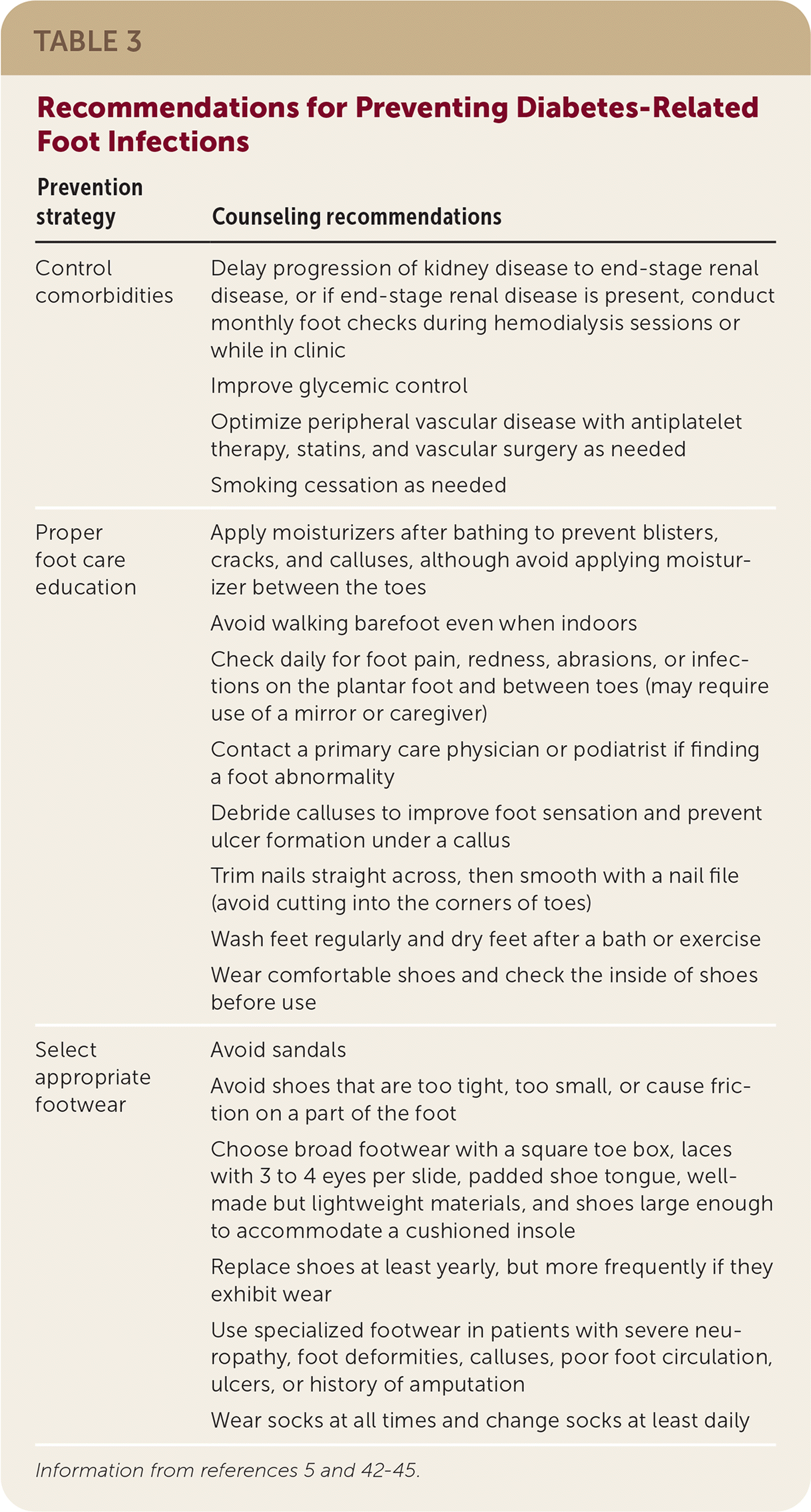
| Control comorbidities | Delay progression of kidney disease to end-stage renal disease, or if end-stage renal disease is present, conduct monthly foot checks during hemodialysis sessions or while in clinic |
| Improve glycemic control |
| Optimize peripheral vascular disease with antiplatelet therapy, statins, and vascular surgery as needed |
| Smoking cessation as needed |
| Proper foot care education | Apply moisturizers after bathing to prevent blisters, cracks, and calluses, although avoid applying moisturizer between the toes |
| Avoid walking barefoot even when indoors |
| Check daily for foot pain, redness, abrasions, or infections on the plantar foot and between toes (may require use of a mirror or caregiver) |
| Contact a primary care physician or podiatrist if finding a foot abnormality |
| Debride calluses to improve foot sensation and prevent ulcer formation under a callus |
| Trim nails straight across, then smooth with a nail file (avoid cutting into the corners of toes) |
| Wash feet regularly and dry feet after a bath or exercise |
| Wear comfortable shoes and check the inside of shoes before use |
| Select appropriate footwear | Avoid sandals |
| Avoid shoes that are too tight, too small, or cause friction on a part of the foot |
| Choose broad footwear with a square toe box, laces with 3 to 4 eyes per slide, padded shoe tongue, well-made but lightweight materials, and shoes large enough to accommodate a cushioned insole |
| Replace shoes at least yearly, but more frequently if they exhibit wear |
| Use specialized footwear in patients with severe neuropathy, foot deformities, calluses, poor foot circulation, ulcers, or history of amputation |
| Wear socks at all times and change socks at least daily |