
Am Fam Physician. 2021;103(8):507-509
Related editorial: Key Recommendations on Managing Dyslipidemia for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction: Stopping Where the Evidence Does
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Key Points for Practice
• In primary prevention, moderate-dose statins are recommended when treatment is indicated.
• In secondary prevention, moderate-dose statins are recommended with intensification by increasing statin dose, adding ezetimibe, or adding a PCSK9 inhibitor in higher-risk patients.
• Because cholesterol values are stable over 10 years, new measurements are not needed for each risk assessment.
From the AFP Editors
Cardiovascular disease caused by atherosclerosis causes significant morbidity and mortality, which can be improved by controlling risk factors through lifestyle interventions and lipid-lowering medications. The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and Department of Defense (VA/DoD) have updated recommendations for evaluation and management of dyslipidemia to prevent cardiovascular disease (Figure 1).
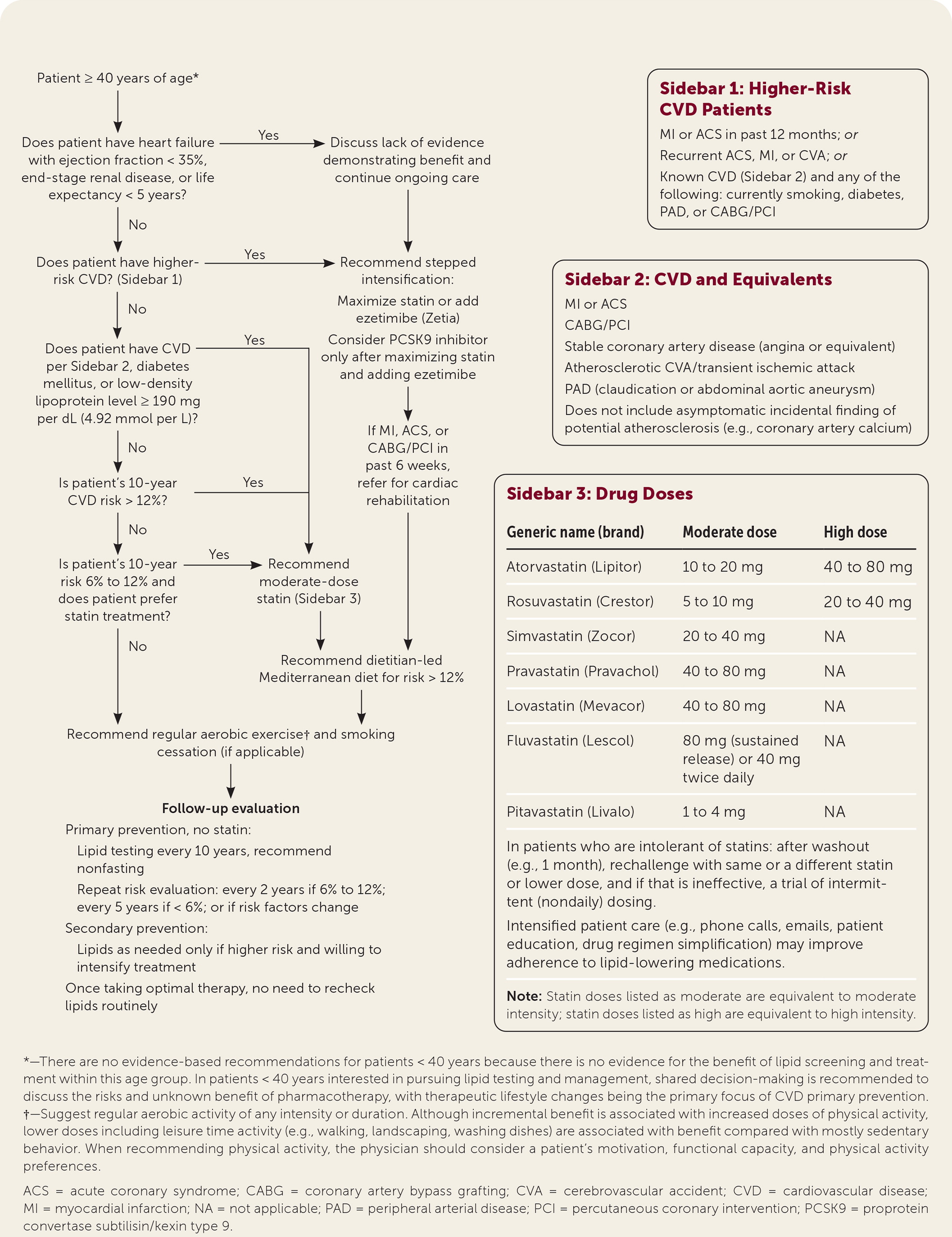
Primary Prevention
Without known cardiovascular disease, treatment decisions should be based on estimated 10-year risk calculators such as the pooled cohort equations (http://tools.acc.org/ASCVD-Risk-Estimator-Plus). Treatment is recommended at a 10-year risk of 12%, which matches the populations that experienced benefit in clinical trials. People with diabetes mellitus and/or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels of at least 190 mg per dL (4.92 mmol per L) are also at high risk and should be offered treatment regardless of estimated risk. Shared decision-making is recommended with 10-year risk between 6% and 12%, which represents populations less studied in clinical trials.
Moderate-dose statins are the sole medication recommended for primary prevention. The group recommends against high-dose statins, citing lack of additional benefit and an increase in risks. The guideline does not suggest one statin over another. Because moderate dosing is recommended for all patients, the guideline does not recommend titrating dosage to a specific cholesterol level. There is no evidence that ezetimibe (Zetia), proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors, icosapent ethyl, fibrates, bempedoic acid, or niacin is beneficial in primary prevention.
Secondary Prevention
Patients with known coronary artery disease are at high enough risk to require treatment. Moderate-dose statins are the baseline in this group because no other treatment has a greater impact on mortality. The guideline recommends considering more intense treatment, especially in higher-risk patients. High-dose statin therapy reduced major cardiovascular events in the higher-risk patients studied. Adding ezetimibe to moderate- or high-dose statins reduces non-fatal cardiovascular events to a similar extent as high-dose statins. PCSK9 inhibitors also decrease nonfatal cardiovascular events in high-risk individuals on maximal tolerated therapy to a similar extent. Because of high cost and uncertain long-term safety, PCSK9 inhibitors are recommended only after increasing statin dose and adding ezetimibe. Icosapent ethyl appears to reduce cardiovascular events and mortality with elevated triglyceride levels, although the single trial results are controversial because of high rates of cardiovascular events in the control group. Target cholesterol levels are not recommended to guide these decisions.
Diet
One diet has clinical evidence of decreasing risk in primary and secondary prevention. A dietitian-led Mediterranean diet decreases rates of cardiovascular events, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality.
Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation has been studied extensively but does not reduce cardiovascular risk. Fiber, ginger, green tea, garlic, and red yeast rice have been suggested for dyslipidemia, but evidence is insufficient for recommendation.
Physical Activity
Physical activity is proven to reduce cardiovascular events. The greatest benefit occurs in sedentary people who pursue limited aerobic physical activity, so no specific target duration is specified.
In the eight weeks following a cardiovascular event or revascularization, structured cardiac rehabilitation has a number needed to treat of 31 to prevent death and myocardial infarction over 10 years.
Risk Assessment and Monitoring
In primary prevention, risk assessment in untreated patients is recommended every two years when risk is 6% to 12% and every five years when risk is less than 6%. This risk assessment can use cholesterol levels obtained in the previous 10 years because cholesterol values have been proven stable, with short-term variation more likely because of error. Risk stratification is not improved by additional tests, including coronary artery calcium, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, and ankle-brachial index.
For patients taking statins, monitoring response by measuring lipid levels is generally unnecessary because titration to a specific cholesterol level is of uncertain benefit. Cholesterol measurement for patients receiving secondary prevention should be limited to only those high-risk patients in whom icosapent ethyl or PCSK9 inhibitors are being considered.
Excluded Populations
This guideline focuses on adults 40 years and older. Younger patients have not been studied and generally are at very low risk. Patients with heart failure with an ejection fraction of less than 35% or a life expectancy less than five years are excluded because of limited data that show an absence of benefit from lipid-lowering therapies. Patients with genetic dyslipidemia conditions were also excluded because of limited evidence to guide treatment.
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Department of Defense, Department of Veterans Affairs, or the U.S. government.
Guideline source: U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs and Department of Defense
Evidence rating system used? Yes
Systematic literature search described? Yes
Guideline developed by participants without relevant financial ties to industry? Yes
Recommendations based on patient-oriented outcomes? Yes
Available at: https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/lipids/
Editor's Note: Drs. Arnold and Buelt are members of the 2020 VA/DoD Dyslipidemia Guideline Working Group.
