
Am Fam Physician. 2023;107(2):145-151
Patient information: See related handout on acute otitis externa (swimmer's ear), written by the authors of this article.
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Acute otitis externa is an inflammatory condition that affects the external ear canal. It is usually of rapid onset and is generally caused by bacterial infection. The primary bacterial infections are Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Acute otitis externa presents with pain (otalgia), redness, and swelling of the canal. It is more common in children and young adults. Tenderness on movement of the pinna or tragus is the classic finding. Analgesics and topical antibiotics are the mainstays of therapy. Topical medications include acetic acid 2%, aminoglycosides, polymyxin B, and quinolones with and without corticosteroids. There is no evidence that any one preparation is clinically superior to another, and the choice of treatment is based on factors such as cost, whether the tympanic membrane is intact, and patient adherence. Oral antibiotics are indicated only if evidence of cellulitis occurs outside of the ear canal or if associated conditions such as immunocompromise, diabetes mellitus, or conditions that would not allow for the use of topical treatment are found. Duration of topical treatment is usually seven to 10 days. Keys to prevention include avoiding injury to the ear canal and keeping it free of water.
Acute otitis externa, also known as swimmer's ear, is an inflammatory condition affecting the external ear canal that is a common problem encountered in primary care offices. This article provides a brief update and summary of the best available patient-oriented evidence for treating acute otitis externa.
| Clinical recommendation | Evidence rating | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Acute otitis externa should be distinguished from other possible causes of ear canal inflammation.5 | C | Expert opinion |
| Patients with otitis externa should be assessed for pain and treated with analgesics.5,9 | C | Multiple consensus guidelines |
| Topical antimicrobial preparations are the first-line treatment for uncomplicated acute otitis externa.5,12 | A | Consensus guidelines, randomized controlled trials, consistent evidence from observational studies |
| Systemic antibiotics should be used only if the infection has spread beyond the ear canal or in patients at high risk of such spread.5,12,13 | B | Multiple consensus guidelines, randomized controlled trials |

| Recommendation | Sponsoring organization |
|---|---|
| Do not prescribe oral antibiotics for uncomplicated acute external otitis. | American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery |
Epidemiology
Acute otitis externa occurs in all age groups. An estimated 10% of people will develop acute otitis externa during their lifetime.1 Younger age groups are most commonly affected, with decreased incidence as one ages (Table 12).
Acute otitis externa is responsible for more than 500,000 emergency department visits each year.3
Risk factors for acute otitis externa are summarized in Table 2,4 with the most common factor being swimming.4,5
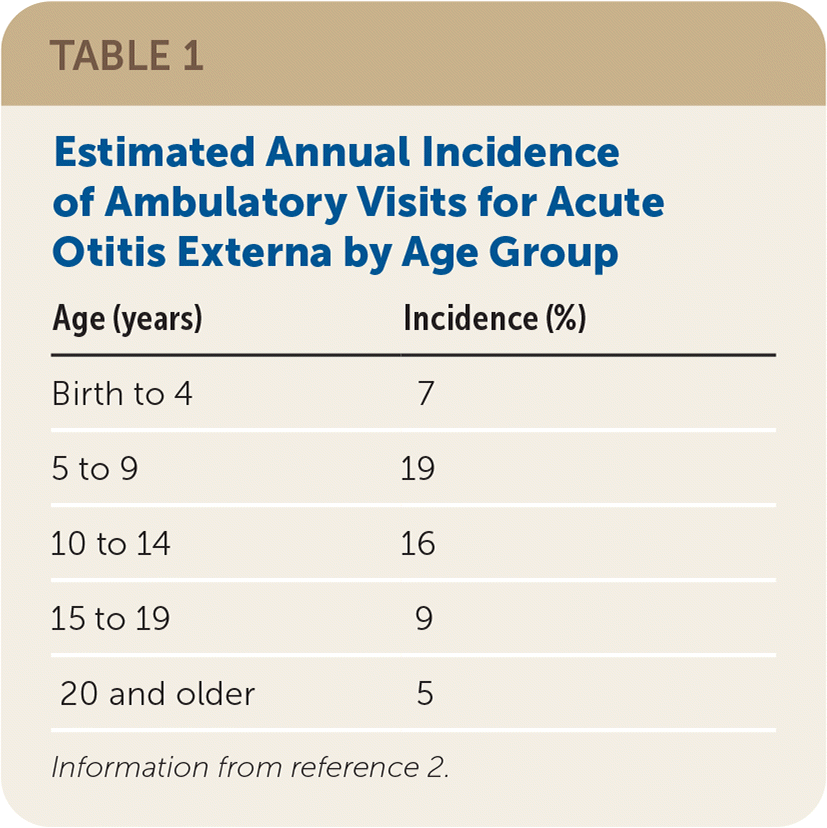
| Age (years) | Incidence (%) |
|---|---|
| Birth to 4 | 7 |
| 5 to 9 | 19 |
| 10 to 14 | 16 |
| 15 to 19 | 9 |
| 20 and older | 5 |
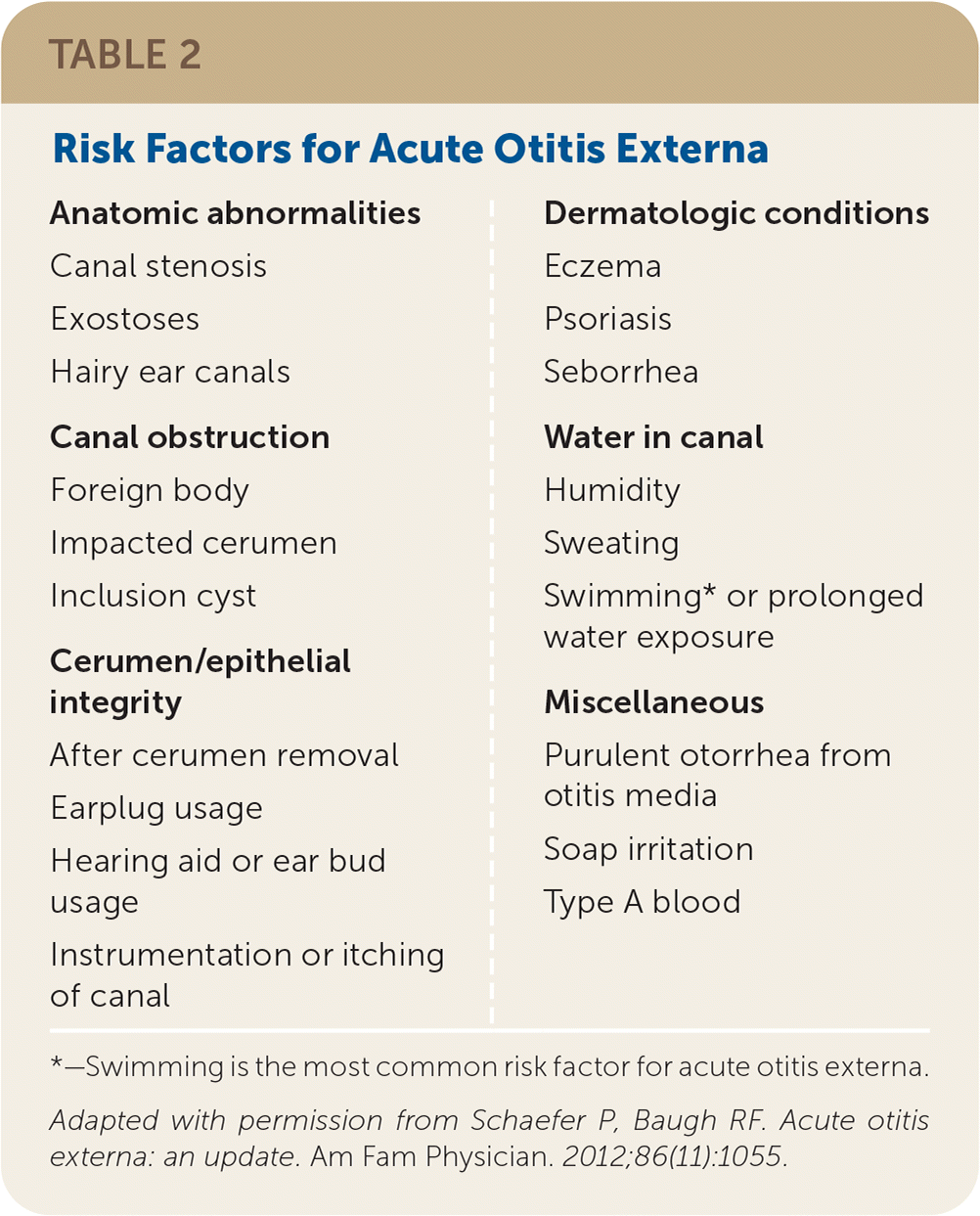
| Anatomic abnormalities Canal stenosis Exostoses Hairy ear canals Canal obstruction Foreign body Impacted cerumen Inclusion cyst Cerumen/epithelial integrity After cerumen removal Earplug usage Hearing aid or ear bud usage Instrumentation or itching of canal | Dermatologic conditions Eczema Psoriasis Seborrhea Water in canal Humidity Sweating Swimming* or prolonged water exposure Miscellaneous Purulent otorrhea from otitis media Soap irritation Type A blood |
Diagnosis
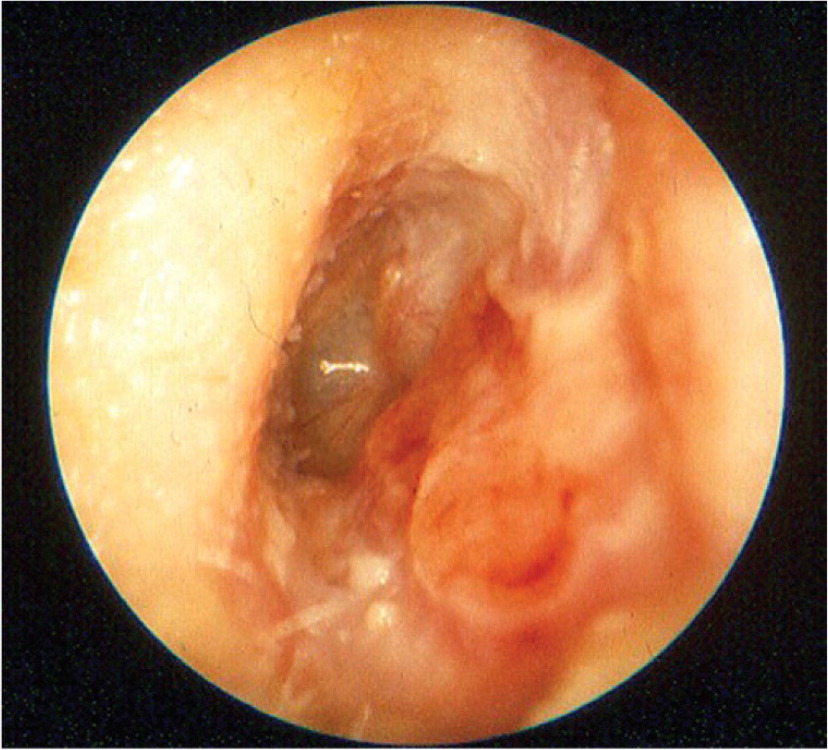
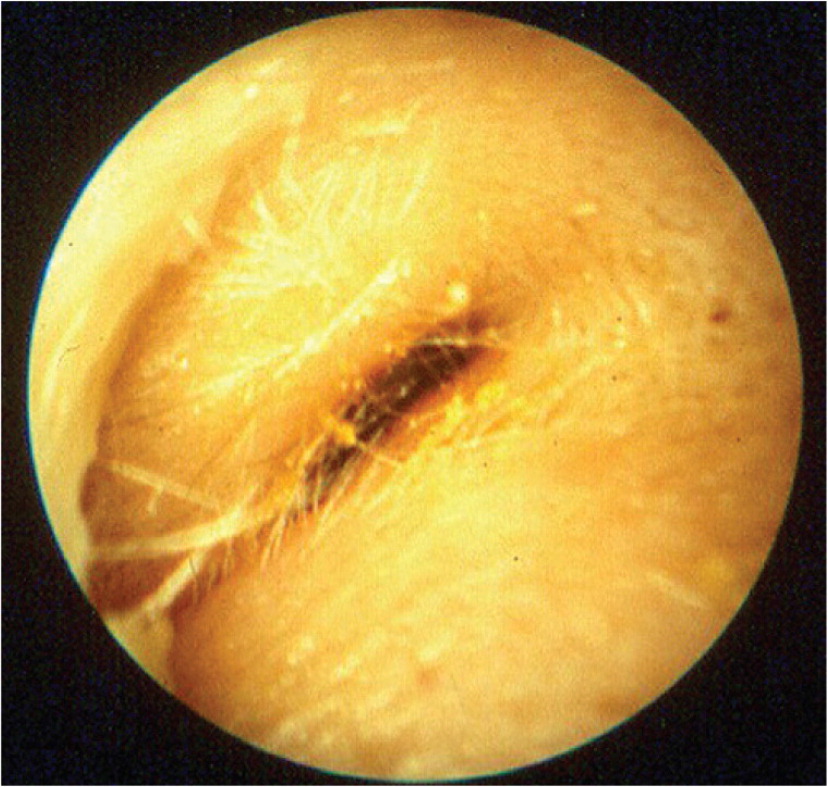
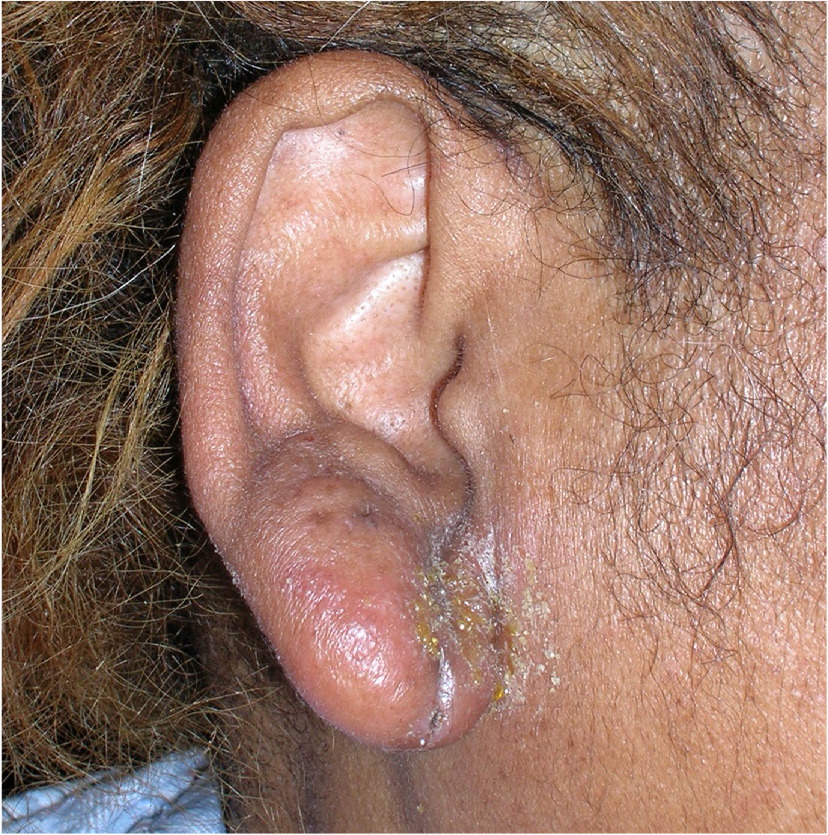
The clinical diagnosis of acute otitis externa is based on symptoms of inflammation in the ear canal. Criteria proposed by the American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery to aid in diagnosis are listed in Table 3.5 Figure 1 and Figure 2 demonstrate the redness and edema of the canal seen with acute otitis externa.4
The most common symptom is pain in the tragus, pinna, or both,6 which is disproportionate to what is expected on visual inspection.5 Other causes that may be included in the differential diagnosis of ear canal inflammation are listed in Table 4.4
Physicians should review the presenting symptom onset and exposure to water (e.g., swimming) as well as any trauma to the canal and history of other skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, or seborrhea. Additional history should include prior surgeries, radiation therapy, or history of systemic illnesses such as diabetes mellitus, or conditions that may predispose to immune suppression.
The pinna, tragus, ear canal, and regional lymph nodes should be examined. Use of pneumatic otoscopy is recommended to help differentiate acute otitis externa from otitis media and to assist in determining that the tympanic membrane is intact without perforation because these determinations have implications for treatment options.4 If a perforation has occurred, the medications that can be used topically are limited.
An examination for signs of cellulitis or extension beyond the ear canal should be performed.
Cultures of otorrhea are usually not performed because most cases of acute otitis externa are caused by bacterial infection,7 predominantly with Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus.

| Rapid onset of symptoms (usually within 48 hours) in the past three weeks |
| Symptoms of ear canal inflammation |
| Ear pain (otalgia) |
| Itching |
| Sense of fullness |
| With or without hearing loss or jaw pain |
| Signs of canal inflammation |
| Pinna or tragus tenderness on movement |
| or |
| Diffuse canal edema or redness |
| May also have otorrhea, tympanic membrane rupture, pinna cellulitis, or local lymphadenitis |
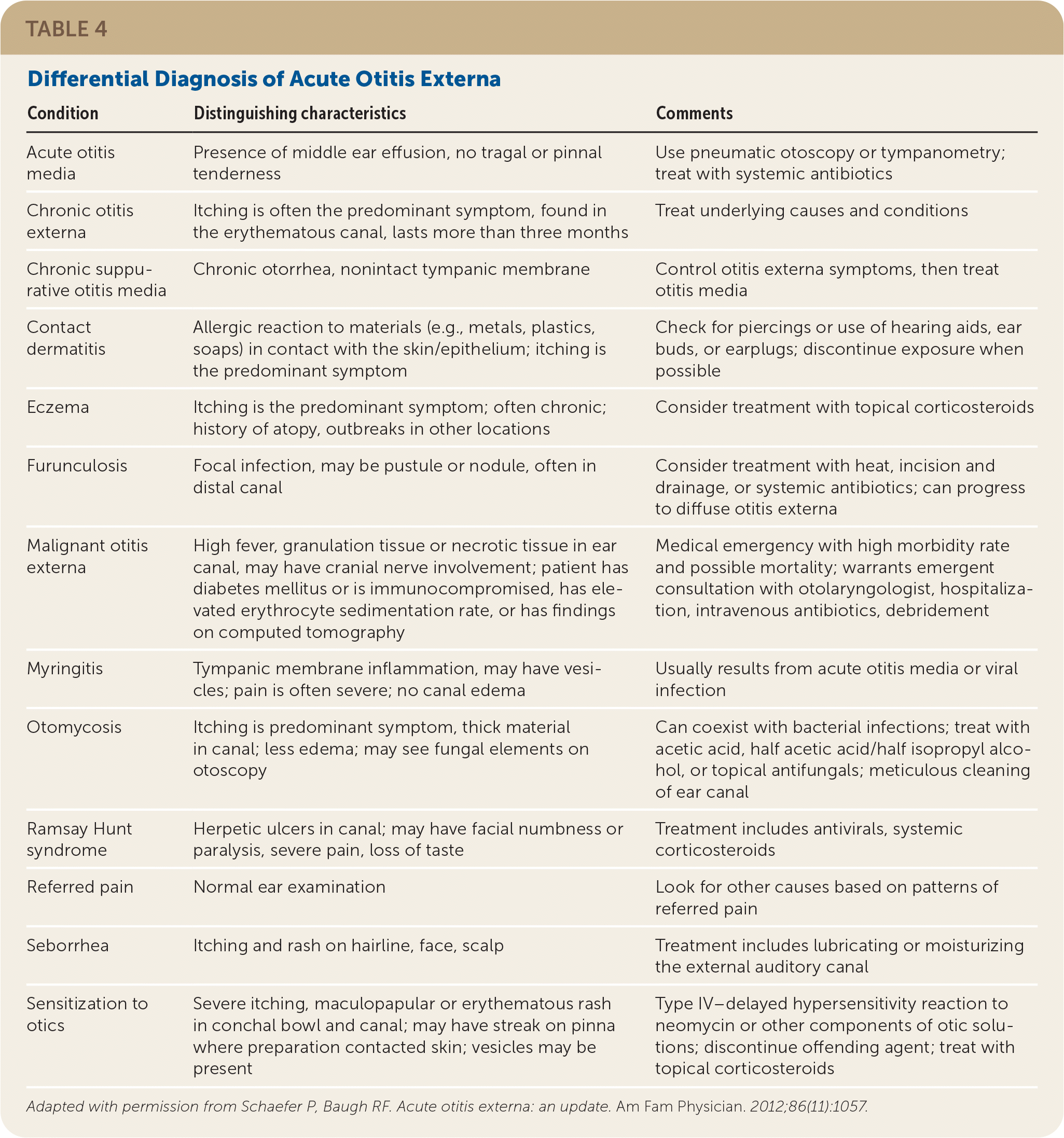
| Condition | Distinguishing characteristics | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Acute otitis media | Presence of middle ear effusion, no tragal or pinnal tenderness | Use pneumatic otoscopy or tympanometry; treat with systemic antibiotics |
| Chronic otitis externa | Itching is often the predominant symptom, found in the erythematous canal, lasts more than three months | Treat underlying causes and conditions |
| Chronic suppurative otitis media | Chronic otorrhea, nonintact tympanic membrane | Control otitis externa symptoms, then treat otitis media |
| Contact dermatitis | Allergic reaction to materials (e.g., metals, plastics, soaps) in contact with the skin/epithelium; itching is the predominant symptom | Check for piercings or use of hearing aids, ear buds, or earplugs; discontinue exposure when possible |
| Eczema | Itching is the predominant symptom; often chronic; history of atopy, outbreaks in other locations | Consider treatment with topical corticosteroids |
| Furunculosis | Focal infection, may be pustule or nodule, often in distal canal | Consider treatment with heat, incision and drainage, or systemic antibiotics; can progress to diffuse otitis externa |
| Malignant otitis externa | High fever, granulation tissue or necrotic tissue in ear canal, may have cranial nerve involvement; patient has diabetes mellitus or is immunocompromised, has elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, or has findings on computed tomography | Medical emergency with high morbidity rate and possible mortality; warrants emergent consultation with otolaryngologist, hospitalization, intravenous antibiotics, debridement |
| Myringitis | Tympanic membrane inflammation, may have vesicles; pain is often severe; no canal edema | Usually results from acute otitis media or viral infection |
| Otomycosis | Itching is predominant symptom, thick material in canal; less edema; may see fungal elements on otoscopy | Can coexist with bacterial infections; treat with acetic acid, half acetic acid/half isopropyl alcohol, or topical antifungals; meticulous cleaning of ear canal |
| Ramsay Hunt syndrome | Herpetic ulcers in canal; may have facial numbness or paralysis, severe pain, loss of taste | Treatment includes antivirals, systemic corticosteroids |
| Referred pain | Normal ear examination | Look for other causes based on patterns of referred pain |
| Seborrhea | Itching and rash on hairline, face, scalp | Treatment includes lubricating or moisturizing the external auditory canal |
| Sensitization to otics | Severe itching, maculopapular or erythematous rash in conchal bowl and canal; may have streak on pinna where preparation contacted skin; vesicles may be present | Type IV–delayed hypersensitivity reaction to neomycin or other components of otic solutions; discontinue offending agent; treat with topical corticosteroids |
Treatment
MANAGEMENT OF PAIN
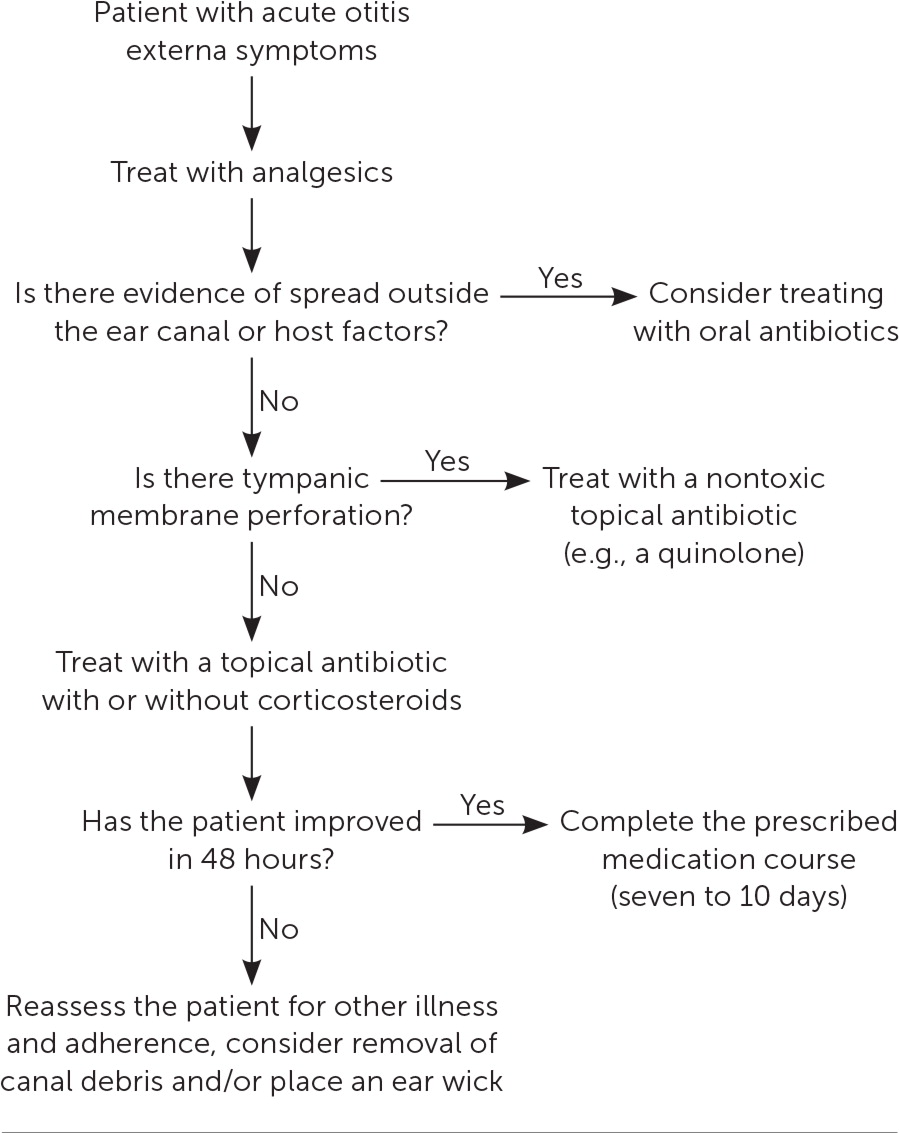
Per 2014 guidelines from the American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery,5 which were endorsed by the American Academy of Family Physicians and reaffirmed in 2019,8 treatment for acute otitis externa should include an assessment of pain. Using analgesics as a mainstay of therapy to help in the management of acute otitis externa allows for increased comfort and more rapid return to normal activities.9 Figure 3 presents an algorithm for treatment.5
Analgesics that can provide relief include acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or, in rare cases, the addition of a short-term opioid. Based on expert opinion, fixed dosing intervals are recommended rather than as-needed dosing.9
Available topical analgesics are limited to over-the-counter homeopathic medications for which there is no evidence of benefit. The use of otic benzocaine with or without antipyrine was withdrawn from the U.S. market in 2015.10 Concerns with the use of topical analgesics include the potential dilution of antibiotic drops and unknown ototoxicity if there is a perforated tympanic membrane.
TOPICAL ANTIBIOTIC THERAPIES
The mainstay of treatment is topical antimicrobials with or without topical corticosteroids. The effectiveness of topical medications has been confirmed using meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.5,11,12 There are no significant clinical outcome differences between the drug classes, quinolone vs. nonquinolone antibiotics, or preparations with or without corticosteroids.5,11,12
Topical agents are available in a variety of combinations; regardless of which agent is used, 65% to 90% of patients had a clinical resolution of symptoms within seven to 10 days.12 A systematic review from 2010 looked at 26 topical agent combinations and came to the same conclusion.11
Cost and patient adherence play a significant role in the selection of which agent to choose. Table 5 lists some common topical antimicrobial preparations.4,5
Duration of topical treatment is typically seven to 10 days.
If a perforation or suspected perforation of the tympanic membrane has occurred, topical medications that are potentially ototoxic (e.g., aminoglycosides, isopropyl alcohol) should not be used; a low pH medication is recommended.13 The only topical agents approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for the middle ear are quinolones.5 There is an explicit warning from the manufacturer of neomycin/polymyxin B/hydrocortisone (Cortisporin) to not use in non-intact tympanic membranes.5,14
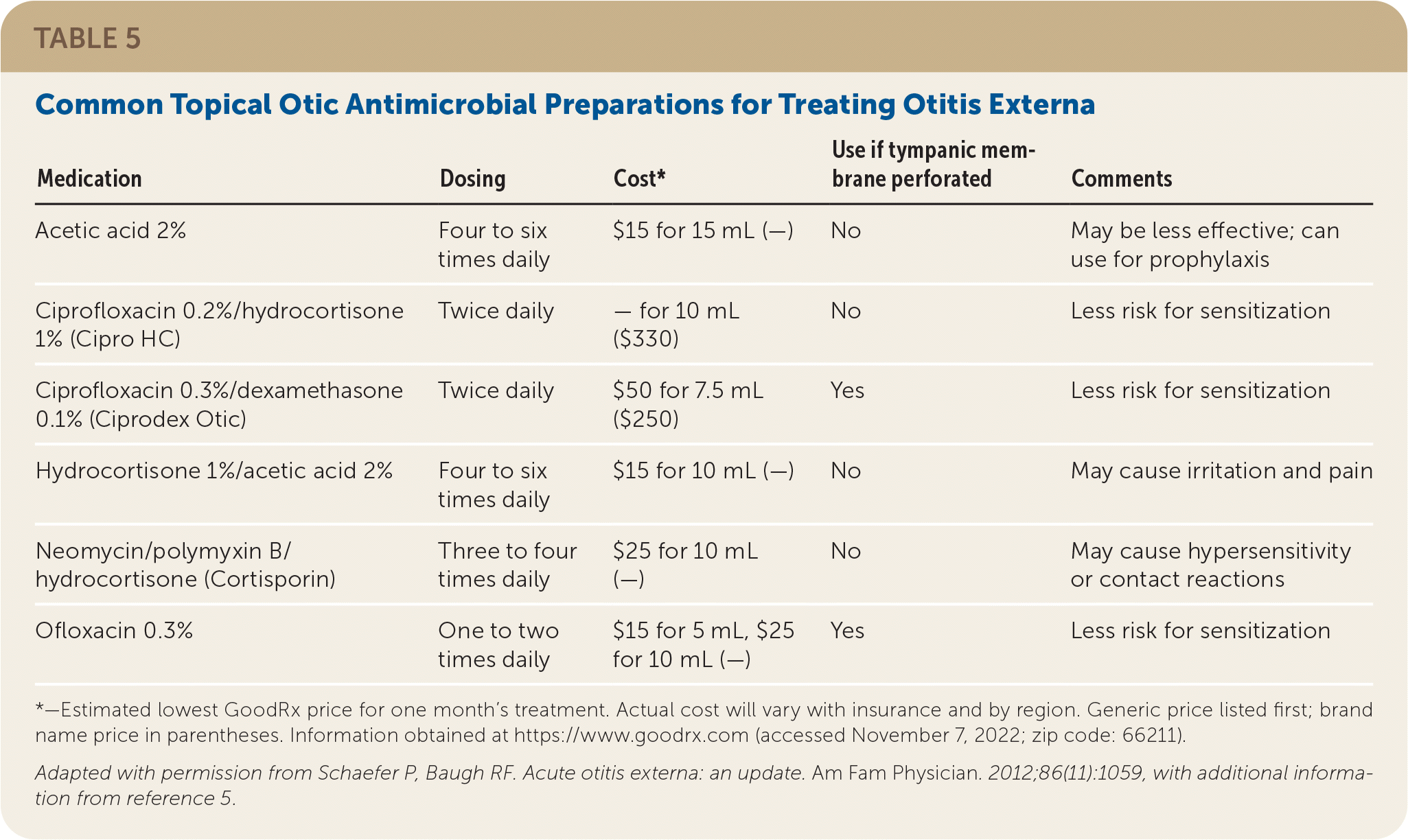
| Medication | Dosing | Cost* | Use if tympanic membrane perforated | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid 2% | Four to six times daily | $15 for 15 mL (—) | No | May be less effective; can use for prophylaxis |
| Ciprofloxacin 0.2%/hydrocortisone 1% (Cipro HC) | Twice daily | — for 10 mL ($330) | No | Less risk for sensitization |
| Ciprofloxacin 0.3%/dexamethasone 0.1% (Ciprodex Otic) | Twice daily | $50 for 7.5 mL ($250) | Yes | Less risk for sensitization |
| Hydrocortisone 1%/acetic acid 2% | Four to six times daily | $15 for 10 mL (—) | No | May cause irritation and pain |
| Neomycin/polymyxin B/hydrocortisone (Cortisporin) | Three to four times daily | $25 for 10 mL (—) | No | May cause hypersensitivity or contact reactions |
| Ofloxacin 0.3% | One to two times daily | $15 for 5 mL, $25 for 10 mL (—) | Yes | Less risk for sensitization |
ORAL ANTIBIOTICS
Oral antibiotics should not be used in most patients with acute otitis externa.5 Nonetheless, 20% to 40% of patients with acute otitis externa are prescribed oral antibiotics, often in addition to topical therapies.5 Many of these chosen oral antibiotics (e.g., amoxicillin, amoxicillin/clavulanate) lacked effectiveness against the most common pathogenic bacteria (i.e., P. aeruginosa, S. aureus). Topical therapy delivers higher concentrations of antimicrobials than can be achieved orally 5 and avoids the risk of developing bacterial resistance.13,15
Oral antibiotics should be reserved for patients who have infections that spread beyond the ear canal, those with immunocompromise or uncontrolled diabetes, and those unable to administer topical preparations.5,12,13 A referral to an otolaryngologist may be needed for these patients. Figure 4 demonstrates spread beyond the ear canal.
OTHER TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS
Patient education on how to administer topical drops is important. See a patient education handout on acute otitis externa, which provides detailed information about how to properly administer topical drops, for more information.
If marked canal edema has occurred, the physician may use a wick to improve drug delivery to the canal. No clinical trials, however, have evaluated wick effectiveness.5
Prevention of Acute Otitis Externa
Preventive measures include avoiding canal moisture by using well-fitted earplugs during swimming (poorly fitting plugs may increase the risk of acute otitis externa), drying the canal with a hair dryer on low setting, removing water from the canal with head-tilt maneuvers, and avoiding irritation of the canal with fingernails or other foreign objects.16 No randomized trials have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of these suggestions.17
Some recommend the use of acetic acid 2% solutions as a preventive measure, but no trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of any of these measures.4
Follow-up and Referral
Most patients will improve within 24 to 72 hours of beginning treatment.4,5 For those who do not improve in that time frame, reassessment is warranted.5
Follow-up should be recommended for any patient who does not have symptom resolution after two weeks of therapy. Alternative diagnoses should be considered if necessary and are provided in Table 4.4
Referral to an otolaryngologist is recommended if there is concern for malignant otitis externa, if the patient's condition worsens despite adequate therapy, if there is a recognized need for enhanced removal of debris in the canal, or if the primary care physician is not comfortable placing a wick or performing lavage on a severely edematous canal.4,5
This article updates previous articles on this topic by Schaefer and Baugh4 and Sander.17
Data Sources: Multiple searches of PubMed Clinical Inquires using the search term otitis externa were conducted. Essential Evidence Plus, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, POEMs, Clinical Rules, National Institute for Health and Care Clinical Excellence guidelines, Ovid, Clinical Key, Web of Science, and UpToDate were also searched. Search dates: February 1 through March 31, 2022; June 16, 2022; and January 2, 2023.
