
Am Fam Physician. 2025;111(5):402-403
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
DETAILS FOR THIS REVIEW
Study Population: 575 children and young adults with active juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
Efficacy End Points: Treatment response, sustained clinically inactive disease, function, pain, and participant global assessment of well-being
Harm End Points: Serious adverse events and withdrawals due to adverse events
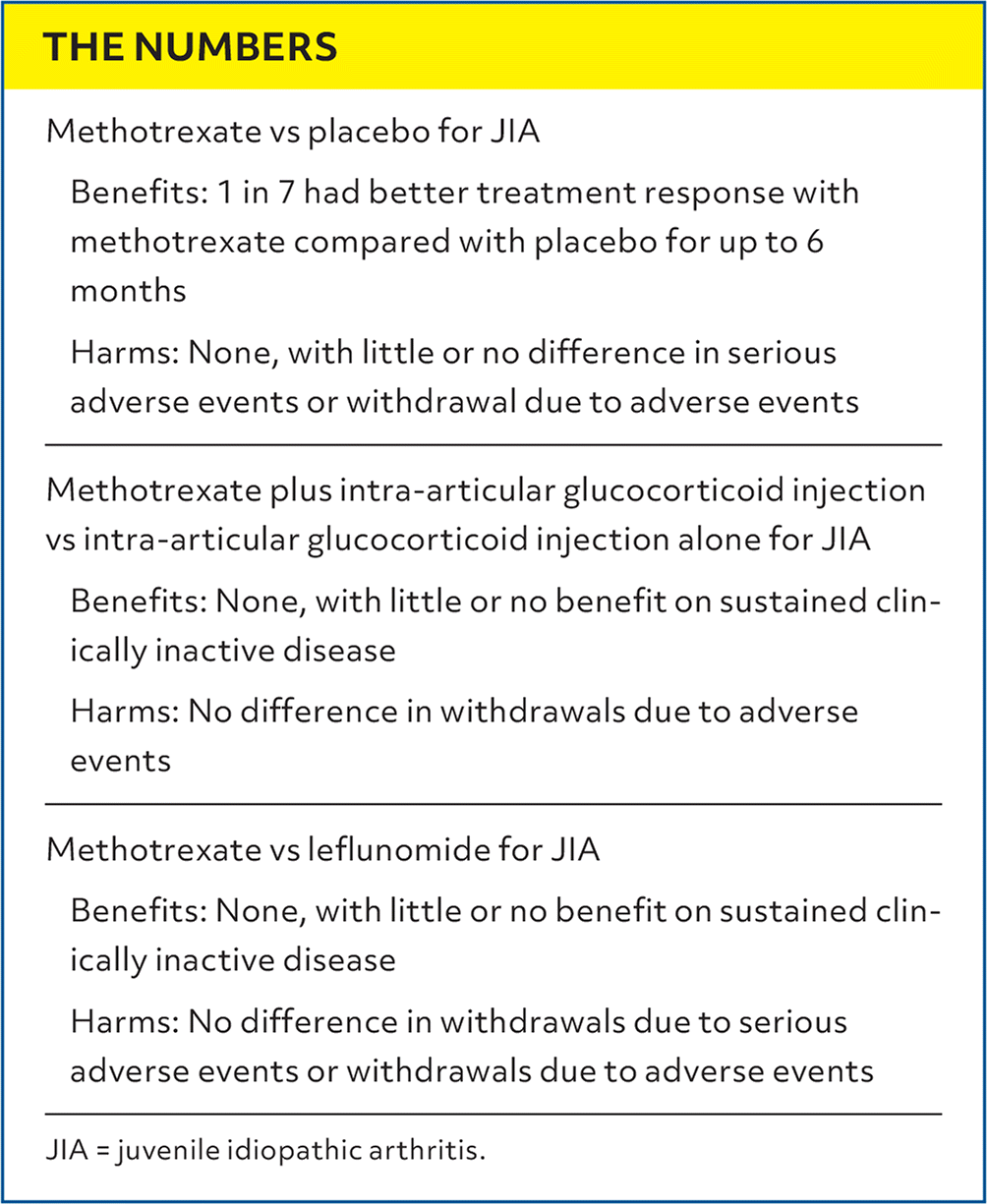
| Methotrexate vs placebo for JIA Benefits: 1 in 7 had better treatment response with methotrexate compared with placebo for up to 6 months Harms: None, with little or no difference in serious adverse events or withdrawal due to adverse events |
| Methotrexate plus intra-articular glucocorticoid injection vs intra-articular glucocorticoid injection alone for JIA Benefits: None, with little or no benefit on sustained clinically inactive disease Harms: No difference in withdrawals due to adverse events |
| Methotrexate vs leflunomide for JIA Benefits: None, with little or no benefit on sustained clinically inactive disease Harms: No difference in withdrawals due to serious adverse events or withdrawals due to adverse events |
Subscribe
From $180- Immediate, unlimited access to all AFP content
- More than 125 CME credits/year
- Print delivery available
Issue Access
$59.95- Immediate, unlimited access to this issue's content
- CME credits
- Print delivery available
