
Am Fam Physician. 2021;104(2):119
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
To the Editor: An 84-year-old patient with a history of tobacco use, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension presented to our office for shortness of breath and diarrhea. The patient had been experiencing fecal incontinence, pain with defecation, and bloody stools for the past three years. More recent symptoms included loss of appetite, weight loss, and fatigue. One year ago, the patient was diagnosed with hemorrhoids and prescribed a topical ointment for relief.
A physical examination was notable for a large perianal mass (Figure 1). Laboratory findings included anemia, hematuria, proteinuria, and an elevated carcinoembryonic antigen level. Computed tomography of the pelvis showed enlarged right inguinal and left perirectal lymph nodes, rectal wall thickening with fat stranding, and potential invasion of the right levator ani muscle, causing suspicion for a locally advanced neoplasm. Computed tomography of the abdomen revealed a 1-cm nodular density in the liver that could be peritoneal metastasis. A biopsy showed an extensive high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion with focal changes that may represent early microinvasion. The patient was diagnosed with squamous cell carcinoma of the anus and treated with surgical debulking of the anal mass, followed by chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
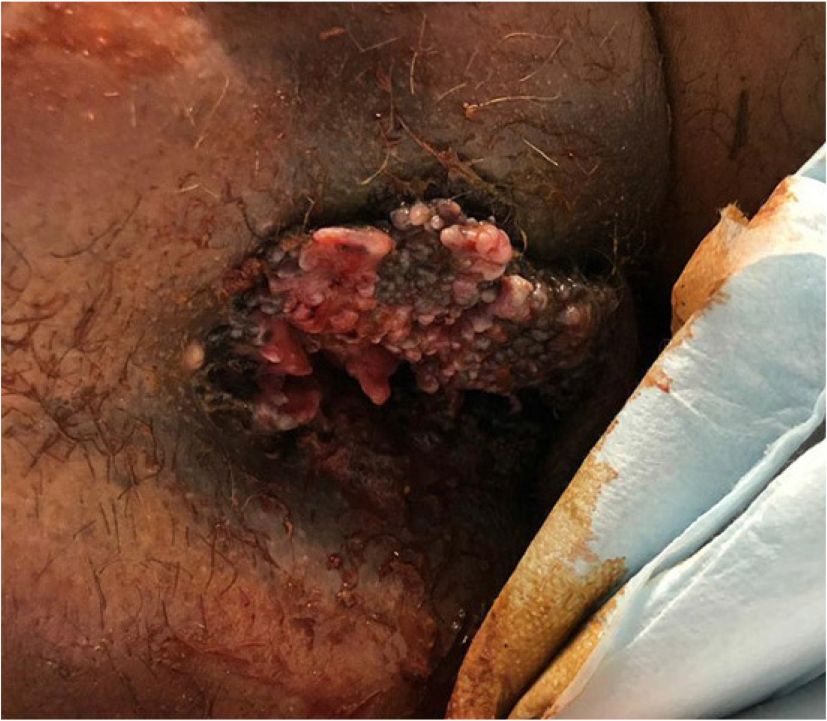
Anal cancer is a rare malignancy with 9,090 new cases diagnosed annually in the United States and an increasing incidence of 2.7% per year.1 In 2020, there were an estimated 1,350 deaths from anal cancer.2 Most anal cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. The most common risk factor for developing anal squamous cell carcinoma is human papillomavirus infection. Additional risk factors include immunosuppression, a history of sexually transmitted infection, and tobacco use.3
Early symptoms of anal cancer can be difficult to distinguish from benign anorectal disorders such as hemorrhoids, condylomas, and anal fissures. In one study, primary care physicians misdiagnosed anal malignancies as hemorrhoids in 27% of first visits, delaying appropriate diagnosis and treatment.4 To decrease delays, physicians should maintain a high index of suspicion with a low threshold to evaluate patients at risk for anal cancer. Efforts to prevent anal cancer should include universal human papillomavirus vaccination in childhood and education of patients at high risk.
