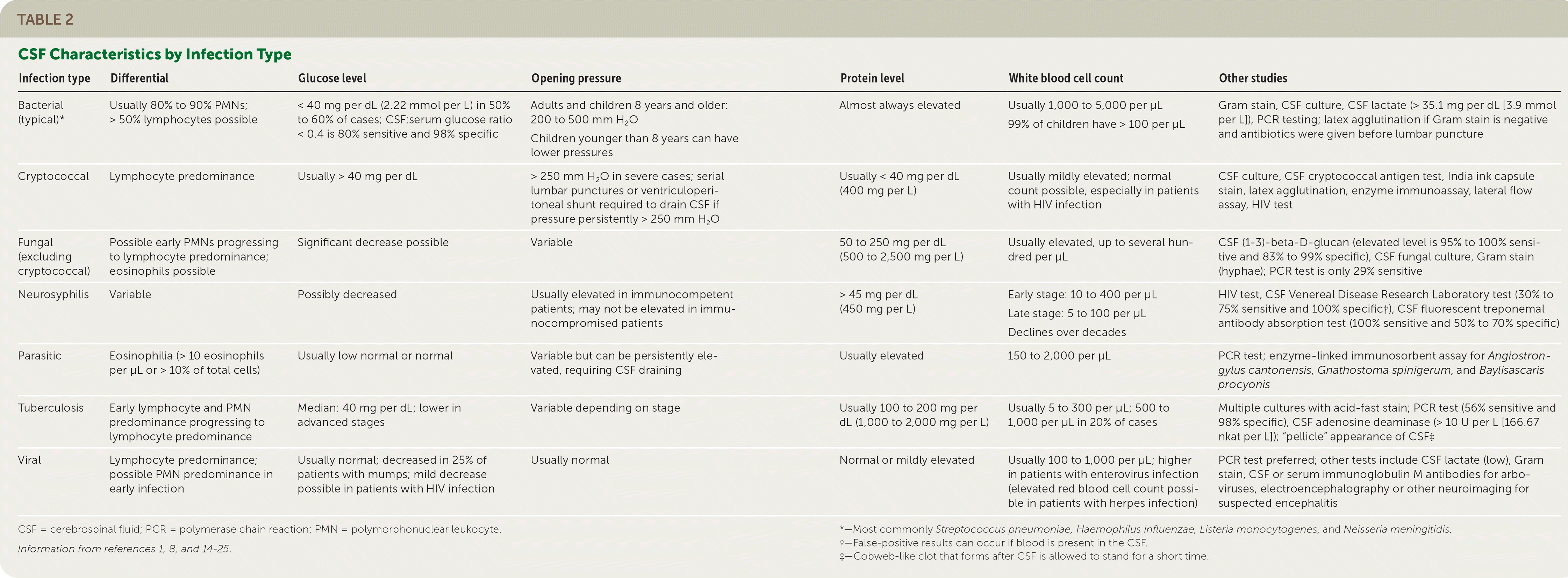
| Infection type | Differential | Glucose level | Opening pressure | Protein level | White blood cell count | Other studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial (typical)* | Usually 80% to 90% PMNs; > 50% lymphocytes possible | < 40 mg per dL (2.22 mmol per L) in 50% to 60% of cases; CSF:serum glucose ratio < 0.4 is 80% sensitive and 98% specific | Adults and children 8 years and older: 200 to 500 mm H2O Children younger than 8 years can have lower pressures | Almost always elevated | Usually 1,000 to 5,000 per μL 99% of children have > 100 per μL | Gram stain, CSF culture, CSF lactate (> 35.1 mg per dL [3.9 mmol per L]), PCR testing; latex agglutination if Gram stain is negative and antibiotics were given before lumbar puncture |
| Cryptococcal | Lymphocyte predominance | Usually > 40 mg per dL | > 250 mm H2O in severe cases; serial lumbar punctures or ventriculoperitoneal shunt required to drain CSF if pressure persistently > 250 mm H2O | Usually < 40 mg per dL (400 mg per L) | Usually mildly elevated; normal count possible, especially in patients with HIV infection | CSF culture, CSF cryptococcal antigen test, India ink capsule stain, latex agglutination, enzyme immunoassay, lateral flow assay, HIV test |
| Fungal (excluding cryptococcal) | Possible early PMNs progressing to lymphocyte predominance; eosinophils possible | Significant decrease possible | Variable | 50 to 250 mg per dL (500 to 2,500 mg per L) | Usually elevated, up to several hundred per μL | CSF (1–3)-beta-D-glucan (elevated level is 95% to 100% sensitive and 83% to 99% specific), CSF fungal culture, Gram stain (hyphae); PCR test is only 29% sensitive |
| Neurosyphilis | Variable | Possibly decreased | Usually elevated in immunocompetent patients; may not be elevated in immunocompromised patients | > 45 mg per dL (450 mg per L) | Early stage: 10 to 400 per μL Late stage: 5 to 100 per μL Declines over decades | HIV test, CSF Venereal Disease Research Laboratory test (30% to 75% sensitive and 100% specific†), CSF fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test (100% sensitive and 50% to 70% specific) |
| Parasitic | Eosinophilia (> 10 eosinophils per μL or > 10% of total cells) | Usually low normal or normal | Variable but can be persistently elevated, requiring CSF draining | Usually elevated | 150 to 2,000 per μL | PCR test; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Gnathostoma spinigerum, and Baylisascaris procyonis |
| Tuberculosis | Early lymphocyte and PMN predominance progressing to lymphocyte predominance | Median: 40 mg per dL; lower in advanced stages | Variable depending on stage | Usually 100 to 200 mg per dL (1,000 to 2,000 mg per L) | Usually 5 to 300 per μL; 500 to 1,000 per μL in 20% of cases | Multiple cultures with acid-fast stain; PCR test (56% sensitive and 98% specific), CSF adenosine deaminase (> 10 U per L [166.67 nkat per L]); “pellicle” appearance of CSF‡ |
| Viral | Lymphocyte predominance; possible PMN predominance in early infection | Usually normal; decreased in 25% of patients with mumps; mild decrease possible in patients with HIV infection | Usually normal | Normal or mildly elevated | Usually 100 to 1,000 per μL; higher in patients with enterovirus infection (elevated red blood cell count possible in patients with herpes infection) | PCR test preferred; other tests include CSF lactate (low), Gram stain, CSF or serum immunoglobulin M antibodies for arboviruses, electroencephalography or other neuroimaging for suspected encephalitis |