
Am Fam Physician. 2025;111(6):493-494
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
DETAILS FOR THIS REVIEW
Study Population: 1,962 adults with initial and recurrent Clostridioides difficile infection enrolled in 74 randomized controlled trials
Efficacy End Points: Sustained symptomatic cure
Harm End Points: Drug-related adverse events
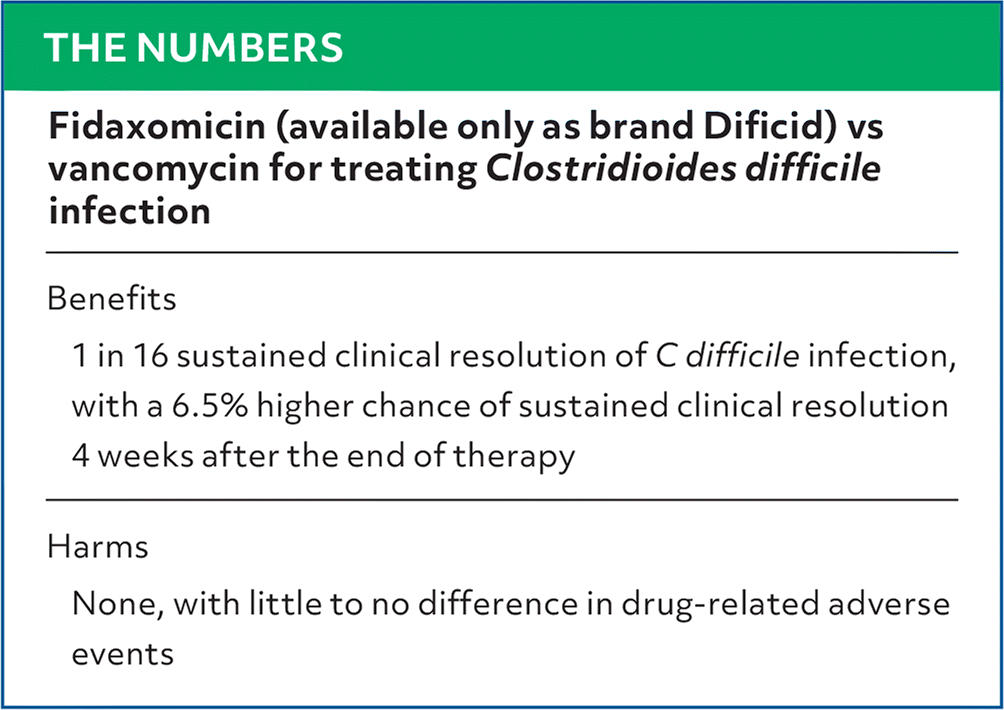
| Fidaxomicin (available only as brand Dificid) vs vancomycin for treating Clostridioides difficile infection |
| Benefits |
| 1 in 16 sustained clinical resolution of C difficile infection, with a 6.5% higher chance of sustained clinical resolution 4 weeks after the end of therapy |
Harms |
| None, with little to no difference in drug-related adverse events |
Narrative: The number of C difficile infections is rising globally, particularly in US health care settings, where these infections were responsible for 29,000 deaths in 2011 and cost $5.4 billion in 2014.1 Between 2001 and 2012, the incidence of C difficile infections increased by 46%, and recurrent infections rose by 189% in the United States. In 2020, the overall incidence of C difficile infections in the United States was 101.3 cases per 100,000 people.2 Despite decades of relying on metronidazole (Flagyl) and vancomycin as standard treatments, their limitations in achieving sustained cures and addressing the escalating severity of C difficile infections underscore the urgent need for innovative therapies.3
Subscribe
From $180- Immediate, unlimited access to all AFP content
- More than 125 CME credits/year
- Print delivery available
Issue Access
$59.95- Immediate, unlimited access to this issue's content
- CME credits
- Print delivery available
