
Am Fam Physician. 2002;65(5):841-849
Osteoarthritis is a common rheumatologic disorder. It is estimated that 40 million Americans and 70 to 90 percent of persons older than 75 years are affected by osteoarthritis. Although symptoms of osteoarthritis occur earlier in women, the prevalence among men and women is equal. In addition to age, risk factors include joint injury, obesity, and mechanical stress. The diagnosis is largely clinical because radiographic findings do not always correlate with symptoms. Knowledge of the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease process aids in prevention and management. Acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications remain first-line drugs. Agents such as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and sodium hyaluronate joint injections offer new treatment alternatives. Complementary medication use has also increased. Therapeutic goals include minimizing symptoms and improving function.
Men and women are equally affected, but symptoms occur earlier and appear to be more severe in women.2 Common synonyms for osteoarthritis include osteoarthrosis and degenerative joint disease. Osteoarthritis is not an inevitable consequence of aging. It is an acquired degenerative process that can be managed effectively by family physicians.
Etiology
The exact etiology of osteoarthritis is unknown. Multiple factors (e.g., heredity, trauma, and obesity) interact to cause this disorder. Any event that changes the environment of the chondrocyte has the potential to cause osteoarthritis (Table 1).3 Although usually occurring as a primary disorder, osteoarthritis can occur secondary to other processes.
| Age older than 50 |
| Crystals in joint fluid or cartilage |
| High bone mineral density |
| History of immobilization |
| Injury to the joint |
| Joint hypermobility or instability |
| Obesity (weight-bearing joints) |
| Peripheral neuropathy |
| Prolonged occupational or sports stress |
Pathogenesis
Although the term “osteoarthritis” is often used,“osteoarthrosis” may be more appropriate.4 Degenerative changes are the predominant factor contributing to disability.4 In joints with osteoarthritis, inflammation may be present; however, it is usually mild and involves only the periarticular tissues.
The pathophysiology involves a combination of mechanical, cellular, and biochemical processes. The interaction of these processes leads to changes in the composition and mechanical properties of the articular cartilage. Cartilage is composed of water, collagen, and proteoglycans. In healthy cartilage, continual internal remodeling occurs as the chondrocytes replace macromolecules lost through degradation. This process becomes disrupted in osteoarthritis, leading to increased degenerative changes and an abnormal repair response.
Joint use provides physiologic stimulation through the noncellular matrix that helps direct chondrocyte synthetic activity and internal tissue remodeling. Prolonged decreased joint use leads to changes in the matrix composition, resulting in subsequent loss of tissue function. The resumption of joint use can help restore the properties of the joint toward normal.5–7
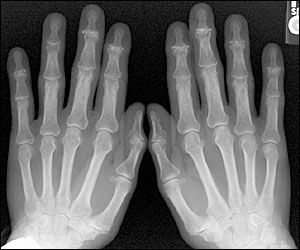
The strong association between age and osteoarthritis may be best explained by age-related changes in the matrix composition and a decrease in chondrocyte function and responsiveness to stimuli. These changes can interfere with continued internal remodeling, maintenance of the tissue, and loss of cartilage. This leads to an increased risk for cartilage degradation and injury to include surface defects in the articular cartilage. The abnormal repair process leads to the formation of osteophytes and subchondral cysts as the disease progresses. These changes are evident on radiographs (Figure 1).
Prevention
Primary and secondary prevention should be emphasized in the management of patients with osteoarthritis. Maintaining appropriate body weight may be the single most important factor in preventing osteoarthritis from occurring in weight-bearing joints.8 A relationship has been shown between weight loss and a reduction in the risk of developing osteoarthritis.9
The role of exercise in the development of osteoarthritis has been difficult to ascertain for a variety of reasons. Results of studies10–12 have demonstrated radiographic evidence of osteoarthritis in former athletes. In some of these studies,10,11,13 the symptoms were greater in the athletes than in the control subjects, while in other studies, the athletes were either asymptomatic or had symptoms similar to those of the control subjects. However, results from case-control and long-term prospective studies of runners have demonstrated that distance running does not increase the risk for osteoarthritis.13–15 Nevertheless, it is clear that a history of significant injury, particularly of the knee or hip, is a risk factor for the development of osteoarthritis.16 A history of menisectomy is also considered a risk factor; therefore, sports that have a high risk for injury may lead to a greater risk for the development of osteoarthritis.17,18 High-risk sports include collision sports and those with a high-loading or torsional impact.
In general, mild-to-moderate activity is not likely to lead to osteoarthritis in normal joints. Persons with previous joint injury or surgery, or abnormal joint alignment, are likely to be at a higher risk for developing osteoarthritis.
Vitamin D intake may also affect osteoarthritis. Low dietary intake or serum levels of vitamin D are associated with increased rates of progression.19
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of osteoarthritis is largely made by obtaining a detailed history and conducting a complete physical examination. Ancillary diagnostic tests may occasionally be necessary when the diagnosis remains uncertain. The usual presenting symptom is pain involving one or only a few joints. Joint involvement is usually symmetric. Morning joint stiffness that usually resolves within 30 minutes or occurs with mild-to-moderate activity is also common. As the disease progresses, prolonged joint stiffness and joint enlargement are evident. Crepitus, or a grating sensation in the joint, is a late manifestation. Limitation of joint movement may be due to flexion contractures or mechanical obstructions.
Secondary causes (Table 2)20 should be considered when making decisions about having ancillary tests performed. Further evaluation is indicated when the diagnosis remains uncertain, response to therapy is not as expected, or significant clinical changes occur. Clinically indicated laboratory work may include tests for erythrocyte sedimentation rate and rheumatoid factor. Synovial fluid analysis may be conducted to help exclude other diagnoses. In osteoarthritis, the white blood cell count is usually less than 500 cells per mm2 (0.5 × 109 per L) and is composed predominantly of mononuclear cells. In inflammatory aspirates, the white blood cell count is usually greater than 2,000 cells per mm2 (2.0 × 109 per L), and the predominant cell type is usually the neutrophil.
| Calcium deposition |
| Congenital or developmental |
| Endocrine |
| Genetic defects |
| Infectious |
| Metabolic |
| Neuropathic |
| Post-traumatic |
| Rheumatologic diseases (other than primary osteoarthritis) |
Radiographs can provide objective evidence of the disease. Findings consistent with osteoarthritis include presence of joint space narrowing, osteophyte formation, pseudocyst in subchondral bone, and increased density of subchondral bone. The absence of radiographic changes, however, does not exclude the diagnosis of osteoarthritis. Many patients with radiographic changes consistent with osteoarthritis are asymptomatic or do not exhibit any disability, suggesting that the presence of radiographic changes in the absence of symptoms should not lead to the diagnosis of osteoarthritis.3,6,10 The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification of osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee are shown in Tables 3,21 4,22 and 5,23 and it should be noted that except for osteoarthritis of the hand, all of these criteria include radiographic findings.21–25 In large joints, radiographs can exclude other causes of joint pain.
Radiographs are not required for every person who presents with symptoms consistent with osteoarthritis. Patients whose clinical history or course suggests other etiologies should undergo radiographic evaluation. This includes patients with trauma, joint pain at night, progressive joint pain (without prior radiography), significant family history of inflammatory arthritis, and children younger than 18 years.
Treatment
The primary goals of treatment are improved function and quality of life. Treatment should be tailored to the needs of the individual patient. Patient education, rehabilitation, exercise, modification of activities of daily living, pharmacotherapy, alternative medicine and surgery are all treatment modalities that should be considered.
Patients should be thoroughly educated about the natural course of osteoarthritis. Their role in the management of the disease is critical, and a proper understanding will allow appropriate expectations of treatment to be established. Family physicians should be familiar with pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic treatment modalities to maximize effective utilization and a thorough understanding of the short- and long-term complications and cost. Some treatment modalities (e.g., heat, ice, and electrical stimulation) may make the patient feel better but may not be sufficient alone. Most modalities and therapies do not change the outcome.
Combinations of treatment modalities for symptom control are better than isolated therapy for symptom relief. The proper mix of modalities and exercises is based on individualized treatment goals agreed on by the family physician and the patient.
Patients with osteoarthritis often demonstrate significant disability.26 The symptoms and disability may limit their ability to participate in regular physical activity, and they may also be reluctant to exercise for fear that it will exacerbate their symptoms. It has been shown that aerobic and resistance exercises do not exacerbate symptoms in patients with osteoarthritis and do not appear to produce or exacerbate joint symptoms in persons without osteoarthritis.27,28 Results of randomized studies29–32 have demonstrated that aerobic and resistance exercises produce only modest gains in measures of improving disability, physical performance, and symptoms. Participation in regular exercise appears to be safe and effective in managing the symptoms and disability associated with osteoarthritis. Exercise programs such as those sponsored by the Arthritis Foundation should be recommended to patients with osteoarthritis. It is important for patients to note that any lifestyle changes they make are not curative and must be continued throughout life.
Pain is the primary symptom of osteoarthritis, and multiple medications are available to relieve pain and improve function33 (Table 6). The choice of a pain-control medication must be individualized, prescribing medications with the best side effect profile first and adding other pain-control medications as indicated. In comparison with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, in a dosage of 1 g four times daily, is considered an initial drug of choice.34 NSAIDs and aspirin have analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties but also have adverse effects on the stomach and kidney, especially in elderly patients.35 The cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors celecoxib (Celebrex) and rofecoxib (Vioxx) cause fewer gastrointestinal side effects and, while thought to be no more effective then other NSAIDs, can be considered for use in patients with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding or those who may be taking certain medications (e.g., warfarin [Coumadin] or oral steroids). The COX-2 inhibitors have not been shown to be safer than aceta-minophen.36,37 Cost should be a consideration in treatment decisions. In addition, there is accumulating data about the side effects of the COX-2 inhibitors. Early evidence indicated that side effects might vary between the medications in this class.38
| Acetaminophen | |
| NSAIDs | |
| Salicylates (aspirin) | |
| Propionic acids (ibuprofen [Motrin], naproxen [Anaprox], oxaprozin [Daypro], flurbiprofen [Ansaid], ketoprofen [Orudis]) | |
| Acetic acids (diclofenac [Voltarin], tolmetin [Tolectin], etodolac [Lodine], sulindac [Clinoril], indomethacin [Indocin]) | |
| Oxicams (piroxicam [Feldone]) | |
| Cyclooxygenase inhibitors (celecoxib [Celebrex], rofecoxib [Vioxx]) | |
| Irritants/counter-irritants | |
| Capsaicin 0.025 percent cream | |
| Hyaluronic acids | |
| Hylan G-F 20 (Synvisc) | |
| Sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan) | |
| Glucocorticoids | |
| Prednisone* | |
Sodium hyaluronate (Synvisc, Hyalgan) is indicated only for the treatment of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. This treatment is an alternative to consider in patients who do not respond to NSAID therapy or who have a history of gastric ulcer disease, with some evidence suggesting symptomatic and functional improvement following a series of weekly injections.39
Intra-articular steroid injections are another treatment option but should not, in most circumstances, be administered more than three to four times per year.25 Results of a multicenter, randomized study demonstrated that intra-articular knee injections significantly reduced pain for up to four weeks. No functional improvement was noted compared to placebo. Results from this same study revealed that joint lavage significantly relieved pain for up to 24 weeks.40 The effects of steroid injection and joint lavage on pain relief were additive, but neither procedure significantly improved functional status. Topical capsaicin cream should be considered for adjunctive treatment of focal joint pain.41
Alternative medicines (e.g., glucosamine sulfate, chondroitin sulfate) in the prevention and treatment of osteoarthritis continue to receive coverage in the media; however, research evaluating their efficacy and potential benefits is incomplete. Glucosamine sulfate, a popular treatment for osteoarthritis, is an amino-monosaccharide and a substrate of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans. These are substrates of hyaluronic acid, a major component of joint fluid. Glucosamine is often taken alone or in combination with chondroitin sulfate. Results from some studies have shown glucosamine to be as effective as ibuprofen in relieving the pain of osteoarthritis. Chondroitin sulfate also has demonstrated efficacy in improving the symptoms of osteoarthritis.42–44 A full review of alternative treatment modalities is beyond the scope of this article.
Family physicians should be aware of commonly used alternative treatments. This allows monitoring of potential benefits and possible interactions with other medications. An awareness of the medical literature also permits physicians to provide evidence-based recommendations for individual patient therapeutic trials. Alternative care should be critically assessed like any other medical care. It is through such assessments that a medication such as capsaicin, which is derived from the red pepper plant, has become part of conventional medicine.
Therapeutic Considerations
This article briefly covers multiple areas (pathology, diagnosis, radiographic findings, and treatment) related to osteoarthritis. An emphasis is placed on pathology to focus consideration on diagnostic and therapeutic choices. Radiographic findings are included as part of the American College of Rheumatology diagnostic criteria for osteoarthritis.21–23 Because of low correlation with disease, radiographic studies beyond plain radiographs should only be obtained if the physician is looking for specific disease sequelae. Laboratory evaluation should be conducted only as clinically indicated.
New advances in therapy should be critically reviewed and compared to older treatments. Short- and long-term effects and outcomes should be compared. Because no medication has been shown to be curative, the risk and benefits of therapy should be clearly explained to patients. COX-2 agents are a potentially useful therapeutic addition; however, they have not been shown to be more efficacious than NSAIDs or acetaminophen, do not appear to be safer than acetaminophen, and are more expensive. Alternative treatments abound, but many have no proven effectiveness.
In patients whose symptoms persist despite appropriate treatment (patient education, drug intervention, exercise, modification of activities of daily living, and physical therapy), referral to an orthopedic surgeon should be considered.