Am Fam Physician. 2021;104(5):476-483
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
Medical consultations before dental procedures present opportunities to integrate cross-disciplinary preventive care and improve patient health. This article presents recommendations related to patients with certain medical conditions who are planning to undergo common dental procedures, such as cleanings, extractions, restorations, endodontic procedures, abscess drainage, and mucosal biopsies. Specifically, prophylactic antibiotics are not recommended for preventing prosthetic joint infections or infectious endocarditis except in certain circumstances. Anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapies typically should not be suspended for common dental treatments. Elective dental care should be avoided for six weeks after myocardial infarction or bare-metal stent placement or for six months after drug-eluting stent placement. It is important that any history of antiresorptive or antiangiogenic therapies be communicated to the dentist. Ascites is not an indication for initiating prophylactic antibiotics before dental treatment, and acetaminophen is the analgesic of choice for patients with liver dysfunction or cirrhosis who abstain from alcohol. Nephrotoxic medications should be avoided in patients with chronic kidney disease, and the consultation should include the patient's glomerular filtration rate. Although patients undergoing chemotherapy may receive routine dental care, it should be postponed when possible in those currently undergoing head and neck radiation therapy. A detailed history of head and neck radiation therapy should be provided to the dentist. Multimodal, nonnarcotic analgesia is recommended for managing acute dental pain.
Integrating patients' medical and dental health care is important because there are correlations between periodontal disease and some medical conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, hypertension, kidney disease, and rheumatoid arthritis.1–7 Medical consultations before dental procedures present opportunities to integrate cross-disciplinary preventive care and provide recommendations for treatment considerations before, during, and after a dental visit. Although dentists are ultimately responsible for the treatments they provide, they need the patient's complete medical information and often consult physicians when planning common dental procedures, such as cleanings, extractions, restorations (e.g., fillings, crowns, bridges, implants), endodontic procedures, abscess drainage, or mucosal biopsies.8
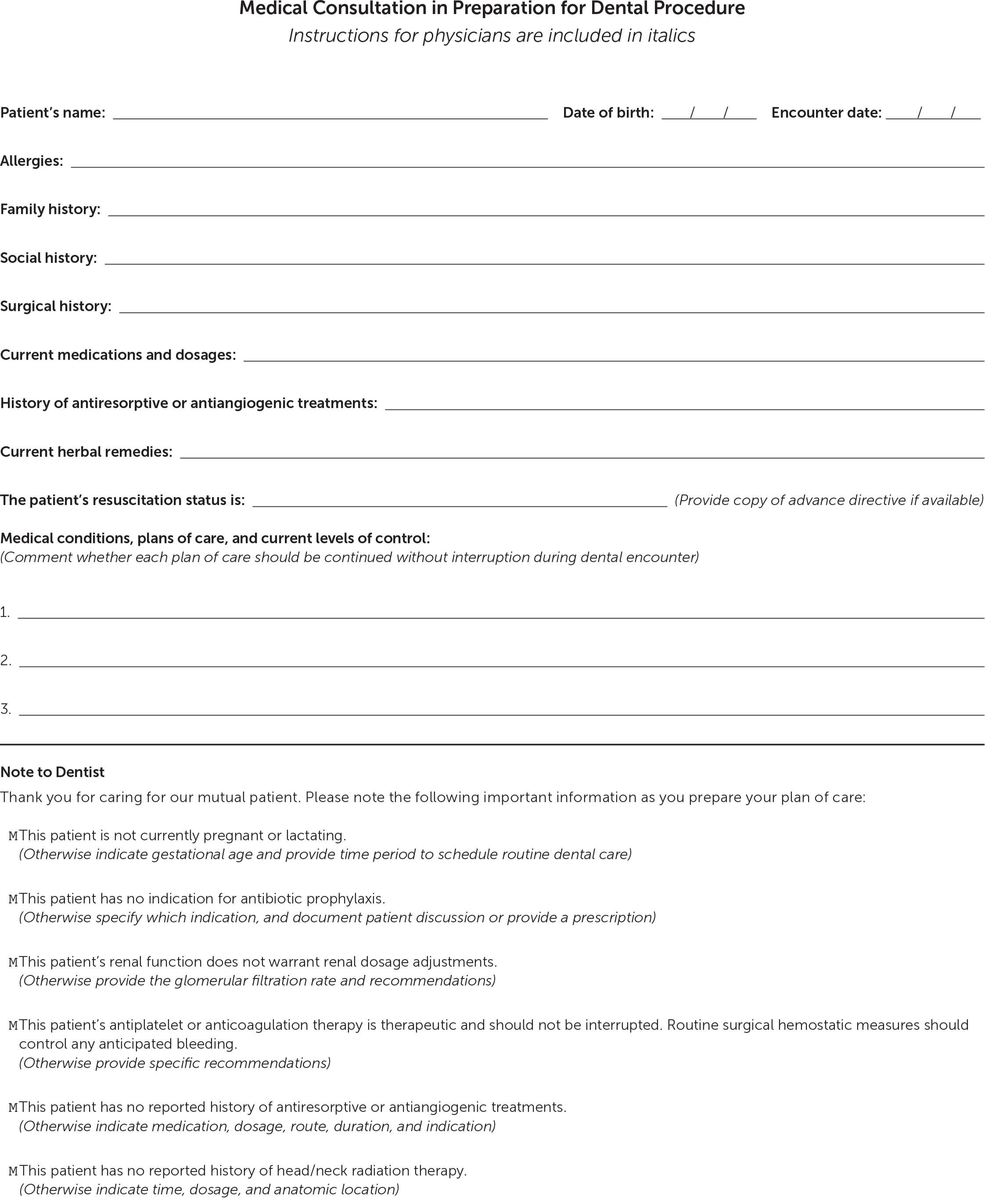
A medical consultation in preparation for a dental procedure should detail the patient's medical conditions, treatment plans, and current levels of management.7 A medical history, including allergies and use of herbal remedies and prescribed and over-the-counter medications, should be provided. It is essential to include any history of bisphosphonate use or cancer treatments.9 A relevant psychiatric history, including special needs, and the patient's resuscitation wishes or advance directive may be helpful.10
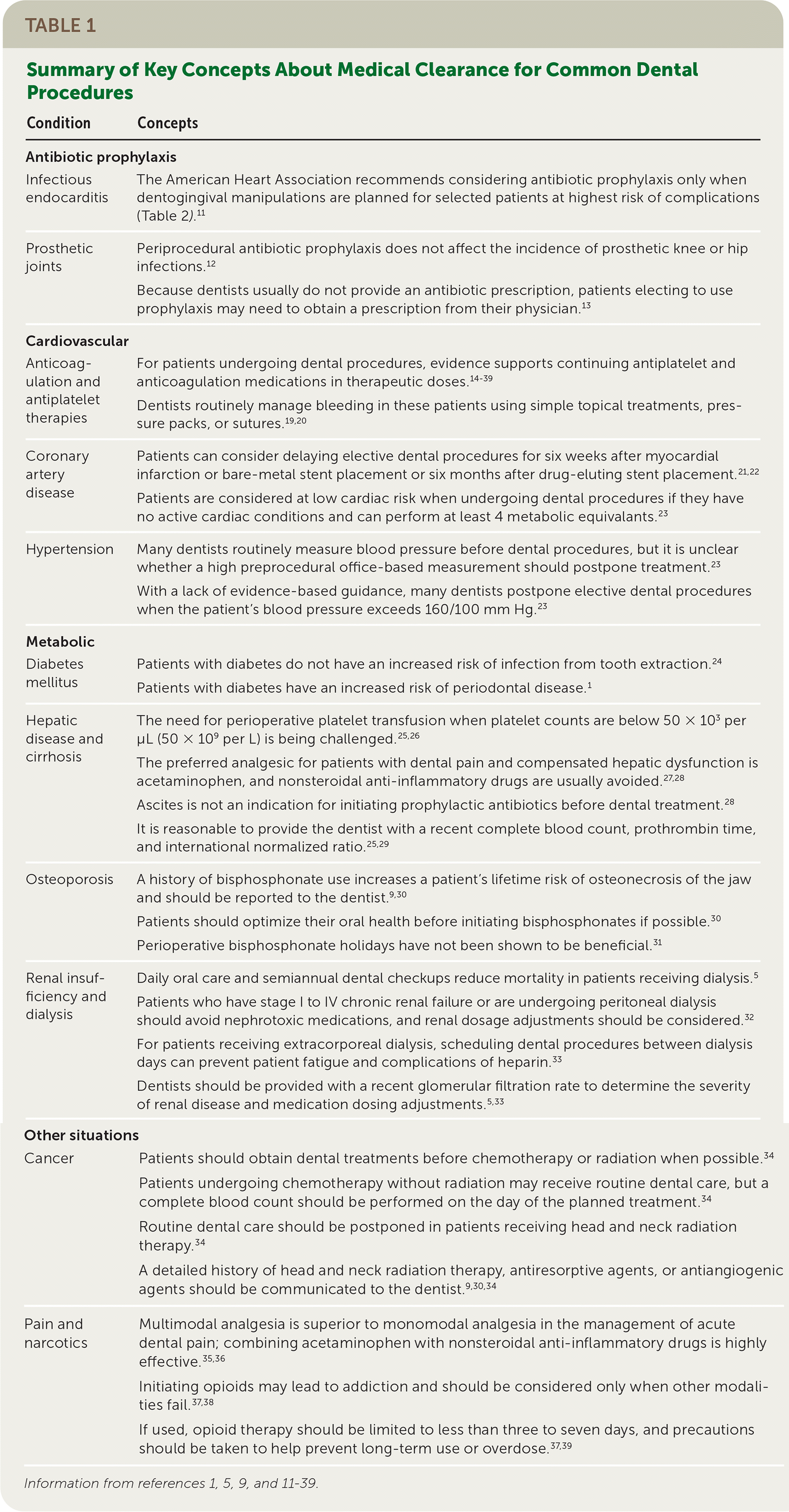
| Condition | Concepts |
|---|---|
| Antibiotic prophylaxis | |
| Infectious endocarditis | The American Heart Association recommends considering antibiotic prophylaxis only when dentogingival manipulations are planned for selected patients at highest risk of complications (Table 2).11 |
| Prosthetic joints | Periprocedural antibiotic prophylaxis does not affect the incidence of prosthetic knee or hip infections.12 Because dentists usually do not provide an antibiotic prescription, patients electing to use prophylaxis may need to obtain a prescription from their physician.13 |
| Cardiovascular | |
| Anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapies | For patients undergoing dental procedures, evidence supports continuing antiplatelet and anticoagulation medications in therapeutic doses.14–39 Dentists routinely manage bleeding in these patients using simple topical treatments, pressure packs, or sutures.19,20 |
| Coronary artery disease | Patients can consider delaying elective dental procedures for six weeks after myocardial infarction or bare-metal stent placement or six months after drug-eluting stent placement.21,22 Patients are considered at low cardiac risk when undergoing dental procedures if they have no active cardiac conditions and can perform at least 4 metabolic equivalants.23 |
| Hypertension | Many dentists routinely measure blood pressure before dental procedures, but it is unclear whether a high preprocedural office-based measurement should postpone treatment.23 With a lack of evidence-based guidance, many dentists postpone elective dental procedures when the patient's blood pressure exceeds 160/100 mm Hg.23 |
| Metabolic | |
| Diabetes mellitus | Patients with diabetes do not have an increased risk of infection from tooth extraction.24 Patients with diabetes have an increased risk of periodontal disease.1 |
| Hepatic disease and cirrhosis | The need for perioperative platelet transfusion when platelet counts are below 50 × 103 per μL (50 × 109 per L) is being challenged.25,26 The preferred analgesic for patients with dental pain and compensated hepatic dysfunction is acetaminophen, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are usually avoided.27,28 Ascites is not an indication for initiating prophylactic antibiotics before dental treatment.28 It is reasonable to provide the dentist with a recent complete blood count, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio.25,29 |
| Osteoporosis | A history of bisphosphonate use increases a patient's lifetime risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw and should be reported to the dentist.9,30 Patients should optimize their oral health before initiating bisphosphonates if possible.30 Perioperative bisphosphonate holidays have not been shown to be beneficial.31 |
| Renal insufficiency and dialysis | Daily oral care and semiannual dental checkups reduce mortality in patients receiving dialysis.5 Patients who have stage I to IV chronic renal failure or are undergoing peritoneal dialysis should avoid nephrotoxic medications, and renal dosage adjustments should be considered.32 For patients receiving extracorporeal dialysis, scheduling dental procedures between dialysis days can prevent patient fatigue and complications of heparin.33 Dentists should be provided with a recent glomerular filtration rate to determine the severity of renal disease and medication dosing adjustments.5,33 |
| Other situations | |
| Cancer | Patients should obtain dental treatments before chemotherapy or radiation when possible.34 Patients undergoing chemotherapy without radiation may receive routine dental care, but a complete blood count should be performed on the day of the planned treatment.34 Routine dental care should be postponed in patients receiving head and neck radiation therapy.34 A detailed history of head and neck radiation therapy, antiresorptive agents, or antiangiogenic agents should be communicated to the dentist.9,30,34 |
| Pain and narcotics | Multimodal analgesia is superior to monomodal analgesia in the management of acute dental pain; combining acetaminophen with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is highly effective.35,36 Initiating opioids may lead to addiction and should be considered only when other modalities fail.37,38 If used, opioid therapy should be limited to less than three to seven days, and precautions should be taken to help prevent long-term use or overdose.37,39 |
Antibiotic Prophylaxis
INFECTIOUS ENDOCARDITIS
For decades, the American Heart Association recommended prophylactic antibiotics for patients with cardiac conditions that might increase the risk of contracting infectious endocarditis during dental procedures. However, because studies have found that bacteremia occurs routinely with common activities such as chewing, brushing, and flossing and there is a lack of evidence that procedural prophylaxis is effective,40 the American Heart Association now recommends considering it only when dentogingival manipulations are planned for selected patients at highest risk of complications (Table 2).11

| Prosthetic heart valves or heart valve repairs using prosthetic material |
| History of infectious endocarditis |
| Unrepaired cyanotic congenital heart disease or repaired congenital heart disease, with residual shunts or valvular regurgitation at the site of or adjacent to the prosthetic patch or device |
| Cardiac transplant with valve regurgitation due to a structurally abnormal valve |
PROSTHETIC JOINTS
A high-quality prospective, case-control study found that antibiotic prophylaxis does not affect the incidence of prosthetic knee or hip infections.12 A 2013 joint guideline from the American Dental Association (ADA) and the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons suggests that physicians consider discontinuing routine procedural antibiotic prophylaxis after discussing risks and benefits of antibiotic prophylaxis with patients.41 Since 2015, the ADA has recommended against routine prophylaxis for patients with prosthetic joints.13 Because dentists usually follow ADA guidelines, they often do not provide an antibiotic prescription; patients electing to use prophylaxis may need to obtain the prescription from their physician.13
Cardiovascular Conditions
ANTICOAGULATION AND ANTIPLATELET THERAPIES
For simple cleanings or single tooth extractions, evidence supports continuing antiplatelet and anticoagulation medications at a therapeutic international normalized ratio (INR) because the indications for these medications usually outweigh the risks of dental complications.14 Studies have demonstrated that patients taking a vitamin K antagonist at a therapeutic INR, direct oral anticoagulants, or daily aspirin are not at increased risk of uncontrollable bleeding after outpatient oral surgeries.15–19 Another study of patients on nonaspirin antiplatelet therapy, alone or in combination with aspirin, demonstrated a negligible increased risk of bleeding after invasive dental treatments.20 Dentists routinely manage such perioperative bleeding using simple topical treatments, pressure packs, or sutures.19,20
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
Elective dental treatments have traditionally been deferred for patients with unstable angina and postponed for six weeks after myocardial infarction or bare-metal stent placement or for six months after drug-eluting stent placement.14,21,22 However, evidence suggests that, when necessary, invasive procedures (e.g., extractions) may be safely performed shortly after myocardial infarction or in patients with unstable angina, particularly if dentists provide effective anesthesia, control postoperative pain, and take measures to reduce perioperative anxiety.22 Patients are considered at low cardiac risk when undergoing dental procedures if they have no active cardiac conditions and can perform at least 4 metabolic equivalents.23
HYPERTENSION
Dental treatments are rarely contraindicated in patients with hypertension who have no other significant symptoms or comorbidities.23 Many dentists routinely measure blood pressure before dental procedures, but it is unclear whether a high preprocedural office-based blood pressure measurement should postpone treatment.23 With a lack of evidence-based guidance, many dentists postpone elective dental procedures when the patient's blood pressure exceeds 160/100 mm Hg to avoid the possibility of a hypertensive crisis.23 By documenting a history of adequate blood pressure control, physicians can help patients avoid the setback of canceled dental appointments.23
Metabolic Conditions
DIABETES
People with type 1 or 2 diabetes have an increased risk of periodontal disease, increasing their need for preventive dental care.1 Although people with diabetes have a well-documented increased risk of infection in general, research suggests that this does not extend to tooth extractions, regardless of the level of glycemic control.24 Thus, diabetes alone is not an indication for using antibiotics in patients undergoing routine extractions.24 Studies are not as clear about dental implant procedures, and research is ongoing to investigate whether the success of implants is influenced by glycemic control.42 It may be helpful for physicians to include a recent A1C level in the medical consultation.
HEPATIC DISEASE AND CIRRHOSIS
Cirrhosis is associated with coagulopathy, thrombocytopenia, renal failure, anemia, ascites, and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. A dental assessment and treatment are critical in preparing patients with cirrhosis for liver transplantation by optimizing oral health and minimizing the risk of oral infections.25,29
The traditional practice of performing a perioperative platelet transfusion for patients with platelet counts below 50 × 103 per μL (50 × 109 per L) has been challenged by studies showing that dental extractions are safe when platelet counts are as low as 10 × 103 per μL (10 × 109 per L).25,26 Studies also show that the risk of hemorrhage during dental extraction in patients with cirrhosis is not predicted by laboratory values.25 Given the lack of consensus, it may be reasonable for physicians to include a recent complete blood count, prothrombin time, and INR in the medical consultation for a dental extraction.25,29
The preferred analgesic for patients with dental pain and compensated hepatic dysfunction or cirrhosis who abstain from alcohol is acetaminophen, sometimes limited to 2 g per day.27,28 Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), except aspirin when prescribed for cardiovascular disease, are usually avoided because of platelet, kidney, and gastric risks.28,29
OSTEOPOROSIS
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw is a serious complication associated with the use of bisphosphonates and other antiresorptive agents or antiangiogenic cancer treatments (Table 3).9,30 A history of exposure to these drugs can increase the patient's lifetime risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw by up to 100-fold, depending on the treatment regimen and indication for which it was prescribed.9 Dental extraction and implant procedures are known to trigger osteonecrosis; therefore, the dentist may need to modify the care plan in these patients.30
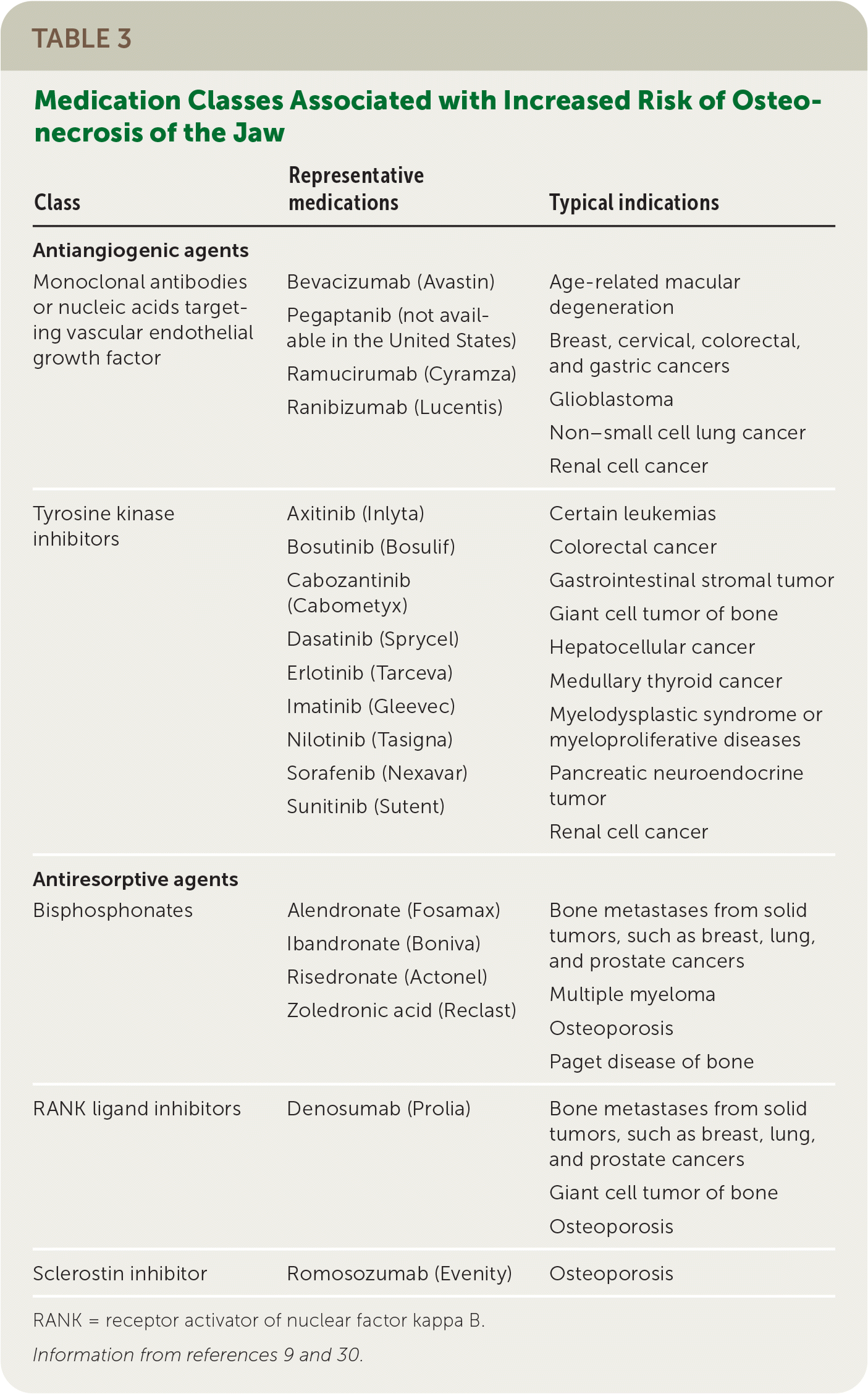
| Class | Representative medications | Typical indications |
|---|---|---|
| Antiangiogenic agents | ||
| Monoclonal antibodies or nucleic acids targeting vascular endothelial growth factor | Bevacizumab (Avastin) Pegaptanib (not available in the United States) Ramucirumab (Cyramza) Ranibizumab (Lucentis) | Age-related macular degeneration Breast, cervical, colorectal, and gastric cancers Glioblastoma Non–small cell lung cancer Renal cell cancer |
| Tyrosine kinase inhibitors | Axitinib (Inlyta) Bosutinib (Bosulif) Cabozantinib (Cabometyx) Dasatinib (Sprycel) Erlotinib (Tarceva) Imatinib (Gleevec) Nilotinib (Tasigna) Sorafenib (Nexavar) Sunitinib (Sutent) | Certain leukemias Colorectal cancer Gastrointestinal stromal tumor Giant cell tumor of bone Hepatocellular cancer Medullary thyroid cancer Myelodysplastic syndrome or myeloproliferative diseases Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor Renal cell cancer |
| Antiresorptive agents | ||
| Bisphosphonates | Alendronate (Fosamax) Ibandronate (Boniva) Risedronate (Actonel) Zoledronic acid (Reclast) | Bone metastases from solid tumors, such as breast, lung, and prostate cancers Multiple myeloma Osteoporosis Paget disease of bone |
| RANK ligand inhibitors | Denosumab (Prolia) | Bone metastases from solid tumors, such as breast, lung, and prostate cancers Giant cell tumor of bone Osteoporosis |
| Sclerostin inhibitor | Romosozumab (Evenity) | Osteoporosis |
For patients with a history of treatment with the drugs listed in Table 3, details such as drug name, dosage, route of administration, indication, and treatment duration should be communicated to the dentist.9,30 Patients should optimize their oral health before initiating bisphosphonates if possible.30 For those already taking bisphosphonates, current literature has not shown a benefit to discontinuing the treatment perioperatively.31
RENAL INSUFFICIENCY AND DIALYSIS
Patients who have stage I to IV chronic renal failure with or without peritoneal dialysis usually do not need special accommodations for dental procedures other than the avoidance of nephrotoxic medications, such as NSAIDs, and consideration of renal dosage adjustments.32 It is helpful to provide the dentist with a recent glomerular filtration rate to determine the severity of renal disease.5,33 For patients receiving extracorporeal dialysis, scheduling dental procedures between dialysis days can prevent patient fatigue and complications of heparin. Providing a current INR (if taking warfarin), hemoglobin level, and platelet count may help the dentist assess the risk of bleeding.33
Other Situations
CANCER
When considering cancer treatment, it is recommended to involve the patient's dentist early to provide timely preventive or proactive dental care and avoid sequelae.9,30,34,44 Patients currently undergoing chemotherapy without radiation may receive routine dental care. The dentist should be provided with a current medication list, and a complete blood count should be performed on the day of the planned treatment to ensure the absolute neutrophil count is greater than 1,000 per μL (1 × 109 per L) and platelet count is greater than 50 × 103 per μL.34 Any history of antiangiogenic treatments (Table 39,30) should be disclosed.
Routine dental care should be postponed in patients currently undergoing head and neck radiation therapy.34 A history of head and neck radiation is associated with numerous oral complications, such as increased dental caries, xerostomia, and osteoradionecrosis of the jaw, and dentists should be provided with a detailed oncology history (i.e., type of radiation treatment, dose, and specific anatomic site). This information is important because most cases of osteoradionecrosis of the jaw occur at sites exposed to greater than 60 Gy of radiation, and perioperative hyperbaric oxygen or other precautions may be indicated.34,45
PAIN AND NARCOTICS
Studies show that multimodal analgesia is more effective than monomodal analgesia in the management of acute dental pain; combining acetaminophen with NSAIDs is highly effective.35,36 Despite a declining trend, opioids are often prescribed for dental pain.46 Long-term opioid use often begins with treatment of acute pain; therefore, the risks of opioid addiction, including death, should be discussed with patients considering opioids.37–39
Accessing the state prescription drug monitoring program, required in some jurisdictions, can help verify medication histories and help ensure that benzodiazepines are not being used concurrently.37 Physicians should consider prescribing a naloxone antidote for patients at risk of an opioid overdose.37 Communicating any history of addiction or contraindications to NSAIDs or acetaminophen can help the dentist select an appropriate analgesic regimen.
Data Sources: PubMed literature searches were completed using combinations of the following terms: analgesia, anemia, antibiotic prophylaxis, anticoagulation, antiplatelet, antithrombotic, ascites, atrial fibrillation, cancer, chemotherapy, cirrhosis, clearance, consult, coronary artery disease, dental care, dental clearance, dental procedure, diabetes, dialysis, end stage renal disease, epilepsy, guidelines, heart valve, hemoglobin A1C, hepatic disease, hypertension, infective endocarditis, joint prosthesis, joint replacement, myocardial infarction, narcotic, nitrous oxide, osteonecrosis of the jaw, pain, periodontitis, periprocedural management, prostheses, radiation therapy, recommendations, renal insufficiency, seizure, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, thrombocytopenia, and venous thromboembolism. References therein were also reviewed. Literature searches included clinical trials, UpToDate, Cochrane reviews, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and systematic reviews. Search dates: March 1, 2020, to July 19, 2020, and May 15, 2021.
The authors thank Frank Perez for his editorial contribution.