Am Fam Physician. 2019;99(11):712
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Clinical Question
What are the best screening tools for the evaluation and diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
Evidence-Based Answer
The Conners Abbreviated Symptom Questionnaire has the best combination of positive and negative likelihood ratios (eTable A). (Strength of Recommendation [SOR]: B, based on a meta-analysis of observational studies.) The Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Teacher and Parent Rating Scales also have moderate sensitivity and specificity in elementary school–aged children. (SOR: B, based on a single cohort study.)
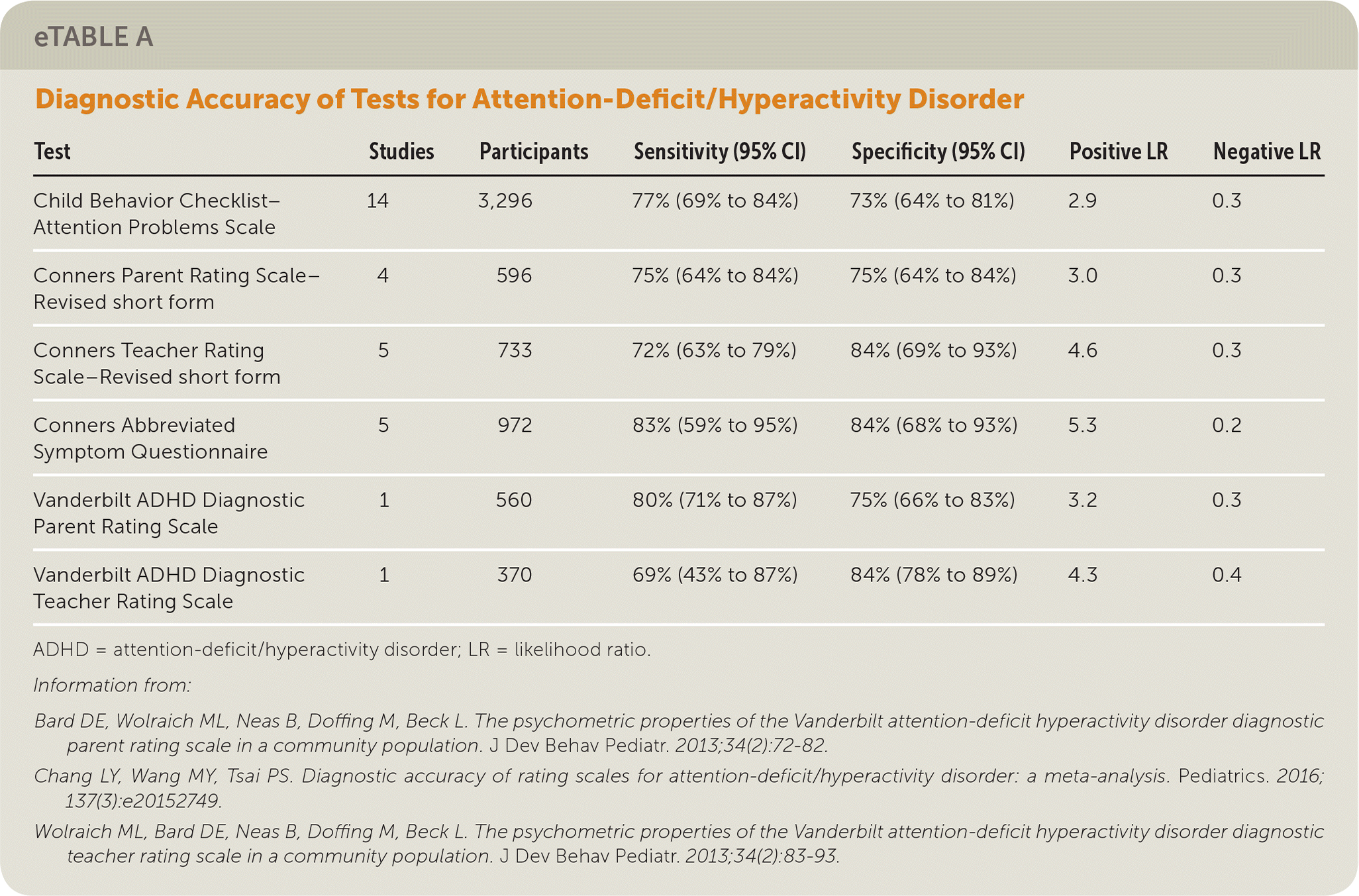
| Test | Studies | Participants | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | Positive LR | Negative LR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Child Behavior Checklist–Attention Problems Scale | 14 | 3,296 | 77% (69% to 84%) | 73% (64% to 81%) | 2.9 | 0.3 |
| Conners Parent Rating Scale–Revised short form | 4 | 596 | 75% (64% to 84%) | 75% (64% to 84%) | 3.0 | 0.3 |
| Conners Teacher Rating Scale–Revised short form | 5 | 733 | 72% (63% to 79%) | 84% (69% to 93%) | 4.6 | 0.3 |
| Conners Abbreviated Symptom Questionnaire | 5 | 972 | 83% (59% to 95%) | 84% (68% to 93%) | 5.3 | 0.2 |
| Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Parent Rating Scale | 1 | 560 | 80% (71% to 87%) | 75% (66% to 83%) | 3.2 | 0.3 |
| Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Teacher Rating Scale | 1 | 370 | 69% (43% to 87%) | 84% (78% to 89%) | 4.3 | 0.4 |
Evidence Summary
A 2016 meta-analysis of 25 cross-sectional, cohort, and case-control studies evaluated the accuracy of the Child Behavior Checklist–Attention Problem Scale (CBCL-AP) and three versions of the Conners Rating Scales–Revised (CRS-R) for diagnosing ADHD in children and adolescents three to 18 years of age.1 Patients had all three types of ADHD: predominantly hyperactive/impulsive, predominantly inattentive, and combined. In addition to the CBCL-AP (14 studies) and the three versions of the CRS-R, the Conners Parent Rating Scale–Revised short form (four studies), the Conners Teacher Rating Scale–Revised short form (five studies), and the Conners Abbreviated Symptom Questionnaire (five studies) were evaluated. The reference standard was a clinical examination performed by a qualified professional using diagnostic criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM), 3rd or 4th ed., and corresponding diagnosis codes from the International Classification of Diseases, 9th or 10th revision. All scales had moderate sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative likelihood ratios for diagnosing ADHD. The Conners Abbreviated Symptom Questionnaire may be the most effective diagnostic tool for ADHD because of its brevity and high diagnostic accuracy, and the CBCL-AP could be used for more comprehensive assessments.
A 2013 cohort study compared the Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Parent/Teacher Rating Scales with a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview using DSM-IV criteria.2,3 Participants were selected from a random sample of elementary school students in urban, suburban, and rural school districts in Oklahoma. The Vanderbilt parent and teacher scales were moderately sensitive and specific for diagnosing ADHD.
Copyright © Family Physicians Inquiries Network. Used with permission.