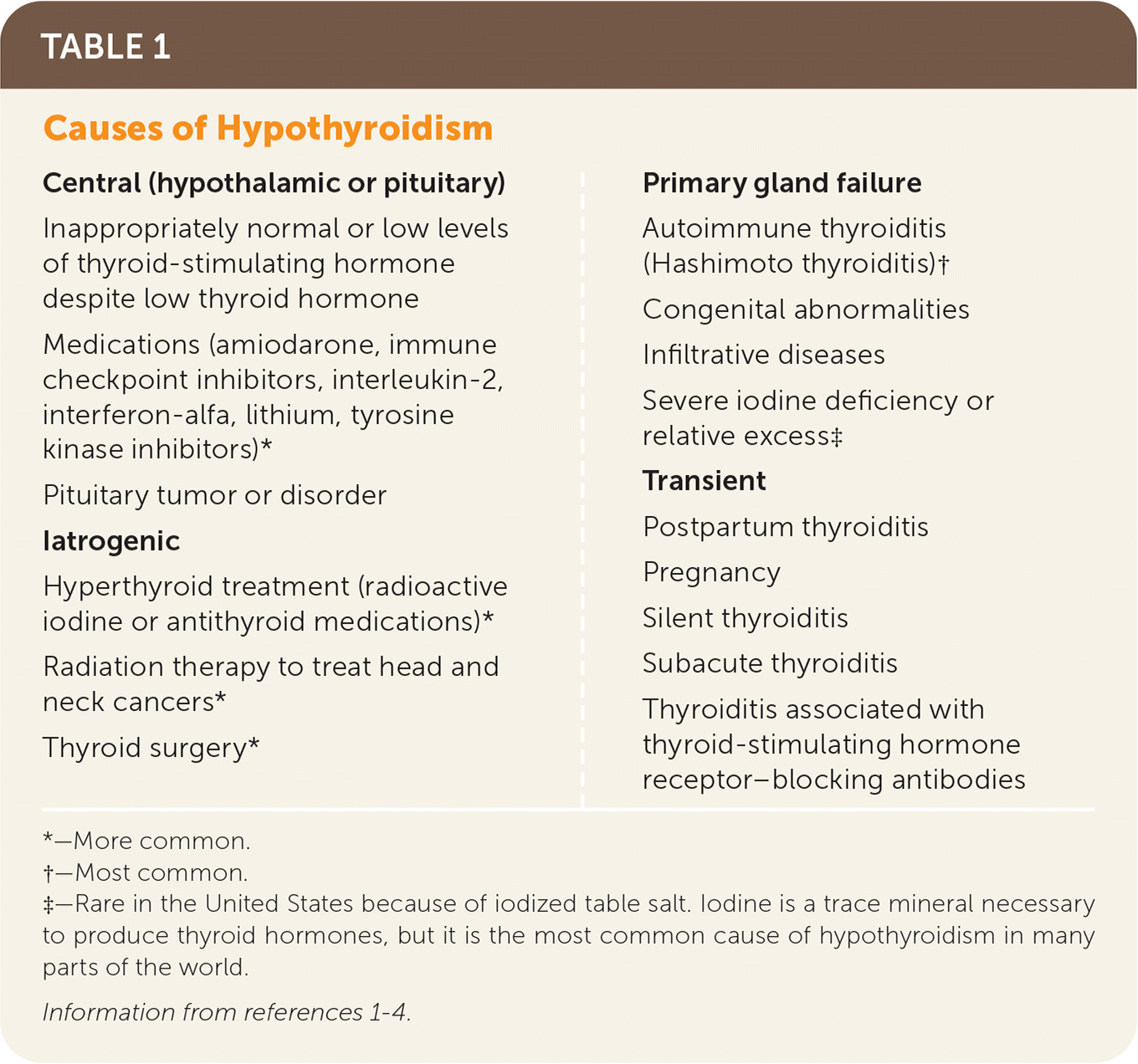
| Central (hypothalamic or pituitary) Inappropriately normal or low levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone despite low thyroid hormone Medications (amiodarone, immune checkpoint inhibitors, interleukin-2, interferon-alfa, lithium, tyrosine kinase inhibitors)* Pituitary tumor or disorder Iatrogenic Hyperthyroid treatment (radioactive iodine or antithyroid medications)* Radiation therapy to treat head and neck cancers* Thyroid surgery* Primary gland failure Autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto thyroiditis)† Congenital abnormalities Infiltrative diseases Severe iodine deficiency or relative excess‡ Transient Postpartum thyroiditis Pregnancy Silent thyroiditis Subacute thyroiditis Thyroiditis associated with thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor–blocking antibodies |