
Am Fam Physician. 2023;108(6):621-622
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
A 32-year-old woman with a history of hypothyroidism presented to the emergency department after two days of worsening facial swelling and associated pruritus. The swelling began after resolution of a five-day episode of sinus congestion and severe pharyngitis while visiting family in another state. Her facial symptoms started with redness and left periorbital swelling (Figure 1) and gradually progressed to generalized facial swelling.
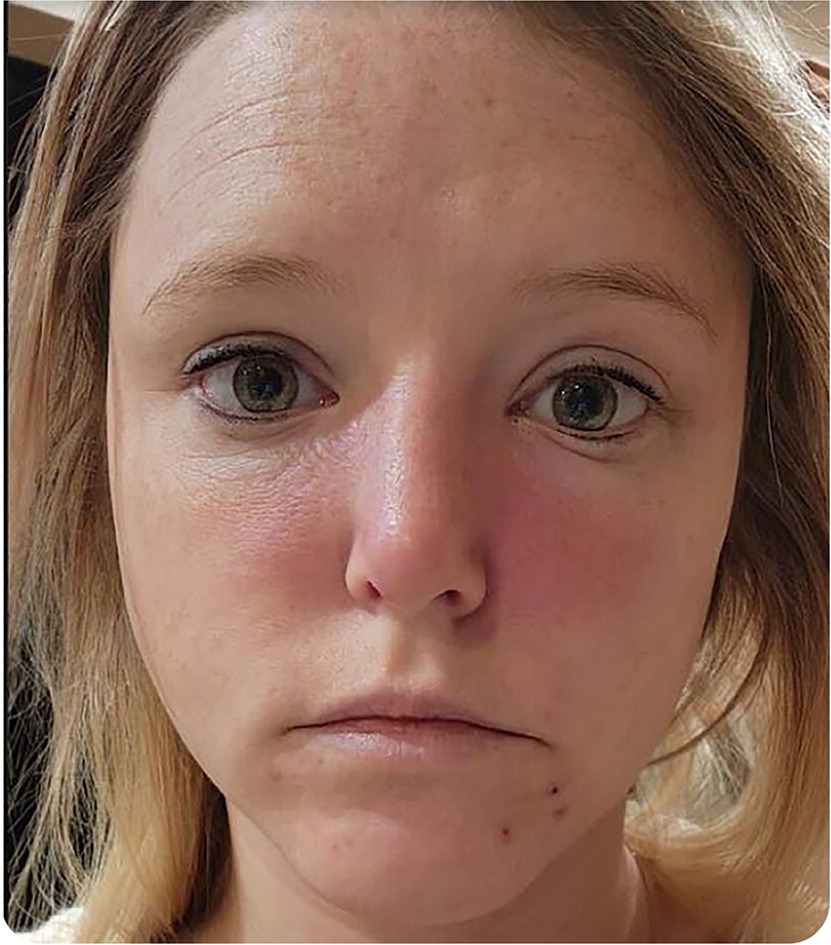
The patient’s family physician treated her with amoxicillin/clavulanate and a steroid. However, her symptoms worsened, and she went to the emergency department. She tested positive for group A streptococcal infection and COVID-19. The facial swelling continued to increase, and she returned to the emergency department the next day.
Physical examination revealed bilateral peri-orbital edema that was worse on the right side and mild facial erythema that had spread overnight (Figure 2).
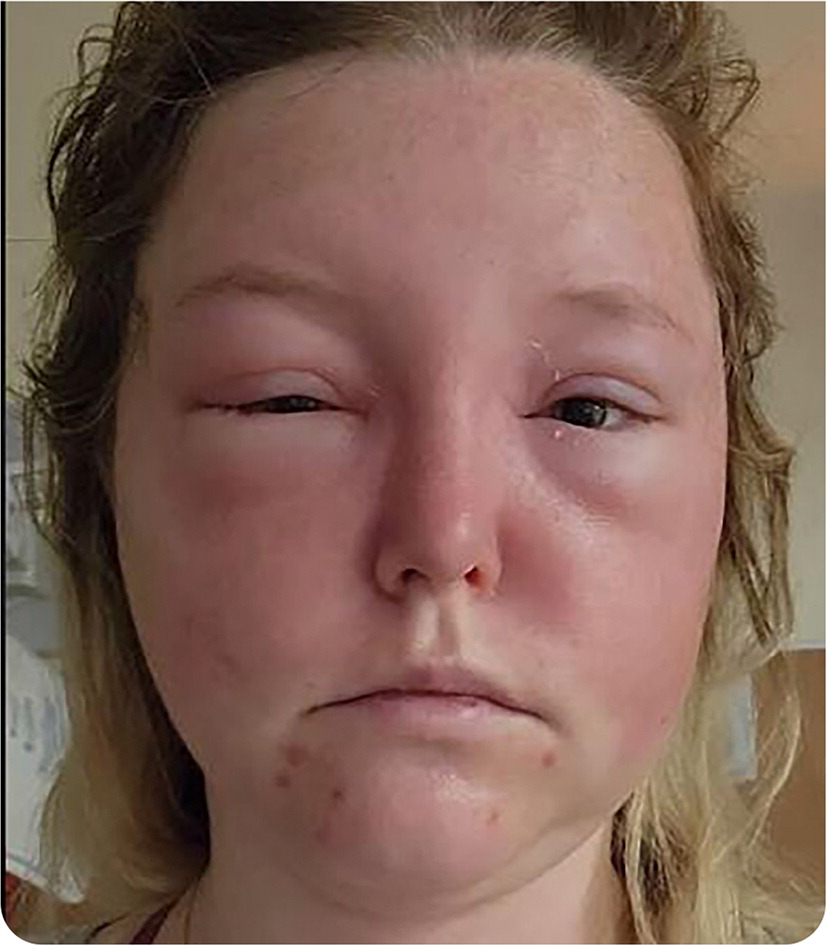
Question
Which one of the following is likely causing this patient’s symptoms?
A. Cellulitis.
B. COVID-19.
C. Myxedema.
D. Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis.
E. Scombroid poisoning.
Discussion
The answer is B: COVID-19. In addition to the typical pulmonary and upper respiratory tract findings, COVID-19 is associated with many other signs and symptoms, including anosmia, swelling, and discoloration of the toes. Several dermatologic symptoms have been reported, including rashes, blisters, and petechiae. Urticaria and angioedema can also occur, although they are less common.1–4 The proposed mechanism for urticaria related to COVID-19 is via the angiotensin-converting enzyme II, which deactivates angiotensin I and II. The interaction of SARS-CoV-2 with angiotensin-converting enzyme II leads to reduced enzymatic activity and increased activity of angiotensin II.
The timing of this patient’s symptoms was consistent with reports from other patients, including the onset of facial swelling five days after the first upper respiratory tract symptoms. Case reports have described different treatment regimens for these symptoms, typically antihistamines alone or with steroids.3,4 The skin manifestations are likely secondary to a systemic inflammatory response after the deactivation of angiotensin-converting enzyme II by SARS-CoV-2; the complement system is activated, which leads to degranulation of mast cells.1
The patient’s symptoms rapidly improved within 15 hours of admission. She responded well to three days of scheduled histamine H1 and H2 blockers, and her facial symptoms resolved within one week.
Cellulitis is characterized by spreading erythema with associated edema, warmth, and tenderness. Facial cellulitis warrants evaluation for orbital involvement, which is a medical emergency. Antibiotics that cover gram-positive organisms, such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, are typically effective.
Myxedema often occurs in patients with long-standing hypothyroidism and can be precipitated by infection. Altered mental status, electrolyte imbalance, generalized edema, bradycardia, hypothermia, and hypotension are common symptoms and often require critical care and admission to the intensive care unit.5 Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is effective.
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is a nephritic syndrome that presents one to two weeks after group A streptococcal throat infection, with associated signs such as hematuria, oliguria, and hypertension. The condition is an immune response to the streptococcal infection and causes renal damage. It is more common in children. Although poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis is self-limiting, with resolution in six to eight weeks, hypertension and edema can be treated with salt and water restriction, with the addition of loop diuretics and/or antihypertensive medications if needed.6
Scombroid poisoning is a histaminic reaction that occurs several hours after consuming fresh, canned, or smoked fish, such as tuna and mackerel, that is contaminated with high levels of histamine. Symptoms include erythema, rash, palpitations, dizziness, and urticaria. It is treated with antihistamines.7
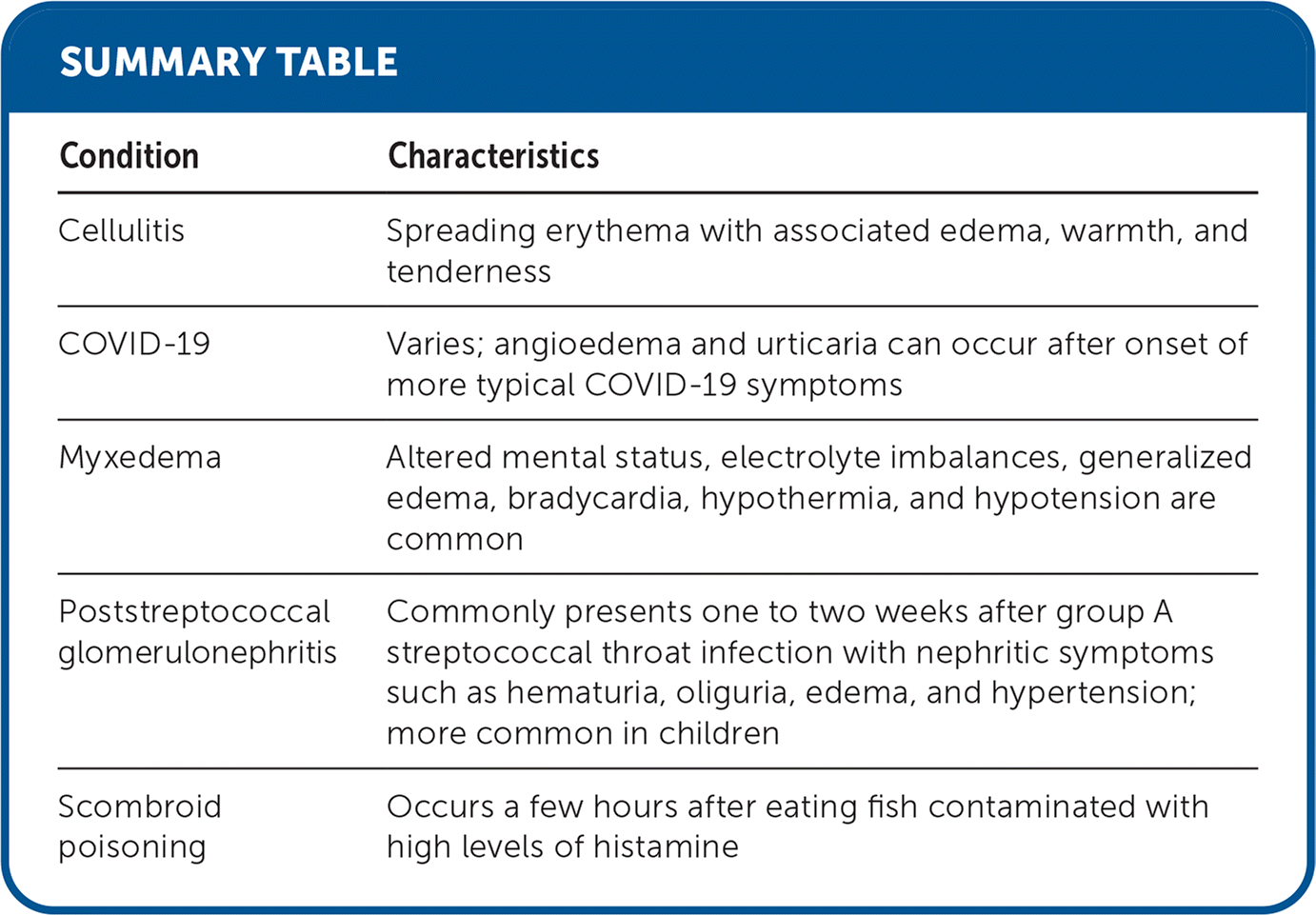
| Condition | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Cellulitis | Spreading erythema with associated edema, warmth, and tenderness |
| COVID-19 | Varies; angioedema and urticaria can occur after onset of more typical COVID-19 symptoms |
| Myxedema | Altered mental status, electrolyte imbalances, generalized edema, bradycardia, hypothermia, and hypotension are common |
| Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis | Commonly presents one to two weeks after group A streptococcal throat infection with nephritic symptoms such as hematuria, oliguria, edema, and hypertension; more common in children |
| Scombroid poisoning | Occurs a few hours after eating fish contaminated with high levels of histamine |
The opinions and assertions contained herein are those of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of the U.S. Air Force, U.S. Department of Defense, or U.S. government.
